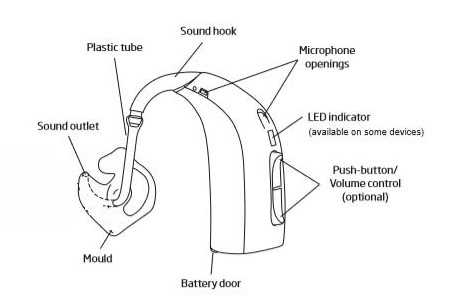
Modern sound amplification devices are complex systems designed to improve auditory perception. These devices consist of several crucial components that work in unison to ensure optimal performance. A deeper understanding of their internal structure can help users make informed decisions and better utilize their devices for enhanced hearing experience.
Each element within these systems has a specific role, whether it’s capturing sound, amplifying it, or delivering clear and crisp audio. The arrangement and functionality of these components are integral to the effectiveness of the device, as each part is carefully engineered to work seamlessly with the others. By exploring the structure of these systems, users can gain insight into how their devices function and how they can maintain peak performance over time.
Key Components of Hearing Aids
The efficiency of sound amplification devices relies heavily on the precise interaction of various internal elements. Each component serves a unique purpose, contributing to the overall function and quality of the device. Understanding the role of these essential components is crucial for users who want to optimize their experience and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Microphone and Sound Capture
The microphone acts as the initial point of contact for external sound waves, converting them into electrical signals. This process is fundamental as it allows the device to pick up surrounding noises and focus on specific sounds. The quality of the microphone directly impacts how clearly the device will capture and process sound, especially in noisy environments.
Amplification System and Sound Processing
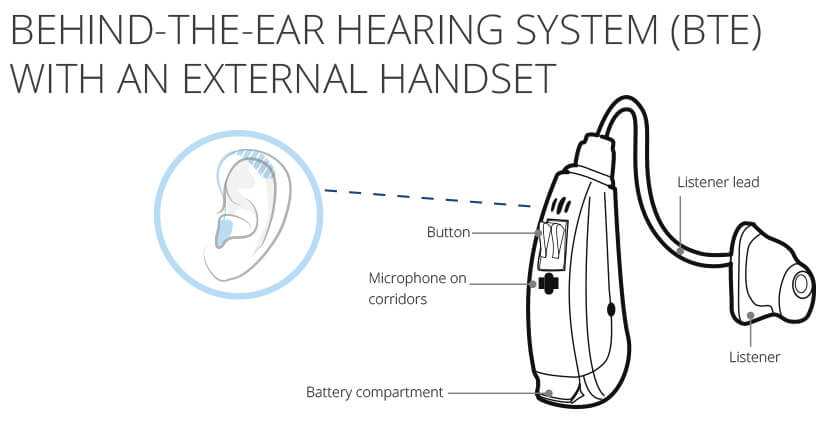
Once the sound is captured, it is passed through an amplification system that boosts its intensity. This system is designed to enhance the signals according to the user’s specific needs, ensuring that even soft sounds are audible. The signal is then processed and modified to match the user’s hearing profile, offering personalized audio output that maximizes clarity and comfort.
How Hearing Aid Parts Work Together

The performance of sound amplification devices depends on the seamless interaction between their internal components. Each element has a specific function, but the true power lies in how these functions combine to deliver a coherent and enhanced auditory experience. Understanding this synergy helps users appreciate the intricacies of their devices and ensure they are using them to their fullest potential.
The process begins with the microphone, which captures the surrounding sounds and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are then directed to the amplifier, where their strength is increased. Afterward, the processed sound is sent to the receiver, which transmits the amplified signals into the ear. Finally, the battery powers the system, ensuring all components function continuously without interruption.
When these components operate together in harmony, the device effectively amplifies and clarifies sounds, making it easier for users to engage with their environment. A slight malfunction in any part can lead to noticeable performance issues, which is why maintenance and understanding each element’s role are vital for optimal use.
Visual Guide to Hearing Aid Structure
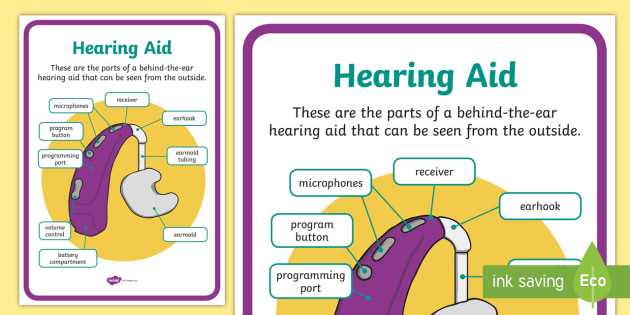
Understanding the internal layout of sound amplification devices is essential for users to fully grasp how each component contributes to overall function. A visual representation can offer clearer insight into the specific arrangement of elements and how they work in concert to improve auditory experiences. This guide will explore the main structures and their roles within the device.
External Shell and Controls
The external casing of these devices not only provides protection but also houses several key components, including buttons and volume controls. This part of the device allows users to interact with it, adjusting settings based on personal preferences or environmental needs. It is also designed for comfort, ensuring the device fits securely and discreetly behind or within the ear.
Internal Circuitry and Signal Processing
Inside the casing lies the complex circuitry responsible for processing captured sounds. The signals from the microphone are filtered and amplified by various electronic components, then fine-tuned to meet the specific needs of the user. These circuits play a critical role in ensuring the clarity and quality of sound, tailoring the experience to individual hearing profiles.