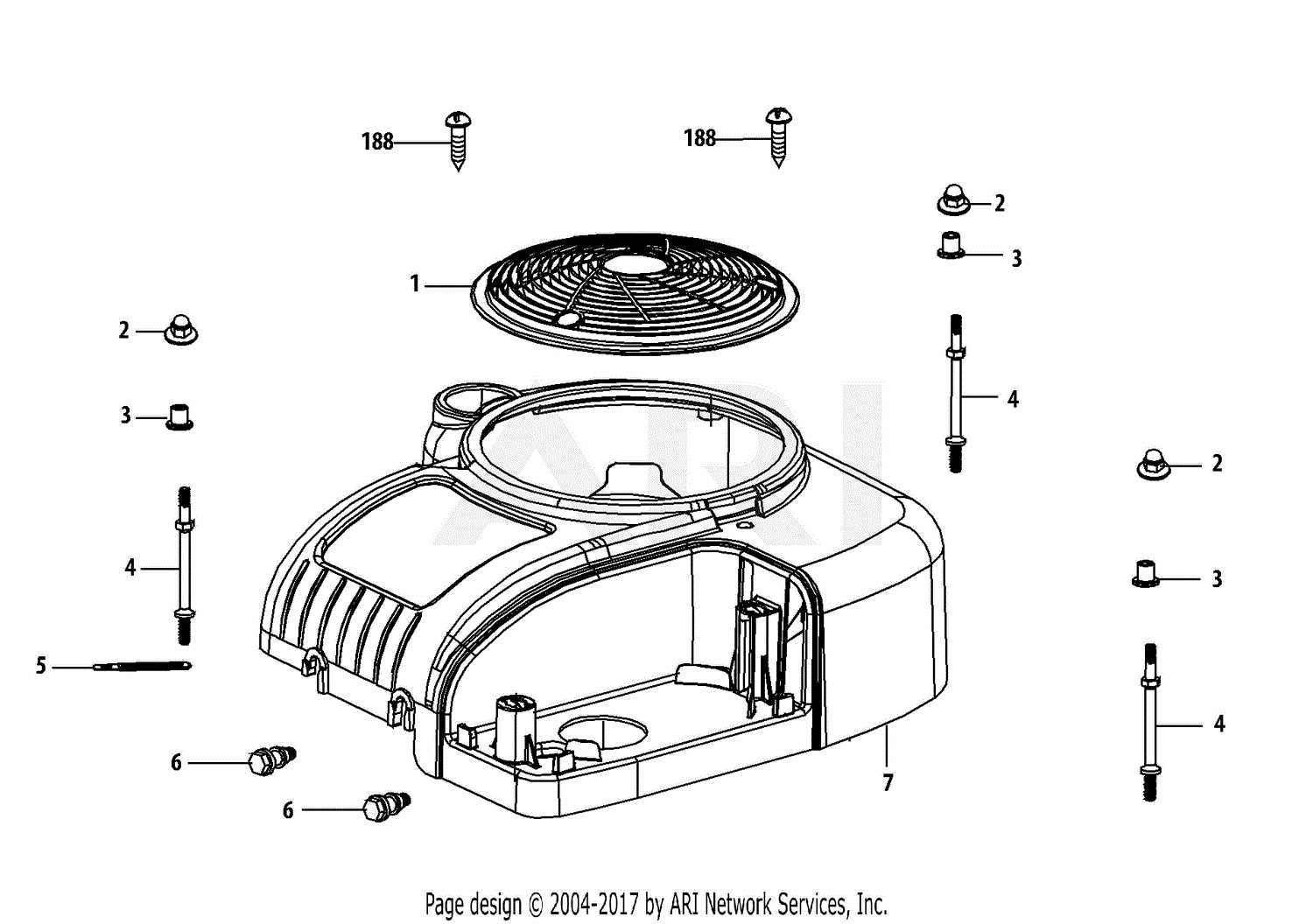
When working with small machinery, having a clear understanding of its inner workings is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Knowing how each component functions together allows you to identify problems early and keep the system running smoothly.
In this guide, we will explore the key elements of a popular small engine, offering insights into their arrangement and function. A detailed visual guide will help you recognize each part’s role, making repairs or adjustments easier and more efficient.
By familiarizing yourself with the layout and connections within the system, you can ensure optimal performance and extend the life of your equipment. With the right knowledge, common issues can be quickly addressed, preventing costly repairs.
Understanding Small Engine Components

For any mechanical system, it’s crucial to understand the role each element plays in its operation. The different components work together in a precise manner to ensure the system runs efficiently. Recognizing how each part interacts and contributes to the overall function is key for maintaining performance and preventing issues.
In small power units, there are several essential components that govern movement, fuel delivery, and exhaust management. These parts, whether internal or external, need to be in proper working order for smooth operation. A breakdown in any one of these can lead to suboptimal performance or complete failure.
Familiarity with these components not only aids in troubleshooting but also helps in making informed decisions about maintenance and repairs. Understanding their structure, function, and connection allows for efficient diagnosis and ensures longevity of the equipment.
How to Read the Small Engine Schematic
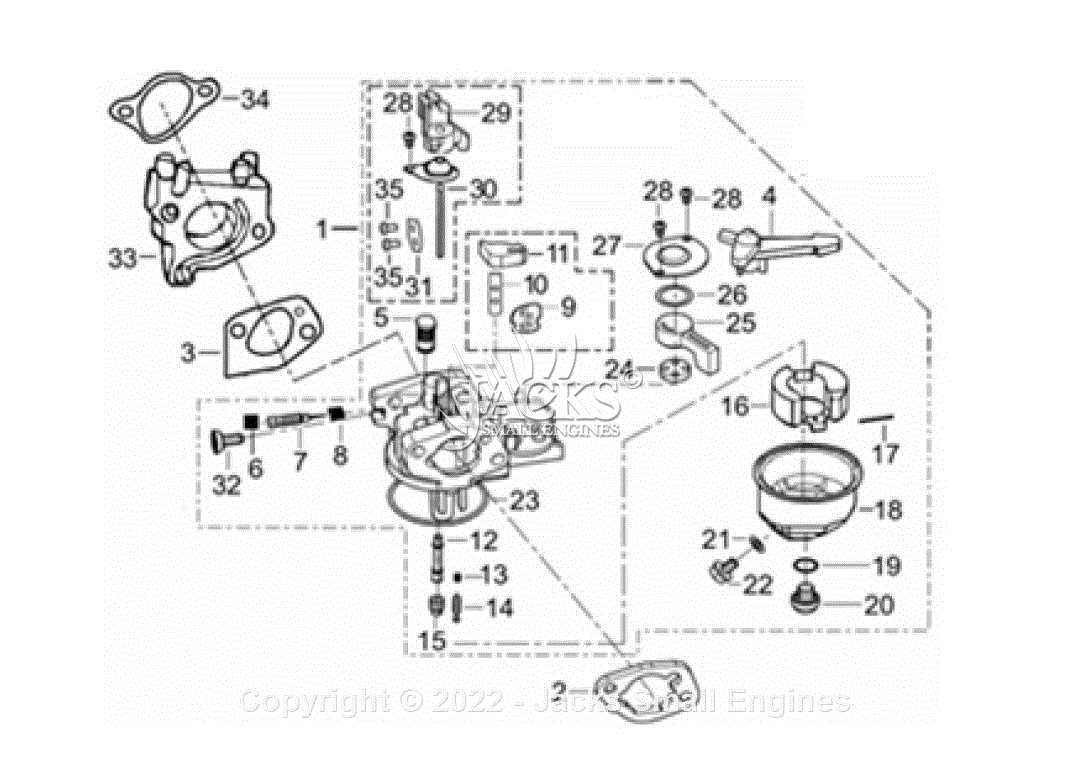
Understanding how to interpret a schematic is essential when working with mechanical systems. A well-organized illustration can provide a clear view of how the different elements are arranged and interconnected, making troubleshooting and maintenance easier. Knowing how to read these illustrations helps in identifying the location and function of each component.
The schematic typically includes labels and symbols that represent each element, with lines indicating how they are linked. Some diagrams may use color coding or shading to highlight specific areas, making it easier to focus on critical sections of the system. It’s important to follow the flow of the diagram from one section to another to grasp how everything works together.
By familiarizing yourself with the structure of these diagrams, you can quickly spot discrepancies or worn-out parts, ensuring you address potential issues before they escalate. A clear understanding of the layout improves repair accuracy and helps maintain optimal system function.
Common Issues and Solutions for Small Power Units

Like any mechanical system, small power equipment can experience various problems over time. Recognizing and addressing these issues early can prevent further damage and costly repairs. By understanding common malfunctions and their solutions, users can troubleshoot and maintain their equipment more effectively.
Some of the most frequent issues include:
- Starting problems: Difficulty starting the system is often caused by issues like stale fuel, clogged filters, or spark plug failure.
- Loss of power: This could be due to fuel delivery problems, worn-out components, or poor compression.
- Excessive vibration: Unbalanced parts or loose fasteners may lead to unwanted shaking during operation.
- Overheating: A blocked cooling system or low oil levels can cause the unit to overheat, damaging internal components.
To solve these issues, it is essential to:
- Inspect fuel lines and replace any old or contaminated fuel.
- Clean or replace the air and fuel filters regularly.
- Check and replace spark plugs as necessary.
- Ensure that all parts are securely fastened and balanced.
- Maintain proper oil levels and clean the cooling system to prevent overheating.
By following these solutions, users can ensure their small power equipment operates efficiently, extending its lifespan and minimizing unexpected downtime.