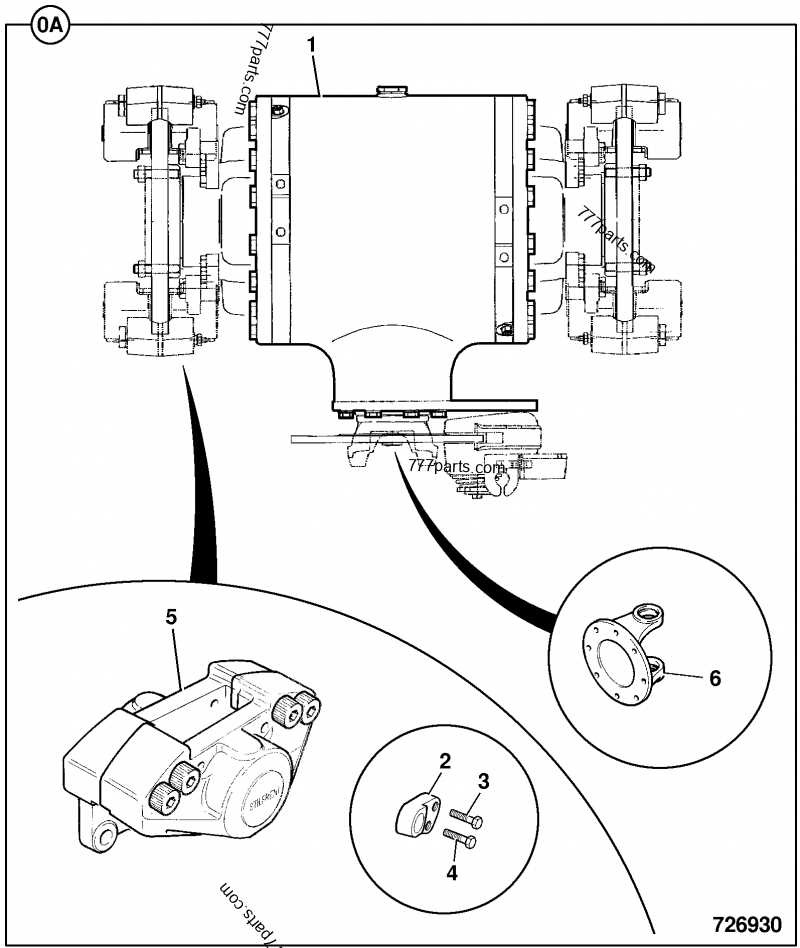
When it comes to maintaining a vehicle’s braking system, understanding the essential elements is crucial. Every component plays a role in ensuring smooth and safe operation, and knowing their layout and function helps with both repairs and preventive care. Visual aids are an excellent way to break down these complex systems and make the intricate relationships between the various parts easier to comprehend.
In this guide, we’ll explore the key elements that make up the braking mechanism, highlighting how each contributes to overall performance. Whether you’re a mechanic or a car enthusiast, having a clear understanding of these components will empower you to make more informed decisions when it comes to maintenance and troubleshooting.
Familiarizing yourself with the structure of the braking system can save time and effort, whether you’re replacing worn-out parts or looking for signs of damage. With the right knowledge, you can identify potential issues early and avoid costly repairs.
Key Components of a Brake System
Understanding the essential elements that make up a vehicle’s braking mechanism is vital for both effective repairs and efficient maintenance. Each component plays a unique role in ensuring that the system works as intended, providing the necessary force to slow down or stop the vehicle. By knowing how these parts interact, you can better assess their condition and make informed decisions during maintenance.
Brake Housing and Piston
The housing acts as the protective casing that holds the other components in place. Inside it, a piston is responsible for creating the force necessary to engage the braking process. When hydraulic pressure is applied, the piston moves, pushing the friction material against the rotating disc, thereby slowing the wheel. The precision of this interaction is crucial for the system’s overall effectiveness.
Friction Material and Guide Pins
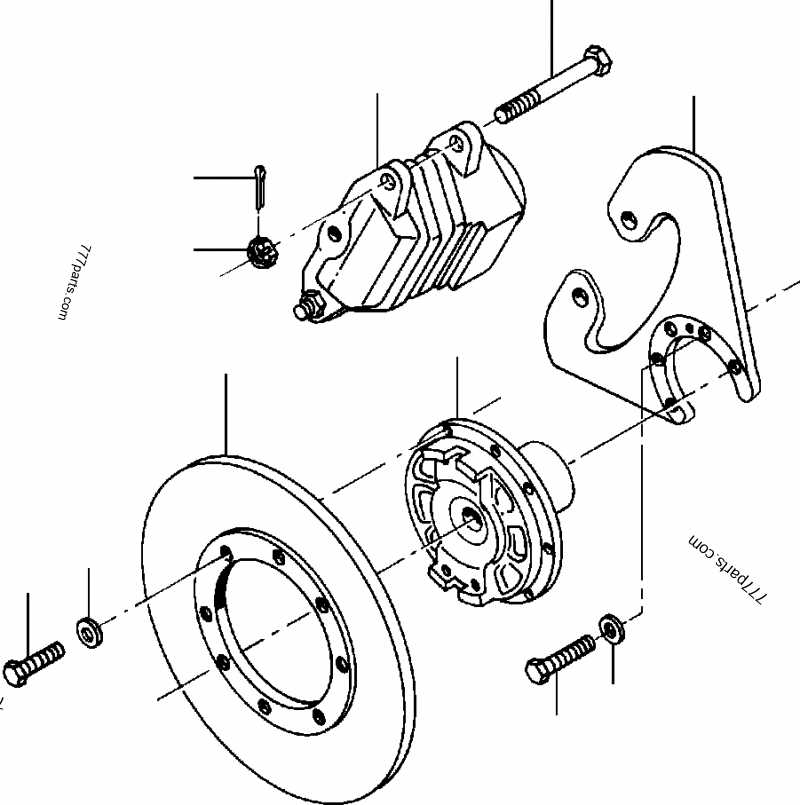
The friction material is what makes direct contact with the wheel disc, providing the resistance needed to slow the vehicle. Over time, this material wears down, which is why regular inspection is necessary. Additionally, guide pins help maintain proper alignment, allowing smooth movement of components during operation. These pins ensure that the friction material is evenly distributed and the braking force is applied consistently.
How to Read a Brake System Layout
Interpreting technical illustrations of braking mechanisms is essential for understanding their structure and functionality. These visual representations help break down the system into individual elements, showing how each component fits together and operates. Knowing how to read such layouts can aid in troubleshooting, repairs, and ensuring the correct alignment of all elements.
The first step is to familiarize yourself with the symbols and labels used in the image. These often include arrows indicating movement, numbers referencing specific components, or lines representing hydraulic flow. Once you understand these visual cues, you can begin to connect each labeled part to its function within the system. For example, a diagram may show how force is applied from one part to another or the sequence in which components engage during braking.
It’s also important to understand the scale and proportions used in the illustration. Some diagrams may not be to exact scale but rather are meant to emphasize certain parts or actions. Recognizing this can prevent misinterpretation of distances and sizes. By carefully analyzing the image and cross-referencing with real-world components, you can gain a clearer understanding of how everything works together.
Maintaining Your Brake System Effectively
Proper upkeep of the braking system is essential for ensuring both safety and optimal performance. Regular inspection and maintenance not only extend the lifespan of the components but also prevent costly repairs. A well-maintained system ensures that all elements function smoothly, providing reliable stopping power when you need it most.
Regular Inspections
Routine inspections are the foundation of effective maintenance. Checking for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks can help identify issues before they become serious. Pay special attention to the housing, piston, and friction material, as these are the most likely to experience wear over time. Early detection of any abnormalities allows for timely replacements or adjustments, reducing the risk of system failure.
Lubrication and Cleaning
Keeping the moving components clean and lubricated is crucial for smooth operation. Dirt and debris can cause friction, which may lead to premature wear or malfunction. Apply appropriate lubricants to the guide pins and other moving parts to ensure smooth movement and prevent unnecessary strain on the system. Regularly cleaning the components helps maintain their efficiency and reduces the buildup of harmful substances that could cause damage.