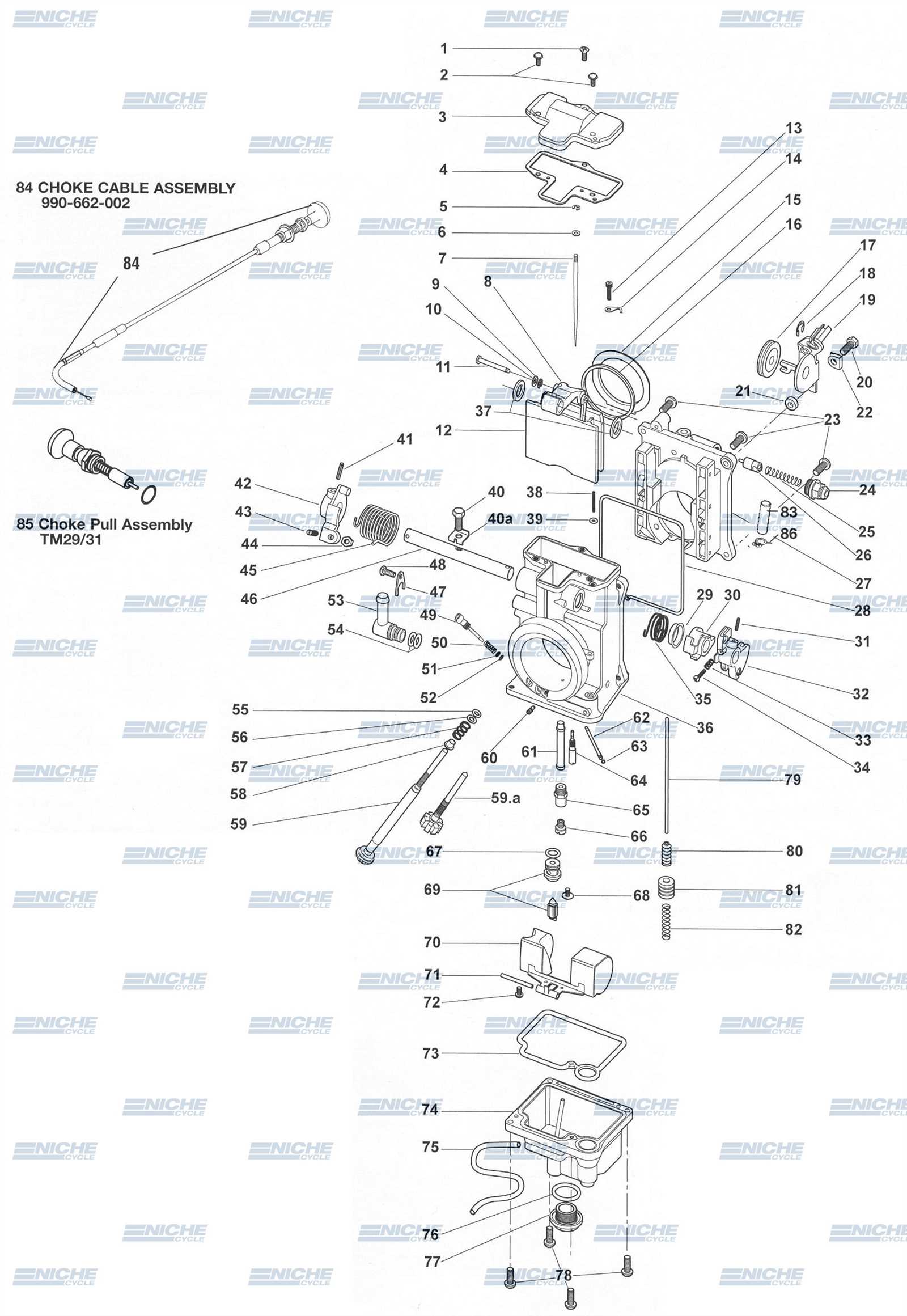
In any engine, the efficient delivery of fuel is crucial for optimal performance. Various components work together to ensure the right amount of fuel is mixed with air before it enters the combustion chamber. The layout of these elements plays a key role in the overall functionality of the engine, affecting everything from fuel efficiency to power output.
The internal structure that facilitates this process consists of several essential mechanisms. Each part serves a unique function, helping to regulate air and fuel mixtures, maintain optimal engine speeds, and control the flow of gases. A thorough understanding of these components allows for better troubleshooting and maintenance of the system.
Exploring the configuration of these elements can shed light on how they interact and contribute to the smooth operation of an engine. By focusing on how each component works, it’s easier to appreciate their collective importance in maintaining engine health and performance.
Key Components of a Carburetor
The internal fuel management system consists of various elements that work together to ensure smooth engine operation. Each component has a specific function in regulating the flow and mixing of fuel and air, which is crucial for combustion. Understanding these individual parts helps in recognizing their role in achieving optimal performance.
One of the most important elements is the throttle valve, which controls the amount of air entering the engine. This valve is essential for regulating engine speed. Another critical component is the fuel bowl, which holds a reserve of fuel to maintain consistent delivery. The metering jet is responsible for determining the fuel flow, making it an essential factor in fuel efficiency.
Additionally, the choke and idle circuit play vital roles in regulating the mixture during different engine conditions, ensuring smooth startups and idle performance. Each of these components must work in unison to deliver the proper air-fuel ratio for efficient engine operation and longevity.
How the Carburetor Regulates Fuel Flow
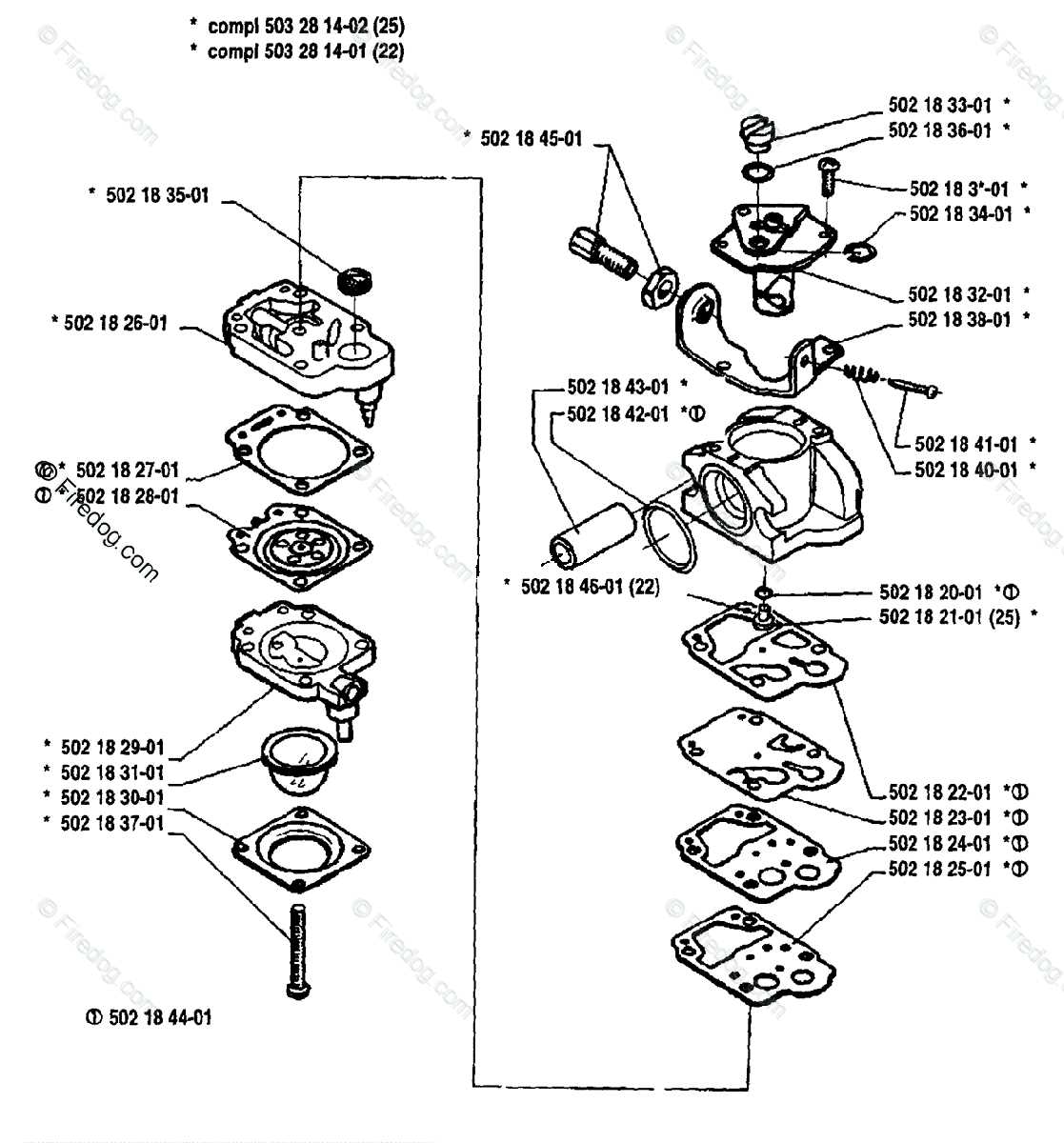
The precise control of fuel flow is essential for an engine’s performance. By managing the balance between air and fuel, the system ensures that combustion occurs efficiently under various operating conditions. Multiple components work together to regulate the amount of fuel entering the engine, adapting to different speeds and load requirements.
The process begins with the throttle valve, which adjusts the air intake based on the driver’s input. As the air intake changes, the system automatically adjusts fuel flow to match. This balance is maintained through several mechanisms:
- Throttle Valve: Controls the amount of air entering the intake, which directly influences fuel delivery.
- Fuel Jets: Regulate the flow of fuel into the air stream, ensuring the proper mixture for combustion.
- Float and Needle Valve: These components maintain the fuel level in the reservoir, preventing overfill or starvation.
- Choke: Restricts airflow when the engine is cold, enriching the fuel mixture for easier startup.
These elements work in harmony to ensure that fuel is delivered in the right quantity and at the correct time. The system constantly adapts to changes in engine speed and load, optimizing fuel efficiency and engine performance. Proper regulation of fuel flow is key to minimizing emissions and maximizing power output.
Understanding the Carburetor’s Functionality
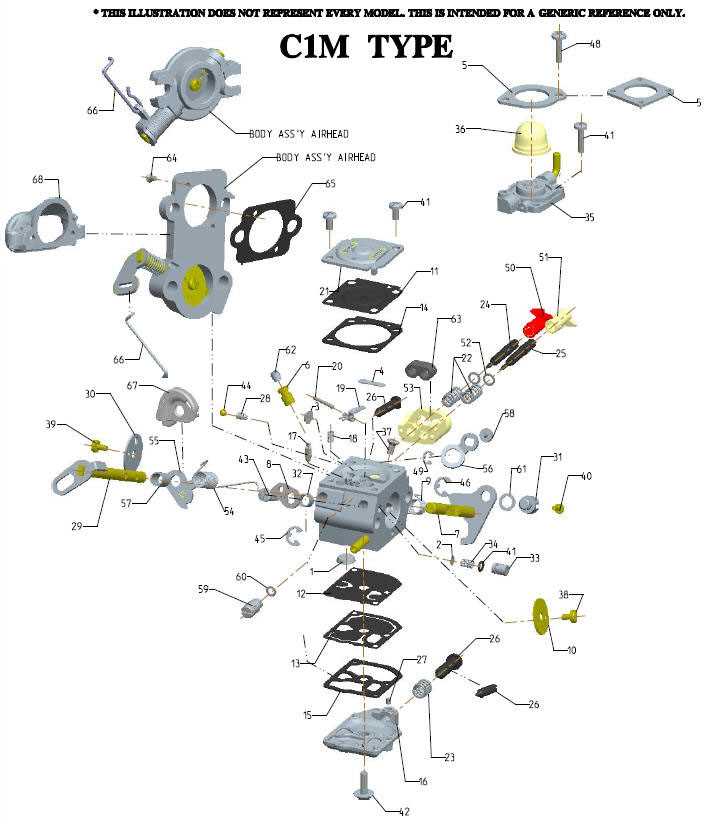
The primary function of this system is to ensure that the engine receives the optimal mixture of air and fuel for efficient combustion. By precisely regulating the amount of fuel that is mixed with air before it enters the combustion chamber, it plays a crucial role in engine performance. Its functionality directly impacts fuel efficiency, power output, and overall engine smoothness.
Fuel and Air Mixture Regulation
One of the most vital tasks of this system is adjusting the air-to-fuel ratio. This adjustment varies depending on engine speed, load, and temperature, ensuring that the engine runs smoothly under different conditions. The system dynamically regulates fuel delivery through mechanisms like jets and valves, which are calibrated to provide the right mix for efficient combustion.
Response to Engine Demand
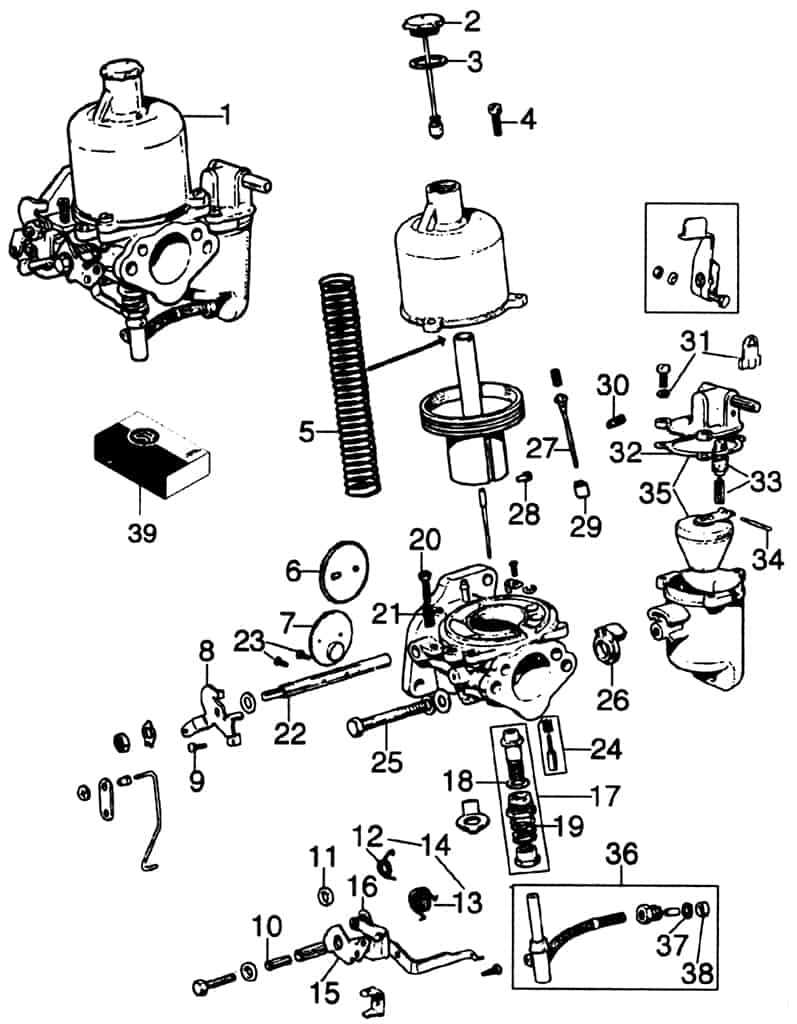
As engine demand changes, the system responds by adjusting both the air intake and fuel flow. When more power is needed, such as during acceleration, it allows a richer mixture. Conversely, during idle or cruising, a leaner mixture is used to conserve fuel. This adaptability ensures that the engine can perform efficiently in all driving scenarios, from low-speed idling to high-speed acceleration.