In modern vehicles, the system responsible for generating and distributing electrical power plays a crucial role in keeping all electrical functions running smoothly. The efficiency of this system depends on the seamless operation of various interconnected elements, each contributing to the overall process.
To fully grasp how this system works, it’s essential to explore the individual components that work together to convert mechanical energy into electricity. Each element within this setup serves a specific function, ensuring the vehicle’s power needs are met reliably.
Whether you’re a professional mechanic or an enthusiast, understanding the structure and function of these components will help in diagnosing issues and performing necessary repairs. The intricate design behind these systems reflects the importance of maintaining every part in optimal condition for overall performance.
Key Components of an Alternator
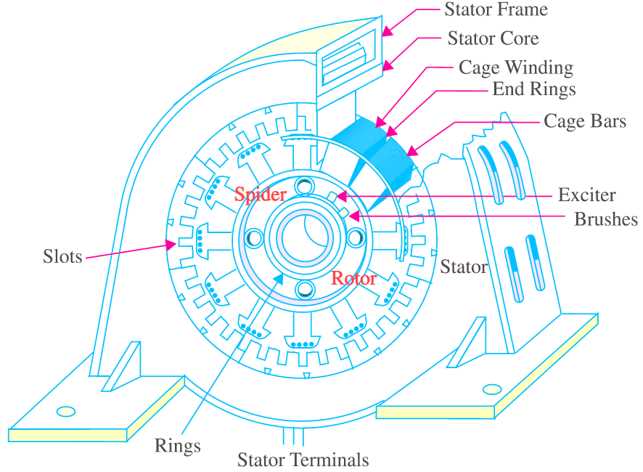
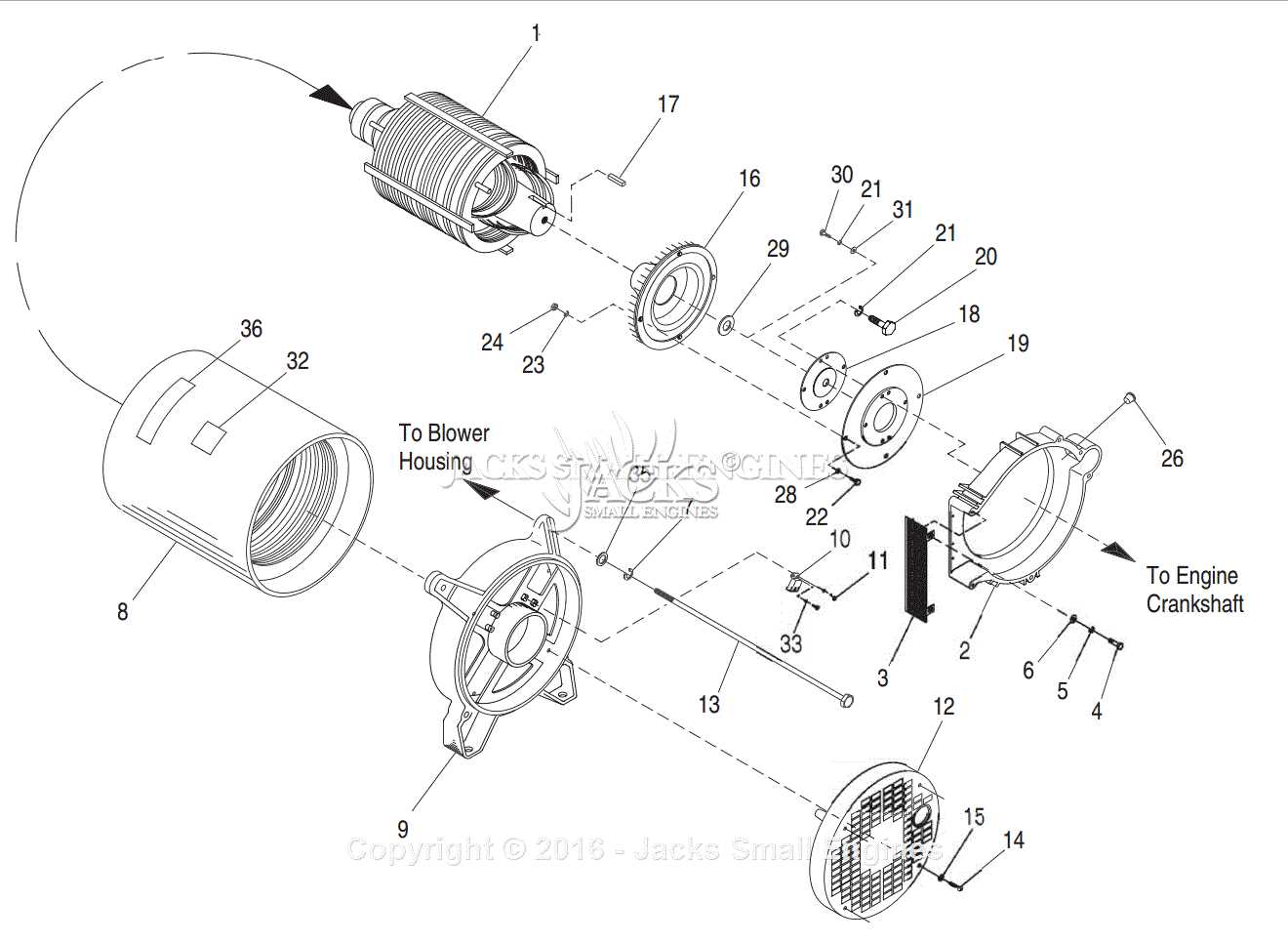
Every electrical generating system in a vehicle relies on a set of core elements that work in unison to create and deliver power efficiently. Understanding these individual components is essential for troubleshooting and ensuring proper operation. These components are designed to handle different functions, from converting mechanical motion to generating electricity, to regulating the output for the vehicle’s needs.
The main components involved in this process include a rotating element, a stationary set of windings, and mechanisms that manage the flow of current. Each plays a vital role in ensuring that electricity is generated and distributed as required. The interaction between these elements determines the overall efficiency and longevity of the system.
By becoming familiar with these core components, you can gain insight into how the entire mechanism functions. This knowledge is especially valuable when diagnosing issues or carrying out repairs to maintain the system’s effectiveness.
How an Alternator Works and Its Parts
The system responsible for generating electrical power in a vehicle operates through a precise process that converts mechanical energy into usable electricity. Understanding how this process unfolds requires examining the roles of each individual component, as they each contribute to the overall function of the system. Together, they ensure that the vehicle’s electrical needs are met reliably and efficiently.
The Role of the Rotor and Stator
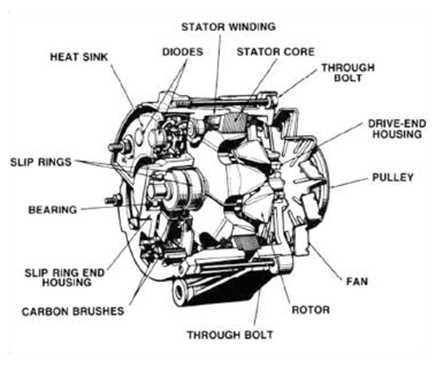
The key to power generation lies in the interaction between the moving and stationary components. The rotor, which rotates within the system, creates a magnetic field that induces current in the surrounding stator windings. This motion is essential for generating electricity and forms the basis of how power is produced.
The Importance of the Rectifier and Regulator
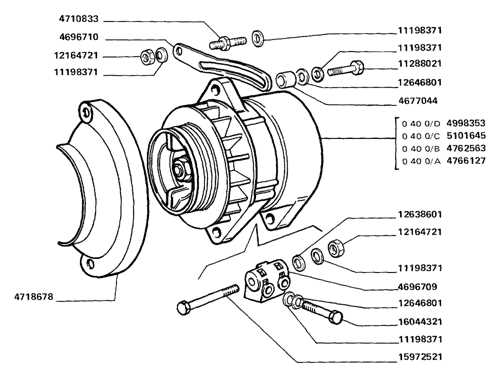
Once electricity is generated, it must be regulated to ensure that the correct voltage is maintained. The rectifier converts the alternating current into direct current, which is then regulated by the voltage regulator. This ensures that the electrical system remains stable, preventing damage to sensitive components and maintaining consistent power delivery throughout the vehicle.
Common Issues with Alternator Components
Over time, the various components responsible for generating and regulating electrical power can experience wear and tear, leading to performance issues. Identifying and understanding these common problems is essential for maintaining the vehicle’s electrical system. Regular inspection and timely intervention can help prevent larger issues and ensure reliable operation.
Wear and Tear of the Rotor and Stator
The rotor and stator, which work together to generate electricity, are susceptible to damage due to friction and heat. Over time, the bearings supporting the rotor may wear out, leading to reduced efficiency or failure. Similarly, the stator windings can develop shorts or open circuits, causing inconsistent power generation or complete loss of output.
Voltage Regulation Problems
The voltage regulator is responsible for maintaining the correct voltage levels within the system. When it malfunctions, it can result in either overcharging or undercharging the battery. Overcharging can damage the battery and other electrical components, while undercharging leads to insufficient power for the vehicle’s systems, causing electrical failures or a drained battery.