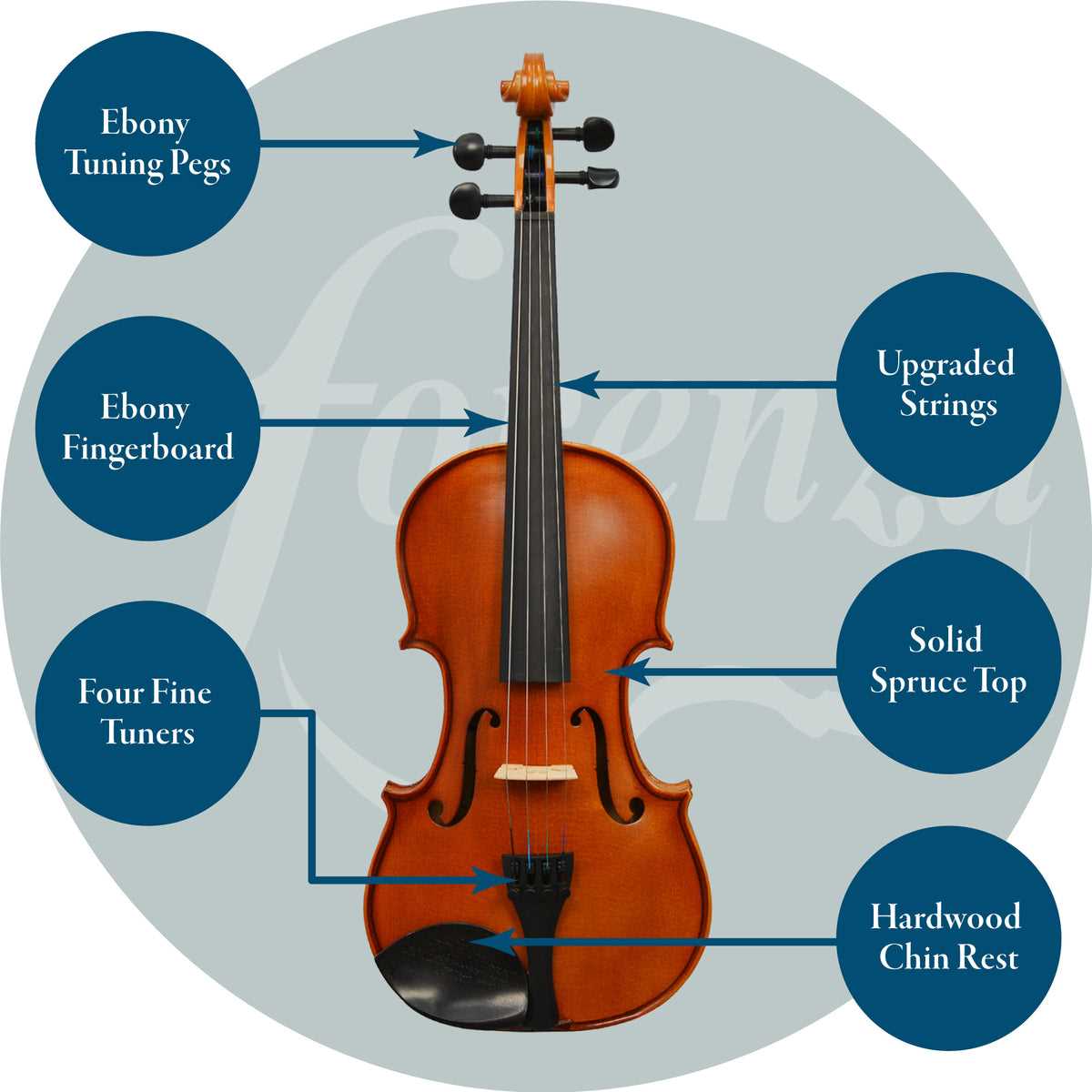
Every musical instrument is a combination of different elements that work together to create its distinct sound. The structure and design play a crucial role in shaping the tone and performance, with each component contributing to the overall experience. Knowing how these elements function helps players and enthusiasts better appreciate the artistry behind the creation of such instruments.
In this guide, we will explore the essential sections that make up this stringed instrument. From the main frame to the smaller supporting features, understanding each aspect is vital to gaining insight into how the instrument produces music. Whether you are a musician or just an admirer, a deeper understanding of these components enhances your connection with the instrument.
Key Components of a Cello
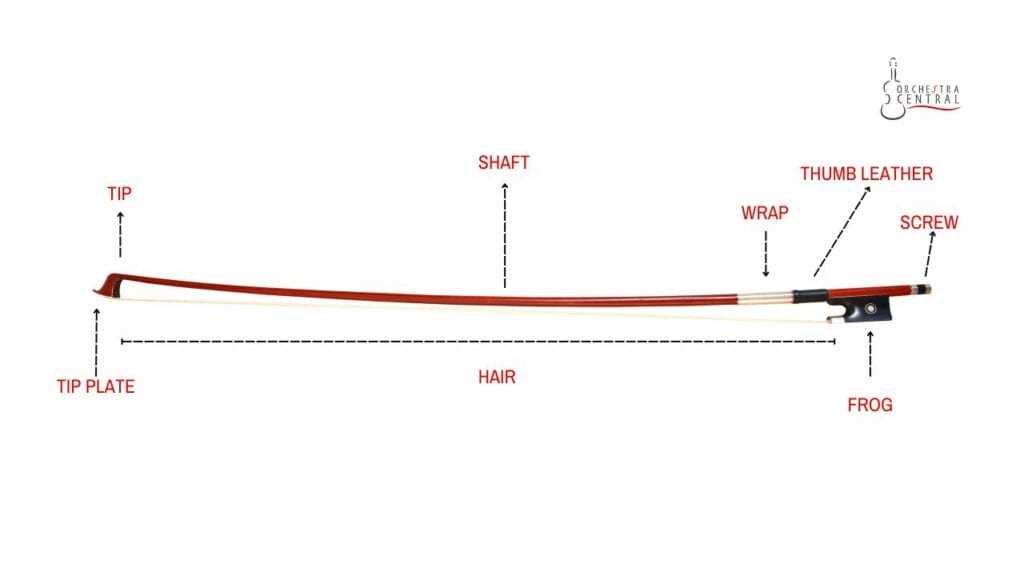
At the heart of any stringed instrument lies a carefully designed structure, with each element serving a unique function to bring the instrument to life. These crucial sections work in harmony to produce the desired sound and playability, making the understanding of their roles essential for musicians and enthusiasts alike.
The body of the instrument provides the resonating space necessary for sound amplification, while the neck and fingerboard allow for precise pitch control. Additional features, such as the bridge and tailpiece, are fundamental in transmitting vibrations from the strings to the body, influencing tone and resonance. Each element contributes to the overall acoustic performance, creating the rich and complex sound that characterizes these instruments.
Understanding the Cello Structure
The structure of a stringed instrument is a complex combination of materials and shapes that work together to create sound. Each element, from the body to the smaller components, plays a significant role in shaping the instrument’s overall function and resonance. A well-designed framework is essential for both the stability and the sound quality, ensuring that every note played resonates with clarity and depth.
The main body provides the essential acoustic chamber for sound amplification, while the neck supports the fingerboard for precise note production. The strings, when tightened across the frame, are integral to generating vibrations, which are then transmitted through the bridge and into the body. This intricate design allows for dynamic expression and tonal variety, making each element indispensable for the performance of the instrument.
How Each Part Affects Sound Quality
The sound quality of a string instrument is the result of how its individual components work together. Each element, from the frame to the strings, plays a vital role in shaping the tonal characteristics and overall resonance. Even small changes in one area can significantly impact the final sound produced, making the design and material selection crucial for achieving optimal performance.
The body, for example, acts as a resonating chamber that amplifies the vibrations of the strings, affecting the richness and volume of the sound. The bridge serves as the conduit that transmits these vibrations from the strings to the body, influencing the tone’s warmth or brightness. The tension of the strings and their contact with the fingerboard also directly affect pitch accuracy and the instrument’s responsiveness, contributing to the musical expression and clarity in each note played.