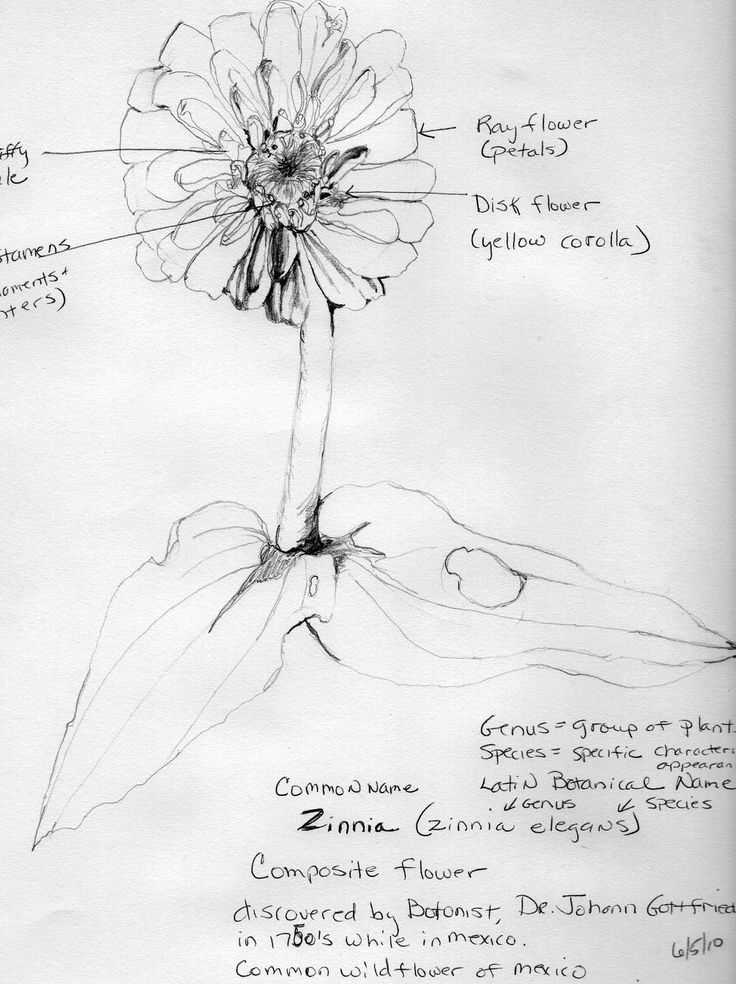
The beauty of nature can be seen in the intricate design of many plants. Understanding how each element of a blossom contributes to its overall form helps appreciate the complexity of life. This section delves into the various components that make up the structure of a blooming plant, revealing how they work in harmony to ensure growth and reproduction.
Each individual section of a plant plays a specific role, whether it is for protection, reproduction, or nutrient absorption. By examining the relationships between these sections, we gain insights into the fascinating processes of plant biology.
The delicate balance of each part is essential for the plant’s survival. From the outer protective layers to the inner reproductive structures, every feature has a specific function, ensuring that the plant flourishes in its environment.
Understanding Zinnia Flower Structure
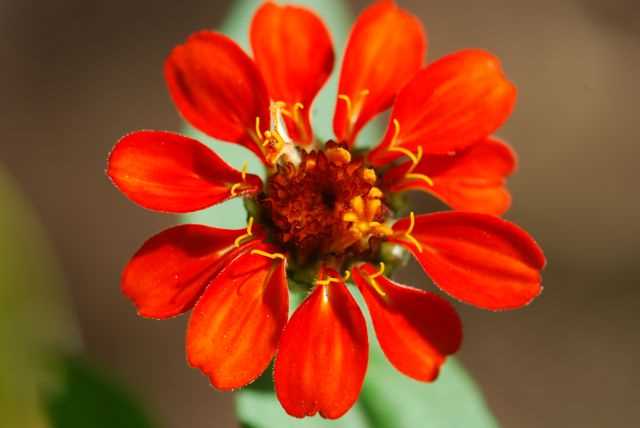

Each blooming plant is a marvel of nature, with every feature carefully designed to serve a purpose. The intricate arrangement of its components allows it to thrive, reproduce, and interact with the surrounding environment. By exploring the various sections, we can gain a deeper understanding of how each element contributes to the overall health and vitality of the plant.
The outermost structures provide protection, while inner components focus on reproduction and nourishment. These elements work together in harmony, enabling the plant to grow and maintain its cycle. By observing these features, one can appreciate how the delicate balance of design ensures survival and success in nature.
Key Components of Zinnia Blossoms
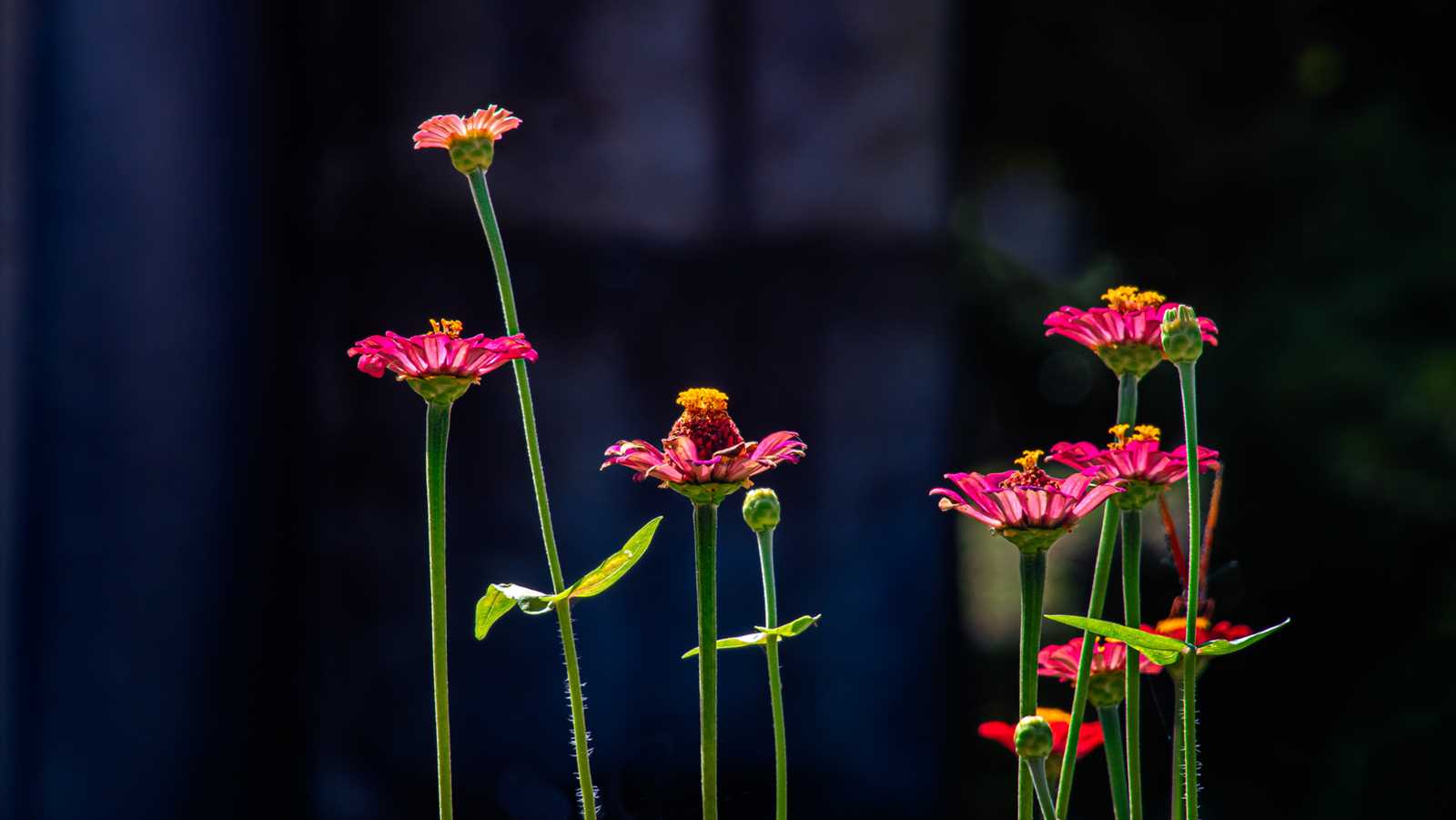

The structure of any blooming plant is a combination of various essential elements, each contributing to the plant’s growth, reproduction, and overall health. By examining these components, we can uncover how they work together to support the plant’s life cycle and environmental adaptation. From protective coverings to reproductive organs, each feature plays a vital role in the plant’s success.
Protective Structures
The outer layers serve as the first line of defense against external threats. These components are designed to protect the more delicate internal sections, ensuring the plant can withstand environmental challenges and continue to thrive. Without these protective elements, the plant would be vulnerable to pests, diseases, and harsh weather conditions.
Reproductive and Nutrient Systems
Internal components focus on reproduction and nutrient transportation. These structures are responsible for the plant’s ability to produce seeds and maintain healthy growth. By fostering the plant’s reproductive capabilities, they ensure the continuation of its species and enable the absorption of vital nutrients from the surrounding soil, supporting the plant’s development over time.
The Role of Each Flower Part
Every element within a plant’s structure has a distinct and essential role that contributes to its overall health and function. Understanding how these components interact and support each other helps us appreciate the complexity of nature’s design. These features are not random but are carefully optimized to ensure the plant’s survival, reproduction, and interaction with its environment.
Support and Protection
The outer sections of the plant provide necessary protection against various environmental threats, such as extreme weather or harmful pests. They also ensure that the internal organs are shielded from external damage, allowing the plant to maintain its integrity. These protective layers are critical for the plant’s overall resilience and survival.
Reproduction and Growth

The internal structures focus on the reproductive processes and the nourishment required for the plant’s growth. These elements enable the plant to produce offspring, ensuring its continuation. Additionally, they manage the intake of vital nutrients from the surrounding soil, promoting healthy development and sustaining the life cycle of the plant.