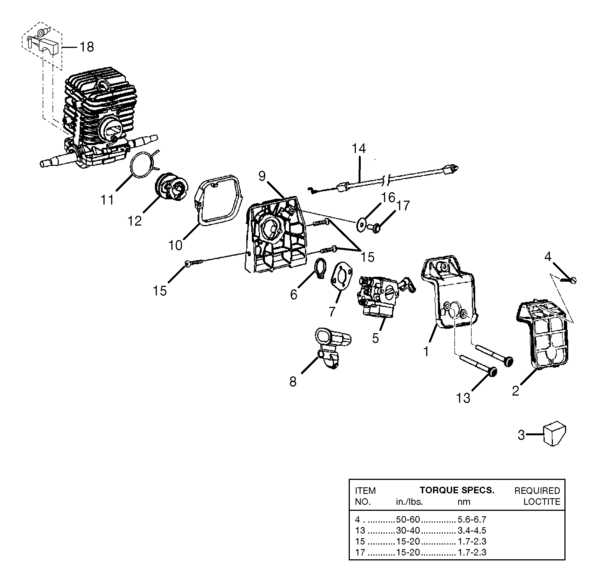
For any tool, knowing how its individual elements work together is essential for proper maintenance and efficient use. This knowledge not only helps in understanding its operation but also in identifying potential issues. Familiarizing yourself with the structure and functions of each component will allow you to tackle repairs with confidence and minimize downtime.
Identifying and understanding key elements of a saw can make a significant difference when it comes to troubleshooting. Each part plays a specific role, and recognizing them ensures that your equipment operates at its best. Properly diagnosing problems becomes easier when you know the location and function of each piece.
Whether you are dealing with wear and tear, damage, or regular maintenance, having a clear reference guide is invaluable. Knowing how to interpret the assembly and functionality of each component will save you time and effort when performing repairs or replacements. With the right tools and knowledge, you can extend the life of your equipment and keep it running smoothly for years to come.
Exploring Saw Component Functions
Every tool consists of a series of interconnected elements, each serving a unique purpose to ensure optimal performance. Understanding how each part contributes to the overall function allows for better handling and maintenance. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at how the key components work together to provide efficiency and power.
The engine, for example, is the heart of the tool, driving the mechanical force that powers the blade. Without proper combustion and fuel flow, the entire system fails to operate. The ignition system ensures that the engine runs smoothly, while the carburetor manages the fuel-air mixture for optimal performance.
The bar and cutting mechanism are crucial for the effectiveness of the tool. The bar supports the chain, guiding it through the material being cut, while the chain itself rotates at high speed to deliver cutting power. Other components, such as the clutch and tensioning system, ensure that the chain operates at the right speed and tension for maximum efficiency.
Additionally, the safety features and ergonomic design of the tool cannot be overlooked. These elements provide the necessary protection for users and contribute to overall comfort and usability. Together, these components form a cohesive system that relies on each part functioning properly to achieve the desired results.
How to Read a Tool Assembly Layout
Interpreting an assembly layout requires understanding the relationships between various components and how they fit together to form a functioning unit. These visual representations are essential for identifying parts, their functions, and their correct placement within the system. Knowing how to read such layouts enables users to troubleshoot, perform repairs, and assemble equipment with ease.
The layout typically features a detailed illustration, labeling each part and showing its position relative to others. By following the labeled lines and referencing the accompanying list, you can match each part with its corresponding number or name. This is crucial when identifying worn or damaged components and knowing exactly where to apply replacements.
Furthermore, understanding these visuals helps in recognizing how different parts interact during operation. For instance, the connection between the motor and the cutting mechanism is essential for proper performance, and an assembly layout makes these connections clear. Pay attention to the orientation and specific markings to ensure the correct assembly and functionality of the tool.
With a clear understanding of how to read such layouts, performing repairs and maintenance becomes a straightforward task. These diagrams not only provide clarity but also ensure that each component is handled in accordance with the manufacturer’s guidelines for optimal performance and safety.
Essential Components of Saws

Every power tool is built around a series of crucial elements, each contributing to its overall functionality. Understanding these components is key to maximizing efficiency, performance, and durability. In this section, we will explore the most important parts that make up the tool and how they work together to achieve the desired results.
Core Functional Elements
The following components are fundamental to the effective operation of the equipment:
- Engine: The power source that drives the tool, converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- Fuel System: Includes the carburetor, fuel lines, and filter, ensuring proper fuel-air mixture and clean operation.
- Cutting Mechanism: Comprising the chain and bar, this is responsible for the actual cutting action.
- Clutch: Engages the cutting mechanism and allows the user to control the tool’s speed.
- Safety Features: Includes mechanisms like the chain brake and vibration dampening, designed to protect the user.
Supportive Systems
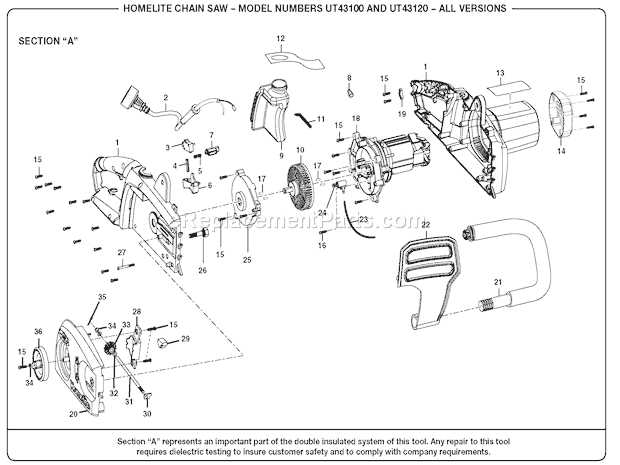
In addition to the core elements, several supporting systems help ensure smooth operation:
- Tensioning System: Maintains the correct tightness of the chain for optimal cutting performance.
- Lubrication System: Delivers oil to the chain and bar, reducing friction and extending the life of the tool.
- Air Filter: Prevents dust and debris from entering the engine, maintaining proper airflow and engine performance.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall operation. Proper maintenance and timely replacements ensure that the tool continues to function at peak performance for an extended period.
Common Issues and Fixes for Power Tools
Even the most reliable tools can experience issues over time due to wear, improper use, or lack of maintenance. Understanding the most common problems and knowing how to address them can help ensure your equipment runs smoothly. In this section, we’ll explore typical issues and provide practical solutions for fixing them efficiently.
Engine and Fuel Problems
One of the most frequent issues encountered with power tools is engine malfunction, often related to the fuel system. Common problems include:
- Engine not starting: This could be caused by stale fuel, clogged fuel lines, or a dirty spark plug. To fix this, drain old fuel and replace it with fresh fuel, clean or replace the spark plug, and inspect the fuel lines for blockages.
- Loss of power: If the engine runs but lacks power, check the air filter for dirt and debris. A clogged filter can restrict airflow, leading to poor performance. Clean or replace the filter to restore engine efficiency.
Cutting Mechanism and Chain Issues
Another common area of concern is the cutting mechanism. Issues such as chain malfunction or poor cutting performance can be due to the following:
- Chain slipping: A loose or improperly tensioned chain can cause slipping. Ensure the chain is properly tightened according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Chain dullness: A blunt chain will not cut effectively. Sharpen the chain regularly or replace it if necessary to maintain optimal cutting performance.
Regular maintenance and proper troubleshooting can extend the life of your equipment and keep it running smoothly for years. Knowing how to identify and resolve these common issues can prevent larger, more costly repairs down the line.
Repairing Your Power Tool
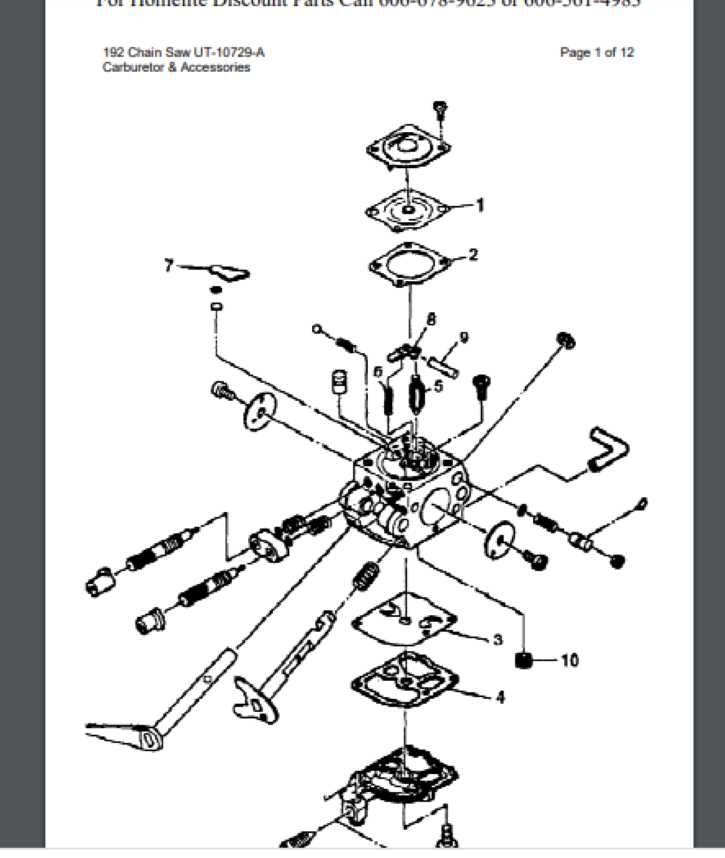
When a tool experiences issues, timely repairs are essential to restore its functionality and ensure longevity. Whether it’s a minor adjustment or a more significant replacement, knowing the correct steps can make the process easier and more efficient. This section provides a guide for troubleshooting and fixing common problems to keep your equipment in top working condition.
Common Repair Steps

Before diving into repairs, it’s important to identify the issue. Here are some of the most frequent problems and their corresponding solutions:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Tool not starting | Old fuel, clogged spark plug | Replace fuel, clean or replace spark plug |
| Chain not moving | Loose or improperly tensioned chain | Tighten the chain to manufacturer’s specifications |
| Increased vibrations | Loose parts or damaged bar | Inspect and replace damaged components |
| Poor cutting performance | Dull chain | Sharpen or replace the chain |
Step-by-Step Repair Process
Once the issue is identified, follow these steps to perform the necessary repairs:
- Turn off the tool and ensure all power sources are disconnected before starting any work.
- Inspect the problem area, noting any visible damage or wear. Refer to the tool’s layout for part identification.
- Remove any damaged components, such as the chain or spark plug, and replace them with new, compatible parts.
- Reassemble the tool and test it to ensure proper operation.
- Regularly maintain your tool to prevent future issues, including cleaning and lubricating parts as needed.
By following these steps, you can effectively repair and maintain your tool, ensuring it remains a reliable and efficient piece of equipment for years to come.