Understanding the internal and external components of a gourd is essential for both agricultural and culinary purposes. By delving into its composition, one can appreciate the complexity and functionality of each segment that makes up this unique vegetable. This knowledge aids in everything from growing to preparing dishes with it.
Key Elements of the Gourd

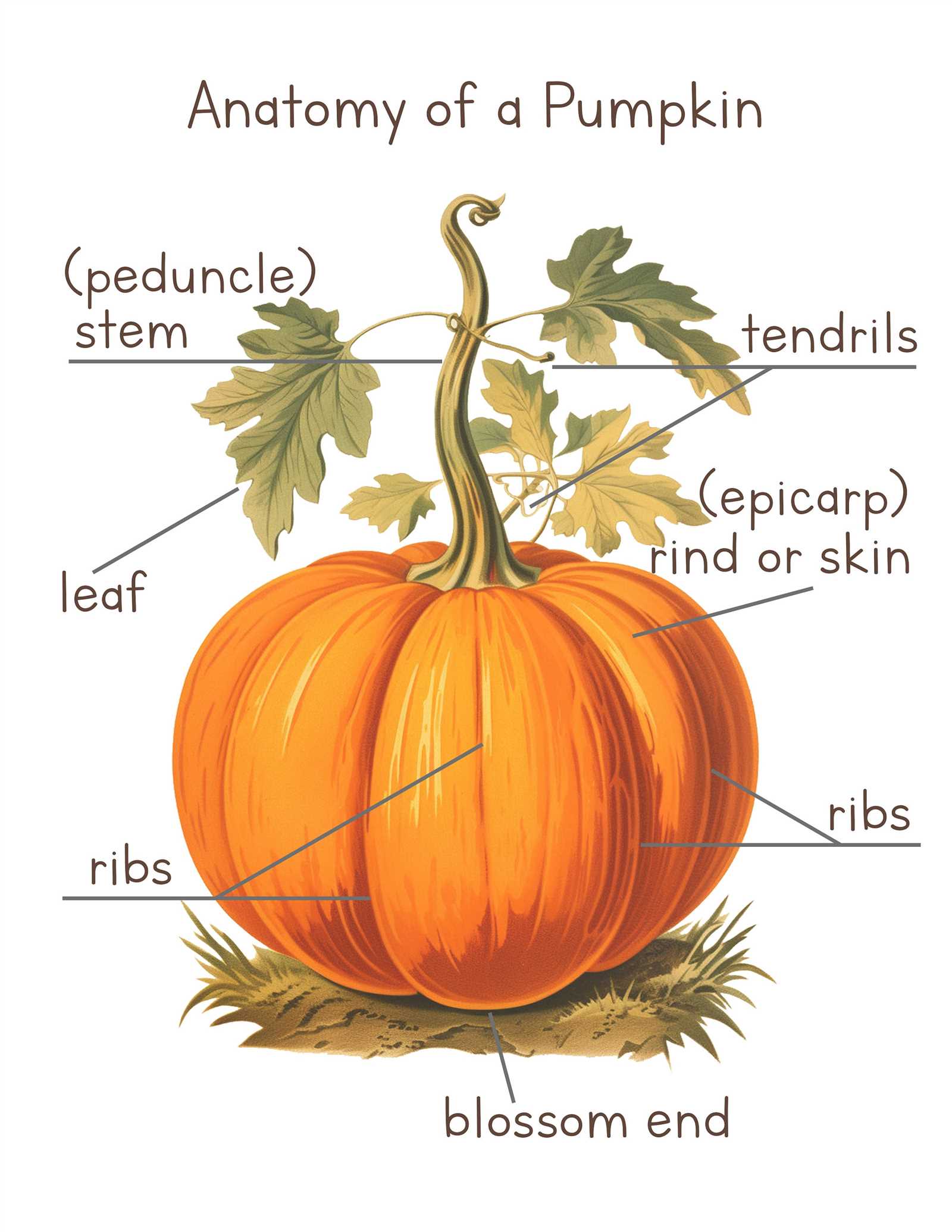
A gourd consists of various sections, each playing a distinct role in its development and growth. The outer layer serves as protection, while the internal sections contribute to its nutrient storage and reproductive capabilities. Each element works in harmony to support the plant’s life cycle.
Outer Layers and Their Functions

- Skin: The tough outer covering protects the inner sections from environmental factors.
- Stem: This connects the fruit to the vine, enabling nutrient transport during growth.
- Rind: The hard surface layer that safeguards the inner contents until it’s harvested.
Internal Structure and Growth Role
Inside, the gourd contains a variety of structures that are essential for its development. The seed cavity is vital for reproduction, while the flesh provides the nutrients needed to support growth and maturity.
Understanding Reproduction and Growth

The growth process begins from the seed and continues as the fruit matures. Throughout its life cycle, each component of the gourd undergoes significant changes, ensuring that the plant reaches its full potential. Knowledge of these stages is crucial for successful cultivation and harvesting.
Essential Elements for Growth and Development
The growth of any gourd relies on several interconnected structures. Each component plays a vital role in its survival and maturity, ensuring that the plant can thrive, reproduce, and ultimately produce the desired harvest. Understanding these parts is crucial for cultivating and caring for the plant effectively.
Outer Protection and Support
The outer shell and stem of the gourd provide essential protection and stability. The skin acts as a barrier against external factors, while the stem facilitates the transportation of nutrients from the root system. Together, they ensure the plant’s overall health and resilience in varying environmental conditions.
Internal Functions for Growth
Within the gourd, the internal components are responsible for storing nutrients, enabling reproduction, and facilitating the plant’s development. The flesh contains valuable nutrients that support growth, while the seed cavity is essential for the next generation of the plant. These inner structures allow the gourd to mature and reach its full potential.
Collaboration Between Elements
Each element of the gourd works synergistically to ensure optimal growth. The outer layers protect, while the internal components nourish and prepare the plant for reproduction. This interconnected system allows the gourd to undergo its life cycle smoothly, from seed to mature fruit.
Visual Representation of Anatomy
A detailed visual guide to the gourd’s anatomy helps to better understand the function of each part. Through diagrams and illustrations, one can easily identify and comprehend the role of every component, from the outer surface to the internal sections that contribute to its growth and development.