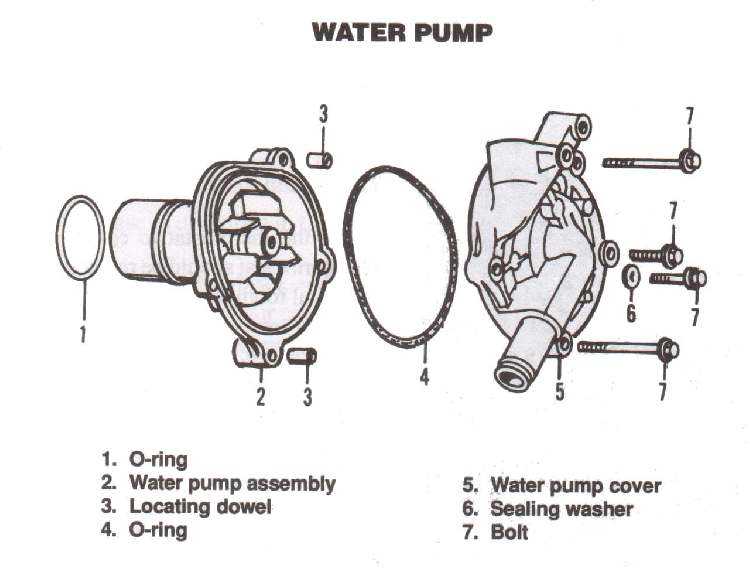
Every mechanical system designed to circulate fluids relies on a set of interconnected elements that work in unison. These individual components serve distinct functions to ensure smooth operation, contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the entire mechanism.
Identifying and comprehending the role of each part is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. A clear understanding of how these elements fit together can prevent costly repairs and extend the system’s lifespan. Regular inspection and knowing what to look for in each part can significantly reduce the risk of malfunctions.
Effective care involves more than just recognizing the basic components; it requires knowing how they interact and what each contributes to the overall flow and performance. By examining these crucial elements, users can gain insight into the system’s functionality and address issues before they escalate.
Key Components of a Circulating System
A circulating system is made up of several critical elements that work together to facilitate the movement of liquids. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining the system’s performance and ensuring its longevity. Understanding the function and importance of these individual parts is essential for troubleshooting and effective maintenance.
Impeller
The impeller is a rotating component that propels fluid through the system. It generates the force necessary to move the liquid from one area to another. Without a properly functioning impeller, the entire mechanism would fail to operate efficiently, leading to poor circulation and potential damage to other components.
Seals and Bearings
Seals and bearings ensure the smooth operation of moving elements within the system. Seals prevent leaks, while bearings reduce friction between moving parts. Both components are essential for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the mechanism, especially when exposed to high temperatures or pressure.
How to Identify Key Components in a Circulating System
Recognizing the individual elements within a fluid-moving mechanism is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. By understanding their shape, position, and function, you can quickly pinpoint issues and take the necessary steps for repair or replacement. Familiarizing yourself with these critical components ensures the system continues to run smoothly.
Start by examining the outer casing of the system. Often, components like the housing or cover can give you an immediate sense of what’s inside. Once opened, look for identifiable features such as the rotating blade or shaft, which are essential for movement. Additionally, check for seals and gaskets that help prevent leakage.
Knowing the function of each element can help you identify which ones need attention. For example, the bearing is typically located near the rotating shaft and ensures smooth movement. If the system is malfunctioning, this part might be worn out or damaged. Regular inspection of these components allows for quicker identification and resolution of potential problems.
Common Issues with Circulating System Components
Over time, various elements of a fluid-moving mechanism can develop issues that affect the system’s efficiency and performance. These problems are often caused by wear, improper maintenance, or external factors such as temperature changes. Identifying these common issues early can prevent further damage and ensure the system operates at its best.
Leaks and Seal Failures
One of the most frequent problems is leakage, often caused by damaged or worn-out seals. When seals no longer provide a tight fit, fluid can escape, leading to reduced efficiency and potential damage to surrounding components. Regular inspection of the seals and gaskets is essential to catch wear before it becomes a serious issue.
Impeller Wear and Damage
The impeller is critical for generating the force needed to move fluid, and it is susceptible to wear and corrosion. Over time, it can lose its effectiveness, leading to insufficient circulation. Signs of impeller damage include noise, reduced flow, or overheating. Replacing or repairing the impeller can restore system performance and prevent further problems.