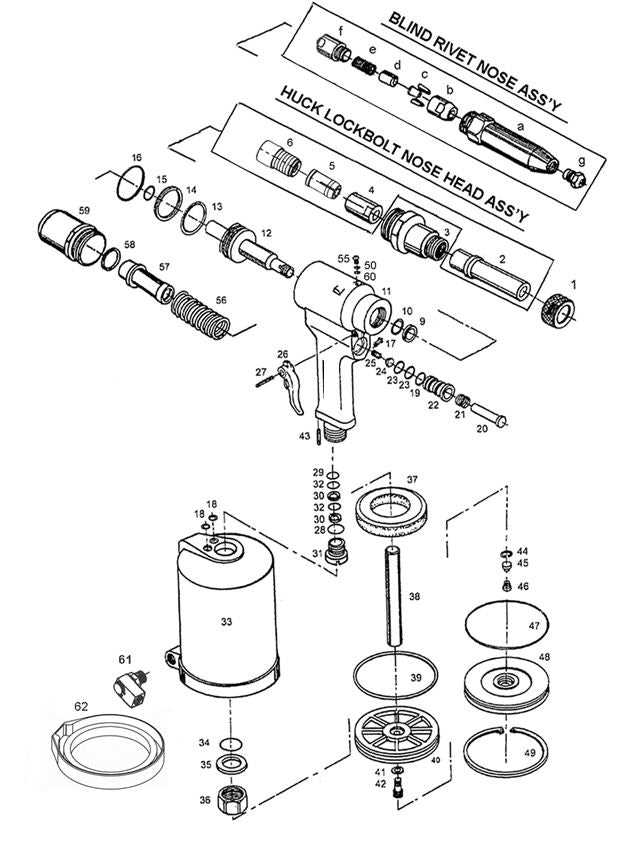
To effectively maintain and operate a fastening tool, it’s essential to understand its internal components and how they work together. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring the tool functions smoothly and efficiently. By gaining insight into the tool’s construction, users can troubleshoot problems and enhance overall performance.
Knowing the different sections of the tool helps users identify specific issues when something goes wrong. Whether it’s a malfunction or a simple need for maintenance, recognizing the function of each component can save both time and money. In this section, we will explore the key elements that make up this type of tool and their respective roles.
Understanding these components not only allows for proper handling but also ensures safer operation. With the right knowledge, users can maximize the lifespan of their tools and use them to their full potential, whether for professional or personal tasks.
Understanding the Main Parts of a Fastening Tool
The efficient operation of a fastening tool depends on the collaboration of several key components. Each element has a specific function that contributes to the tool’s overall performance, from delivering power to ensuring a secure connection. In this section, we’ll break down the primary sections that make up this essential tool and their individual roles in making the process smoother and more effective.
Power Mechanism and Trigger
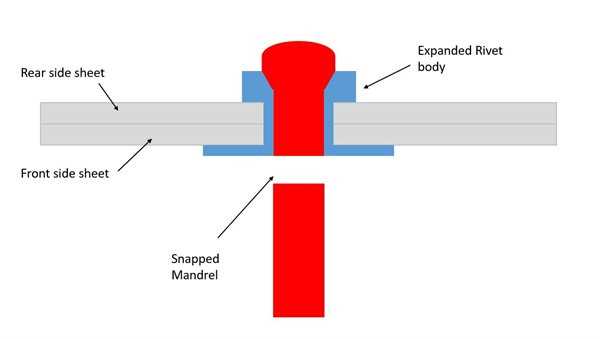
The power mechanism is at the heart of the tool, converting energy into the necessary force to perform the fastening task. This section includes components responsible for generating and directing the energy, such as springs and pneumatic systems. The trigger, usually located at the handle, controls the release of this energy, allowing users to apply force when needed.
Tooling and Holding Mechanism
Another important set of components includes the tooling and the mechanism that holds the fastener in place. These parts secure the fastener and ensure it is properly positioned before the tool exerts force. The durability and material of these components are key to the overall effectiveness, as they must withstand repeated use without compromising the quality of the connection.
How to Read a Fastening Tool Component Layout
Understanding the layout of a fastening tool’s components is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. A well-structured layout will clearly illustrate each part’s location and function, allowing users to quickly identify issues and make repairs. In this section, we will guide you on how to read such diagrams and make the most out of them.
Identifying Key Sections
The first step in interpreting a layout is recognizing the main sections of the tool. These sections are usually grouped based on their function, such as power generation, fastening mechanism, and user interface. Key components will often be labeled with numbers or symbols that correspond to their function or specific location.
- Power System: Includes components responsible for providing force, such as springs, motors, or pneumatic elements.
- Fastening Mechanism: The parts directly responsible for securing and holding the fastener in place.
- Control Interface: Typically the handle or trigger area where the user interacts with the tool.
Understanding Labels and Symbols

Most diagrams use a set of standardized labels and symbols to represent components. These can vary based on the manufacturer, but many use common notations for easy identification. Make sure to check the legend or key provided with the layout to match the symbols with their corresponding parts.
- Look for circles or arrows indicating rotating or moving parts.
- Examine rectangular or square shapes for structural components.
- Note any color coding or shading that differentiates sections based on material or function.
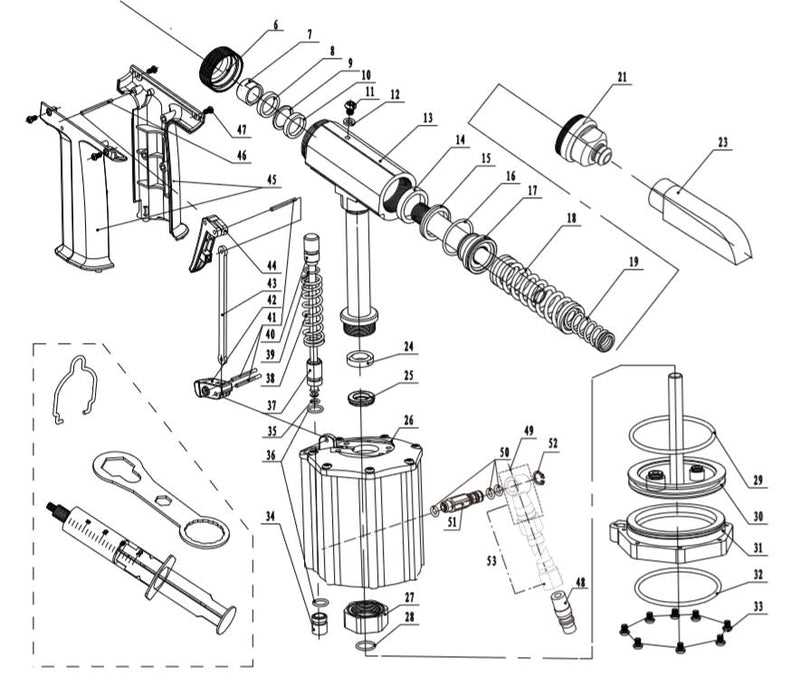
Common Fastening Tool Components and Their Functions
Each tool used for fastening has a set of core components that work together to ensure efficient operation. These elements are designed to carry out specific tasks, such as generating force, holding the fastener, and controlling the tool’s overall action. Understanding the role of each component can help improve tool maintenance and performance.
Energy Source and Mechanism
The energy source and mechanism are central to the tool’s function. These components are responsible for generating the force needed to perform the fastening task. Depending on the tool, this system may include pneumatic, hydraulic, or spring-loaded mechanisms. The energy source provides the necessary power, while the mechanism ensures that power is applied at the right time and in the correct manner.
- Power Cylinder: Houses the energy source, converting energy into motion.
- Trigger Mechanism: Activates the energy transfer when pressed by the user.
- Compression Spring: Stores and releases energy to generate force.
Fastener Holding and Positioning System
Another key set of components ensures that the fastener is correctly held and positioned before the tool applies force. These parts are designed to securely grip the fastener and keep it aligned during operation. A precise holding system is critical to ensure the tool operates smoothly and achieves the desired result.
- Gripping Jaws: Securely hold the fastener in place.
- Holder or Mandrel: Ensures the fastener is aligned for accurate placement.
- Guide Sleeve: Helps guide the fastener into the correct position during use.