
When maintaining or repairing a trimmer, understanding its internal components is crucial. A clear visual representation of each part helps users identify and address specific issues quickly. Whether it’s a replacement or routine maintenance, knowing the layout of the equipment will streamline the repair process.
For efficient repairs, it’s important to recognize the key components and their placement. This knowledge will save time and effort, as well as prevent unnecessary confusion. By referencing a clear visual guide, even novice users can tackle repair tasks with confidence and accuracy.
Understanding the correct assembly and function of the individual components ensures that all parts work in harmony, improving the overall performance and lifespan of the tool. Proper identification allows for targeted solutions, reducing downtime and improving the effectiveness of repairs.
Understanding Trimmer Component Layout
Each tool is made up of a variety of elements, each serving a specific function. Familiarity with the internal structure and how components fit together can help users troubleshoot, repair, and perform maintenance more effectively. A well-structured layout helps in identifying where problems may arise, making repairs easier and faster.
To gain a better understanding, consider the following key elements that form the core structure:
- Engine Assembly: Powers the entire system, including the motor and fuel components.
- Drive Shaft: Transfers power from the motor to the working attachment, allowing it to operate.
- Cutting Head: The part responsible for cutting, often including blades or trimmer lines.
- Housing: Protects internal components and provides the outer casing for all parts.
Each of these components is designed to work together, ensuring the tool operates smoothly. A well-organized layout ensures you can pinpoint and address any issues, whether you’re replacing a worn-out component or performing a routine check-up.
Understanding how these elements interact will enhance your ability to perform repairs, reduce the risk of incorrect assembly, and extend the longevity of your equipment.
How to Identify Trimmer Components
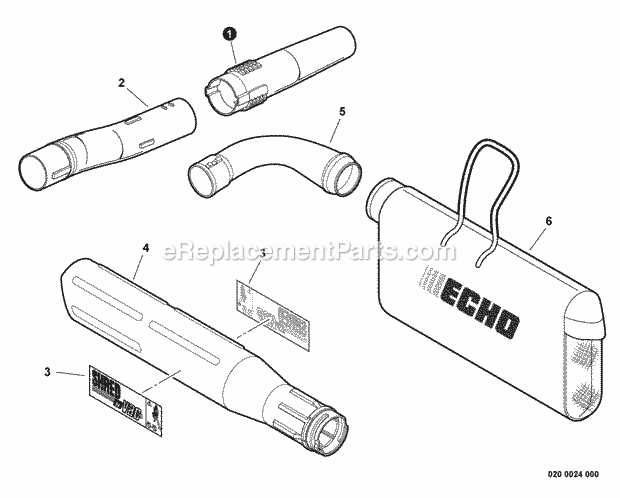
Identifying the individual components of a tool is essential for proper maintenance and repair. Knowing the role and appearance of each part ensures that users can accurately diagnose issues and replace worn-out elements. A methodical approach to component identification reduces confusion and saves valuable time.
Key Components to Recognize
There are several main elements to be aware of when identifying your tool’s components:
- Motor Unit: The central powerhouse, responsible for driving the tool.
- Drive Mechanism: Transfers power from the motor to the cutting head, including shafts and gears.
- Cutting Mechanism: Typically includes blades, trimmer lines, or other attachments designed to handle the cutting function.
- Safety Features: Guards and switches that ensure safe operation during use.
- Housing and Outer Casing: Encloses and protects internal components from debris and damage.
Visual Clues and Markings
Many components have distinguishing features that make them easier to identify. Look for part numbers, logos, and specific shapes or materials that can help confirm what you’re looking at. Additionally, some parts may have distinct wear patterns, especially if they are subject to frequent use, such as cutting lines or motor components.
By carefully studying the overall structure and markings on the individual components, you’ll be able to easily recognize each part and proceed with maintenance or repairs confidently.
Common Repairs Using Trimmer Layout
Routine repairs are an inevitable part of maintaining any tool. Understanding the internal setup and recognizing components that may require attention allows users to effectively perform maintenance. Knowing which parts to focus on and how they interact with each other can significantly simplify common repair tasks.
Replacing the Cutting Mechanism
A frequently needed repair involves the cutting attachment, whether it’s the trimmer line or blades. Over time, these components become worn out due to constant use. To replace them:
- First, identify the attachment type by examining the cutting head.
- Remove the damaged component and replace it with a new one, ensuring it fits securely in place.
- Check the alignment and ensure that it spins freely.
Fixing the Motor Unit
If the motor isn’t functioning properly, the tool won’t operate efficiently. Common motor-related issues may include overheating or lack of power. To address this:
- Disconnect the power source and inspect the motor for any visible damage.
- Clean the motor parts of debris or dirt that may obstruct airflow.
- If necessary, replace motor components such as brushes or connectors.
By referring to the layout, users can easily identify and access these components, allowing for quick and efficient repairs, ultimately extending the tool’s life and ensuring optimal performance.