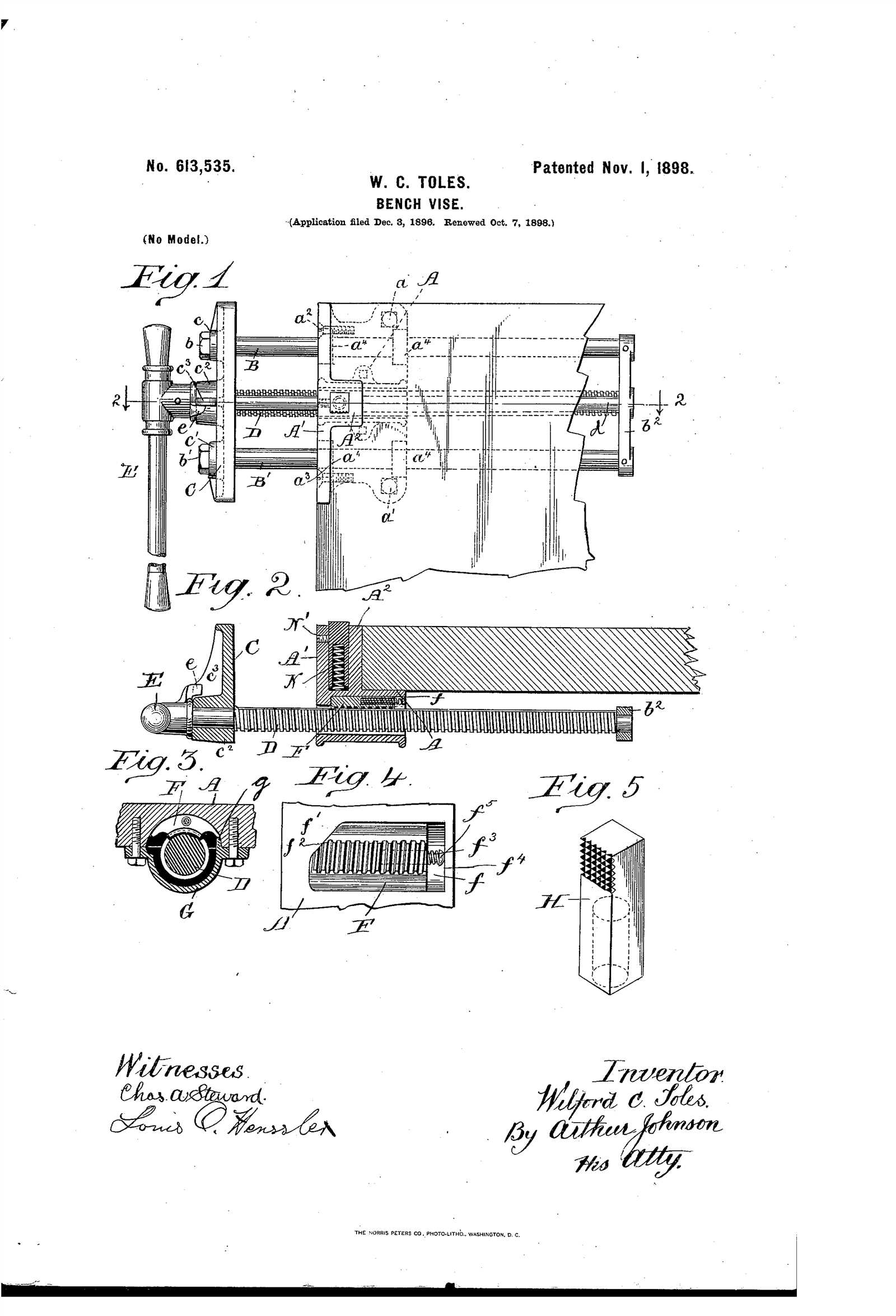
When working with heavy-duty equipment or undertaking DIY projects, it’s crucial to understand the components that make up your workholding tool. These essential elements allow you to secure materials firmly while you perform tasks like cutting, grinding, or assembling. Knowing the function and structure of each piece can improve both the safety and efficiency of your work process.
Each tool is made up of different segments that interact to provide stability and support. Familiarity with the layout and purpose of these components ensures smoother usage and proper maintenance, prolonging the tool’s lifespan and enhancing its overall performance.
Mastering these components helps users maximize productivity, whether they are seasoned professionals or beginners. Understanding the mechanical parts is key to troubleshooting issues and avoiding unnecessary repairs, making this knowledge indispensable for any workshop enthusiast.
Key Components of a Workholding Tool
Each workholding tool consists of several critical components that work together to secure materials in place during tasks. Understanding the function of these key elements is essential for efficient use and maintenance. These components are designed to provide stability, control, and precision, making the overall tool reliable and versatile for various applications.
Clamping Mechanism
The clamping mechanism is the central feature of the tool, responsible for gripping and holding the material securely. It consists of a stationary jaw and a movable jaw that tightens around the workpiece. This system is operated through a threaded spindle, ensuring a tight, adjustable grip suitable for various sizes and shapes of materials.
Base and Support Structure
The base serves as the foundation of the tool, providing stability during use. It is typically mounted to a work surface to prevent movement and enhance accuracy. The support structure helps distribute pressure evenly across the tool, allowing for smoother operation and reducing the risk of instability while working with heavy or tough materials.
How to Identify Workholding Tool Components
Recognizing the various elements that make up a workholding tool is vital for proper usage and maintenance. Each component serves a specific purpose, and understanding its role ensures smooth operation and easy identification when repairs or adjustments are needed. Knowing the names and functions of each segment will help you work more effectively and safely.
Recognizing the Jaw Mechanism
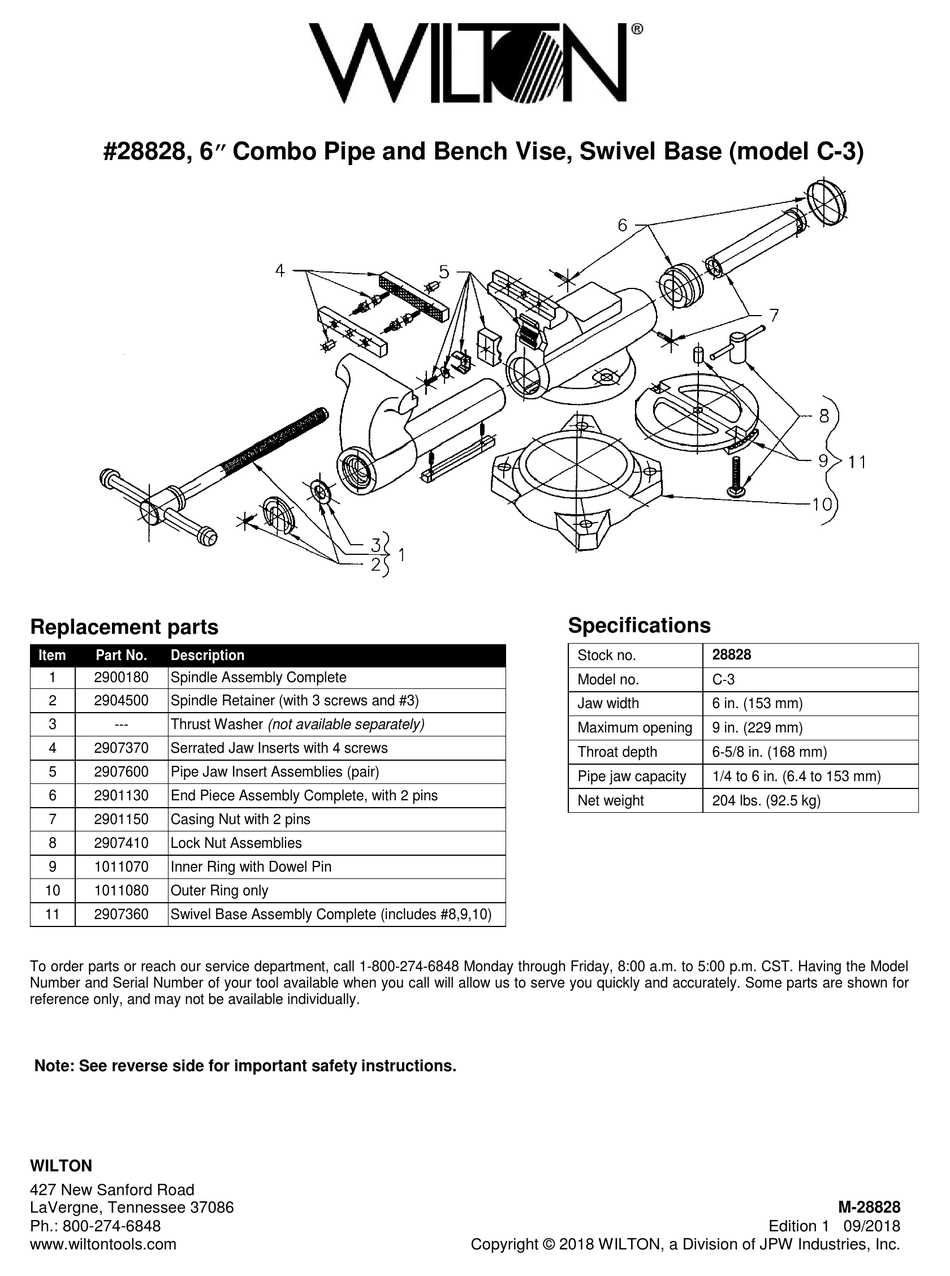
The jaw mechanism is the most noticeable and essential feature. It consists of a fixed jaw and a movable jaw, which clamp around the workpiece. The movable jaw is operated by a rotating screw, making it adjustable to different widths. Identifying this mechanism allows users to understand how materials are securely held in place during tasks.
Understanding the Spindle and Thread System
The spindle is a long, threaded rod that drives the movement of the movable jaw. It is typically turned with a handle to adjust the clamping pressure. Recognizing the threads on the spindle is crucial, as they determine the tool’s ability to handle different material sizes and provide precise pressure when securing items. The efficiency of this system is key to achieving a firm and stable grip.
Maintenance Tips for Workholding Tool Components
Regular upkeep is essential to ensure the longevity and proper function of a workholding tool. Proper maintenance helps prevent unnecessary repairs and keeps the tool performing at its best, allowing users to carry out tasks with precision and ease. A well-maintained tool operates more smoothly, ensuring both safety and efficiency during use.
To maintain optimal performance, it is important to keep the moving parts clean and lubricated. This reduces friction and wear, allowing for smoother operation and extending the life of the tool. Additionally, regularly inspect the clamping mechanism to ensure that it functions properly and adjusts correctly. If parts show signs of damage, it’s best to replace them promptly to avoid compromising the tool’s effectiveness.