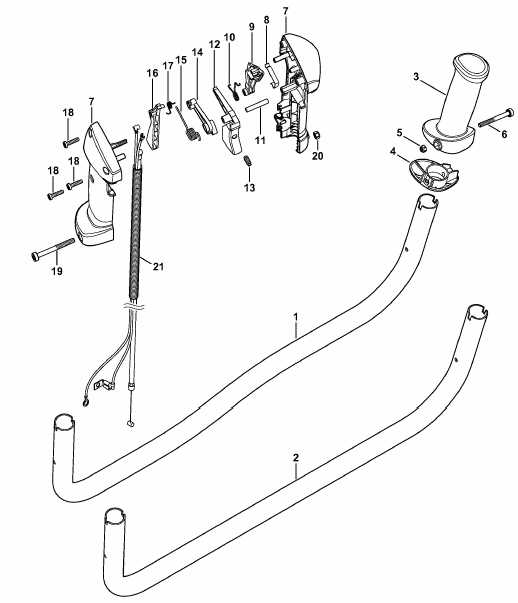
Understanding the intricate assembly of complex equipment is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each piece plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth functioning of the entire system. Having a comprehensive view of all the key elements allows users to maintain and troubleshoot the machinery with confidence.
In this section, we will explore the various segments that make up this tool, focusing on their roles, interconnections, and how they contribute to the overall performance. This knowledge is crucial for anyone looking to enhance their understanding or undertake repairs and upgrades.
Identifying individual components helps in recognizing potential issues early on. By familiarizing yourself with the design and arrangement of these elements, you can ensure that every part is working as intended. In turn, this improves both longevity and reliability.
Understanding the Stihl GS 461 Components
Each tool consists of a variety of interconnected elements, each fulfilling a specific function to ensure proper operation. Gaining a clear understanding of these components is essential for anyone looking to maintain or repair the equipment effectively. By learning how these parts work together, users can identify potential problems and carry out precise repairs when needed.
Key Elements of the Assembly
The equipment features a series of essential components, including mechanical and electrical elements. The core of the machine is built around a motor, which drives various moving parts, allowing the tool to perform its intended functions. Along with the motor, there are key support components such as the housing, gears, and connectors, all of which must be in working order to ensure smooth operation. Understanding these core components helps to streamline maintenance and prevent unnecessary breakdowns.
Function and Interaction of Components
It is crucial to recognize how each part interacts with the others. For instance, the power generated by the motor is transmitted through a series of gears that transfer motion to other parts of the machine. The coordination of these components enables the tool to operate efficiently. Regular checks of these elements ensure that wear and tear do not lead to malfunction, helping to extend the tool’s life and maintain performance standards.
Key Parts and Their Functions
Every tool is built with essential elements that each serve a distinct purpose. Understanding the role of each component is crucial for proper functioning and maintenance. By familiarizing yourself with these key components, you can ensure optimal performance and identify issues early on.
Motor and Power Transmission
The motor is the heart of the machine, converting energy into mechanical motion. This power is then transmitted through various mechanisms such as gears and belts, allowing the equipment to perform its tasks. Without efficient power transfer, the entire system would struggle to operate effectively. Regular inspection of the motor and transmission components is necessary to avoid disruptions in function.
Support Structures and Housing
Support elements, such as the casing and frame, provide stability and protection for the internal components. These parts are designed to withstand the pressures and stresses experienced during operation. Additionally, they house the internal elements safely, ensuring everything remains in place and protected from external damage. A well-maintained support structure prevents unnecessary wear and prolongs the equipment’s lifespan.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of Assembly
Assembling a tool requires attention to detail and precision to ensure every component is correctly positioned. Each step of the process plays a critical role in achieving a functional and reliable machine. By following a systematic approach, users can ensure that all parts are securely fitted and work together seamlessly.
The assembly process begins with the base frame, which provides the structure for other components. Once the frame is in place, the next steps involve adding the motor and aligning the mechanical connections. After securing the power system, other supporting elements, such as connectors and safety features, are added to complete the assembly. Following the correct sequence is essential to ensure that the tool functions as intended.
Once all parts are assembled, it’s important to check for any misalignments or loose connections. A final inspection ensures that each element is in the proper position, preventing potential malfunctions during operation. Regular maintenance and reassembly as needed will help maintain the tool’s effectiveness over time.
How to Assemble the Tool Correctly
Assembling any equipment requires a methodical approach to ensure all components are connected properly. Following each step carefully not only enhances performance but also prevents potential damage. A proper assembly guarantees that the tool will function at its best, making it easier to maintain over time.
Step-by-Step Assembly Process
Start by placing the main frame securely on a flat surface. The first component to install is the motor, ensuring it is aligned with the designated mountings. Next, attach the necessary gears and mechanical linkages that transfer motion from the motor to the working elements. Double-check each connection to ensure a tight fit and no potential for slippage during use.
Final Checks and Adjustments
After all major components are in place, it is important to verify their alignment. Ensure that all connectors are secure and that there is no visible movement in the joints. Once everything is set, run a brief test to check for any unusual sounds or vibrations, indicating a need for adjustment. Regular inspections after assembly will help maintain optimal performance.
Common Issues with Equipment Components
Even the most durable tools can experience malfunctions over time. Understanding the most frequent problems can help in identifying and resolving issues quickly, ensuring continued functionality. Regular maintenance and awareness of potential challenges allow users to extend the lifespan of their equipment and avoid costly repairs.
- Motor Malfunctions: Overheating or failure to start can often be attributed to poor connections or wear in the motor itself.
- Gear Slippage: If the gear system becomes misaligned, it can cause the equipment to lose power or function erratically.
- Loose Connections: Improper assembly or worn connectors can result in parts becoming loose, affecting the performance.
By regularly inspecting these components, users can avoid serious breakdowns. It’s crucial to address issues such as these promptly, as neglecting them may lead to more significant damage.