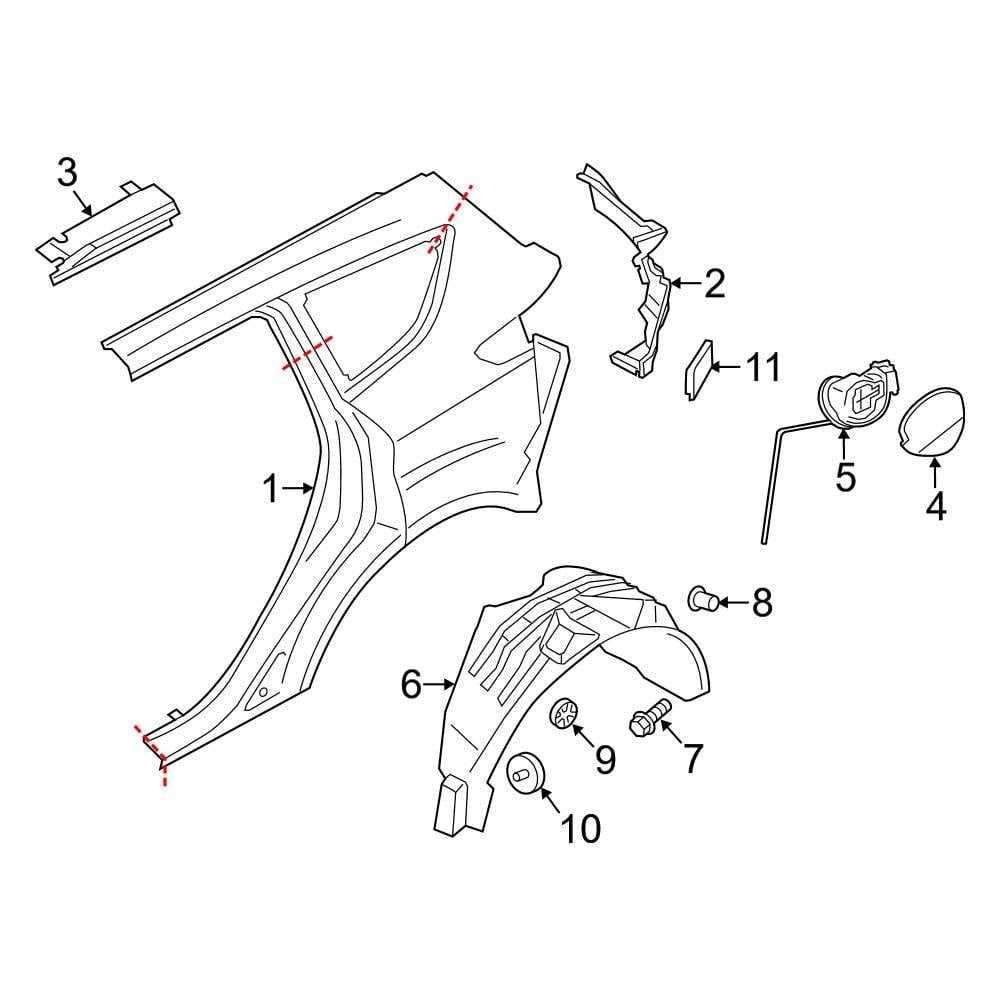
When working on automotive repairs, having a clear understanding of how different elements are arranged and interact is essential. Knowing where each piece fits and how it functions allows for better troubleshooting and efficient maintenance.
Every car has a unique structure, with its own layout of systems and components. Whether you’re replacing a damaged component or upgrading a system, it’s vital to understand how these parts are organized within the vehicle. This can prevent unnecessary confusion and help avoid mistakes during repairs.
Visual aids, like component charts, can be extremely helpful for visualizing the entire system. These guides provide a detailed breakdown of all crucial parts, making it easier for mechanics and DIY enthusiasts to locate and identify necessary components quickly and accurately.
Understanding the 2013 Ford Escape Components
Every vehicle is made up of a series of interconnected systems, each with its own set of components. These elements are designed to work in harmony, ensuring smooth operation and reliability. Understanding the layout of these systems helps in identifying potential issues and performing precise repairs.
Engine and Transmission System
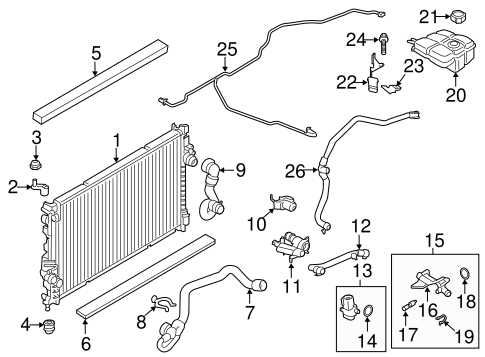
The engine is the heart of any vehicle, and its connection to other systems is crucial for performance. The transmission, which controls the power flow from the engine to the wheels, works closely with the engine components. Identifying individual components within the engine and transmission can aid in diagnosing problems such as power loss or shifting issues.
Suspension and Steering Systems
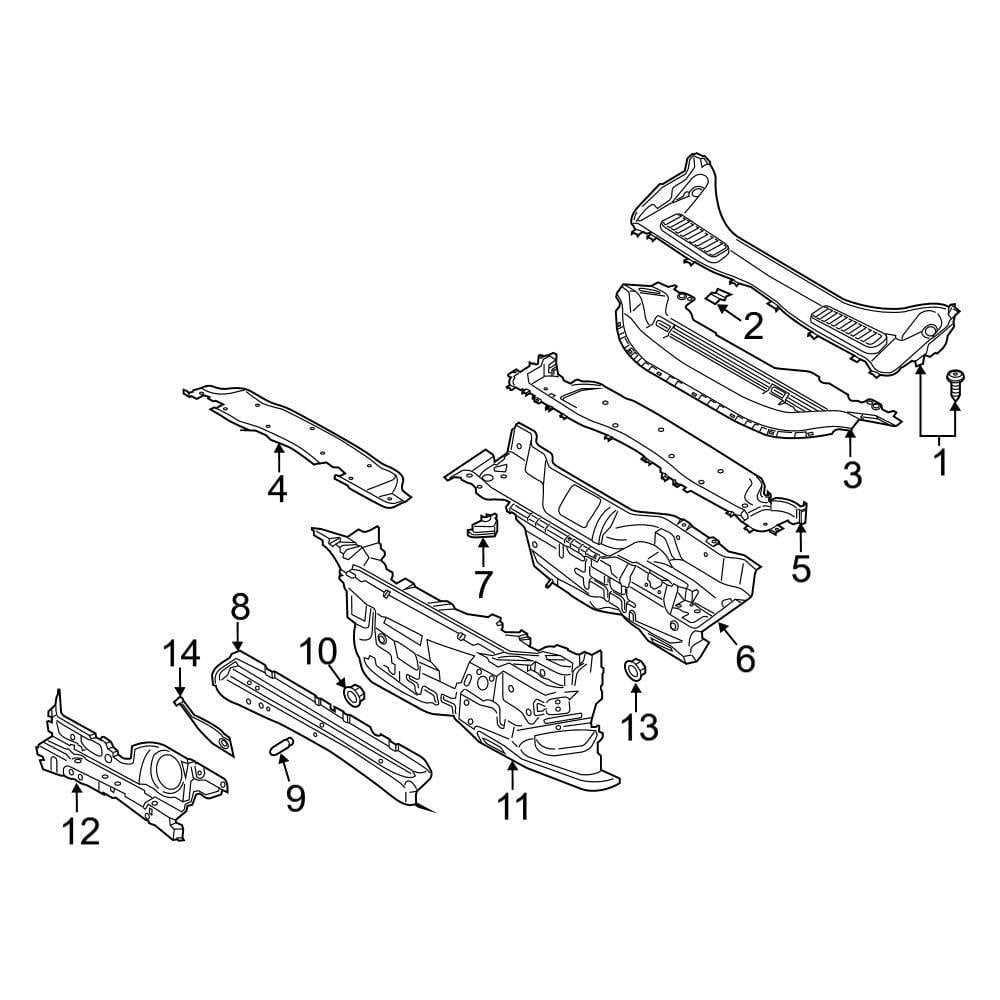
The suspension system supports the vehicle’s weight and ensures a smooth ride. It is made up of various parts such as shocks, springs, and control arms. The steering system, on the other hand, enables precise control of the vehicle’s direction. Knowing the layout and function of these systems allows for effective troubleshooting of handling issues or ride discomforts.
Key Parts and Their Functions
Each vehicle is equipped with various crucial elements, all of which serve specific roles to ensure its proper functioning. Recognizing the importance of each component and understanding how they interact with one another is key to effective maintenance and repairs.
The engine, for example, is responsible for powering the entire vehicle. It converts fuel into energy, which is then transferred through the transmission to the wheels. The fuel system supplies the engine with the necessary resources, while the exhaust system ensures that harmful gases are properly expelled.
Similarly, the braking system plays a vital role in safety, allowing the vehicle to slow down or stop when needed. The suspension system, meanwhile, ensures stability and comfort by absorbing shocks from the road, while the electrical system manages the flow of energy to various components like lights, sensors, and the battery.
How to Read the Parts Diagram
Understanding how to interpret a vehicle’s component chart is essential for any repair or maintenance task. These visual aids offer a comprehensive overview of where each piece fits and how various systems are organized within the vehicle. Learning how to read them accurately allows for more efficient repairs and easier identification of parts that may need replacing.
Identifying Components
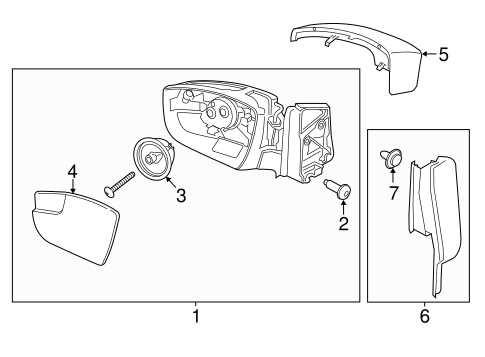
The first step in reading a component chart is to identify the individual elements shown. Each part is typically represented by a number or symbol, which corresponds to a description or reference in the accompanying manual. Here’s how to proceed:
- Look for labeled sections, which group related components together.
- Locate part numbers next to each symbol for easy identification.
- Use the reference list or key to find the description of each component.
Understanding the Layout
Next, focus on the overall layout of the chart. The components will usually be arranged in a way that reflects their location in the vehicle. The layout helps to visualize how parts connect with each other within various systems. Pay attention to:
- The position of parts, showing their relationship to one another.
- How the components are grouped based on their functions.
- The orientation of components to help identify front, back, or side placements.