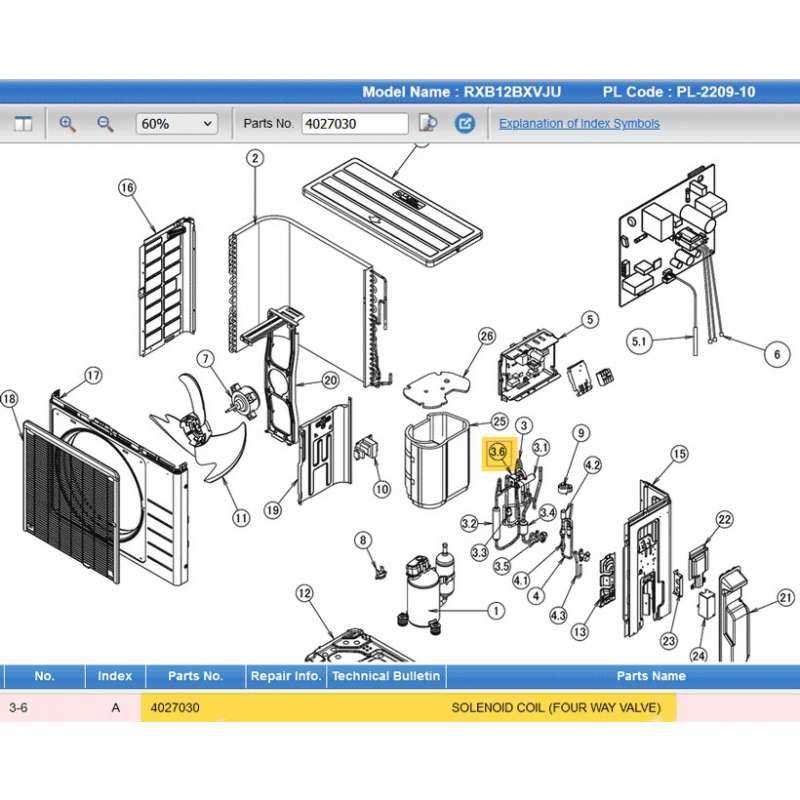
When it comes to maintaining an air conditioning or heating system, knowing the various components and their functions is crucial. These systems are made up of multiple parts that work together to provide optimal performance. Having a clear understanding of each element can significantly ease the troubleshooting process and help with proper maintenance.
Familiarizing yourself with the internal workings and common issues of these systems can save both time and money. Whether you’re performing routine maintenance or dealing with a malfunction, a good grasp of the system’s layout can make the repair process more straightforward.
Identifying specific components quickly and accurately is essential for effective repairs. In the following sections, we’ll break down how to interpret a system’s layout and what to look out for when inspecting or fixing individual parts.
Understanding HVAC System Components
Every air conditioning or heating system consists of various interconnected elements that perform specific functions to ensure the unit operates smoothly. These components vary in size and purpose but work together to regulate temperature and maintain optimal air flow. Understanding each part’s role helps in diagnosing issues and performing efficient maintenance.
Key Components of the System
The core components include the compressor, evaporator, condenser, and expansion valve. The compressor circulates refrigerant through the system, while the evaporator absorbs heat from the indoor air. The condenser releases the absorbed heat, and the expansion valve controls the refrigerant flow, maintaining the system’s efficiency.
Common Challenges with System Components
Wear and tear can cause various issues with these critical components. Common problems include refrigerant leaks, faulty sensors, or damaged coils, all of which can impair the system’s performance. Regular checks and timely repairs can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the unit.
How to Read an HVAC System Layout
Interpreting a system’s layout can initially seem challenging, but once you understand how to read it, troubleshooting and maintenance become much easier. The layout provides a detailed visual representation of the various components, their connections, and their locations within the system. Recognizing the symbols and how they relate to each part is essential for effective repair and upkeep.
Familiarizing Yourself with Symbols and Labels
Each component is usually represented by a unique symbol or label. These symbols can vary between manufacturers, but there are common conventions used in most layouts. Pay attention to the following:
- Compressor: Often depicted as a circle or square with specific markings.
- Evaporator Coil: Typically shown as a series of connected lines or coils.
- Condenser: Usually represented by a rectangle with a heat exchange symbol.
- Refrigerant Lines: Depicted by solid or dashed lines connecting key components.
Understanding the Layout Flow

The layout typically shows how refrigerant and air flow through the system. It’s important to trace the lines from the compressor to the condenser and evaporator, as this helps you understand how energy is transferred and where potential issues may arise.
- Look for arrows indicating refrigerant flow direction.
- Check for connections between components, which show how each part communicates with others.
Once you are familiar with these visual cues, you can quickly identify malfunctioning areas and take appropriate action to repair or replace components as needed.
Common Issues with HVAC System Components
Like any mechanical system, air conditioning and heating units can experience problems over time. These issues often stem from wear and tear, improper maintenance, or external factors such as temperature fluctuations. Identifying common issues early can help prevent costly repairs and ensure the system runs efficiently for longer.
Refrigerant Leaks
One of the most frequent problems is refrigerant leakage. When the refrigerant level is low, the system struggles to absorb or release heat, leading to poor performance and higher energy consumption. Common signs of a refrigerant leak include insufficient cooling or heating and unusual noises from the compressor.
- Check for visible leaks around the refrigerant lines.
- Monitor the system’s pressure to detect imbalances.
Faulty Sensors and Control Issues

Another common issue involves malfunctioning sensors, which can prevent the system from regulating temperature properly. A defective temperature or pressure sensor can lead to improper operation, causing the system to overheat, freeze, or fail to turn on.
- Inspect sensors regularly to ensure accurate readings.
- Test the control board to verify correct signal transmission.
Regular inspections and proactive maintenance can help identify these issues early and avoid more serious damage in the future.