3D printing involves a complex interplay of various elements, each contributing to the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital models. The efficiency and precision of this process depend on the proper functioning of every individual component within the system. In this section, we will explore how these essential elements work together to achieve accurate results in a streamlined manner.
The interaction between these components ensures smooth operation, allowing for rapid prototyping and the creation of custom objects. Understanding their structure and function is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining optimal performance. By diving into their roles, users can gain a deeper insight into how each piece contributes to the overall effectiveness of the system.
Key Components of a 3D Printer
In order for the process of creating objects from digital designs to function smoothly, it is essential to understand the core elements that contribute to the overall system. These critical components work together, each serving a specific role, to enable the precise fabrication of complex models layer by layer. A deeper understanding of their functions allows for better management and troubleshooting when needed.
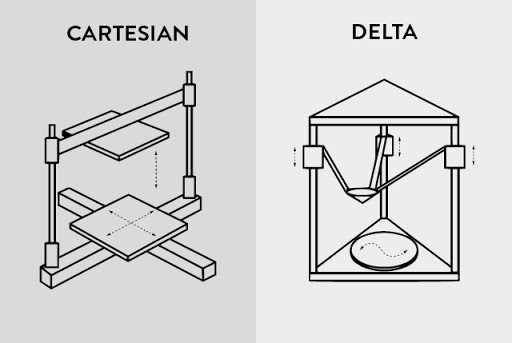
Motion System
The motion system is responsible for moving various components along specific axes during the manufacturing process. It includes elements like motors, belts, and rails, which guide the movement of the extruder and build surface. Precision in these movements is key to ensuring the desired quality and accuracy of the final object.
Extrusion Mechanism
The extrusion mechanism is central to material deposition. It controls the flow of material, ensuring that it is melted and deposited at the correct rate and temperature. This component directly impacts the quality of the layers and the strength of the finished model, making it one of the most critical aspects of the entire process.
How 3D Printer Parts Function Together
The creation of a physical object from a digital model relies on the seamless interaction of multiple system elements. Each component has its specific role, yet they must work in harmony to ensure the accuracy and quality of the final product. Understanding how these elements function together is essential for achieving optimal results and avoiding common issues.
Coordinated Movements
One of the key factors in the successful operation of the system is the precise coordination between various moving components. Motors, belts, and rails guide the material deposition tool and the build surface, ensuring they follow the correct paths. This collaboration allows the system to add material layer by layer, building up the final object with incredible detail.
Material Flow Control
Equally important is the control of material flow. The extrusion mechanism must be in sync with the movement system to deposit the right amount of material at the right speed. Any imbalance between these elements can lead to issues like under-extrusion or excessive material buildup, which negatively impacts the print quality.
Common Issues in 3D Printer Parts
Despite the advanced technology behind 3D object creation, various issues can arise due to the malfunctioning of system elements. These problems may occur at any stage of the process and can affect the overall quality, speed, and consistency of the final model. Identifying and addressing these challenges is essential for maintaining efficiency and achieving the desired results.
Clogging and Flow Problems
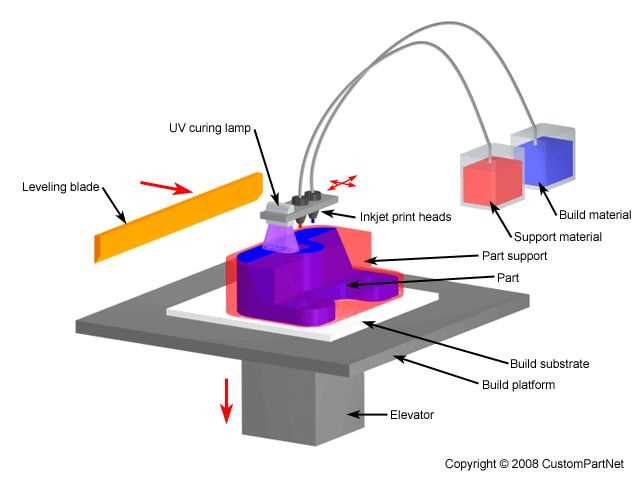
One common issue involves the blockage of the extrusion mechanism. Clogs can happen when material accumulates or hardens inside the nozzle, disrupting the flow. This can result in uneven layer deposition, gaps, or even complete failure to print. Regular maintenance and cleaning can help prevent such problems.
Inaccurate Movements
Another frequent problem is misalignment or poor calibration of the motion system. If motors, rails, or belts are not functioning properly, the tool may not move as expected, leading to errors in the positioning of layers. This can cause objects to appear warped or uneven, significantly reducing print quality. Regular checks and adjustments can help maintain precise movements throughout the process.