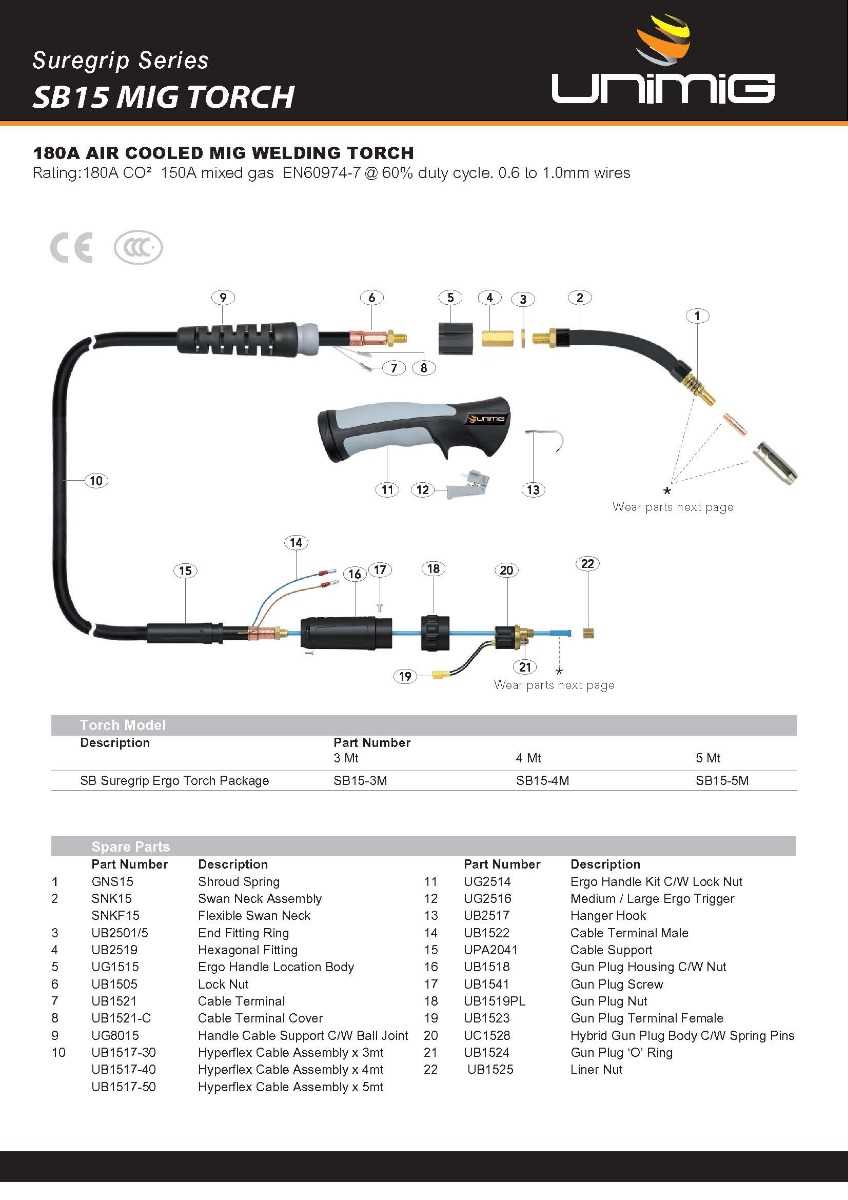
Every welding machine consists of several crucial components that work together to create a strong and durable bond between materials. Having a clear understanding of how these elements interact is essential for efficient operation and maintenance. Identifying each part’s function and role can significantly improve the welder’s performance and longevity.
Various tools and attachments are responsible for different tasks, from controlling heat levels to feeding the welding wire. When these parts are properly maintained, they ensure smoother operation and higher-quality welds. The accuracy of your equipment is directly linked to how well you know and care for each piece.
Being familiar with your machine’s structure also helps when troubleshooting or repairing any malfunction. A well-maintained machine can last longer, perform better, and reduce the risk of failure during critical tasks. Understanding its components will also empower you to make informed decisions when upgrading or replacing parts.
Understanding Key Components of Welding Machines
Welding equipment relies on a variety of critical elements working in harmony to ensure precise and effective results. These components serve distinct functions that contribute to the overall operation, with each part playing an essential role in achieving high-quality welds. Recognizing the significance of each element helps in optimizing the machine’s performance and extending its lifespan.
Main Elements in the Machine
Some of the primary components you will encounter in any welding setup include:
- Power Source: Provides the electrical energy necessary for the welding process.
- Wire Feeder: Delivers the welding wire to the workpiece, ensuring a steady flow for continuous welding.
- Electrode Holder: Holds the electrode in place and ensures proper contact during welding.
- Ground Clamp: Establishes the electrical connection between the machine and the workpiece to complete the circuit.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular inspection and care of these components are essential to avoid equipment malfunction and ensure consistent results. Neglecting any part, such as worn-out wires or damaged connections, can lead to subpar performance or even safety hazards. A well-maintained system guarantees smooth welding operations and prevents unnecessary downtime.
Common Parts of a Welding Machine
Every welding machine contains several components that work together to facilitate the process. These elements are designed to ensure the machine operates efficiently and effectively, allowing for consistent and high-quality results. Understanding the role of each part is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining the equipment.
Some of the most essential elements found in welding machines include:
- Power Supply: This provides the electrical energy required to generate the heat needed for welding.
- Wire Feeder: Delivers a continuous supply of wire to the weld pool, ensuring a stable and controlled welding process.
- Gun and Nozzle: The nozzle directs the flow of shielding gas and helps control the heat during the welding process.
- Ground Clamp: Establishes an electrical circuit between the machine and the workpiece, allowing the flow of current.
- Regulator: Controls the flow of shielding gas to protect the weld from contamination and oxidation.
How to Identify Welding Machine Issues
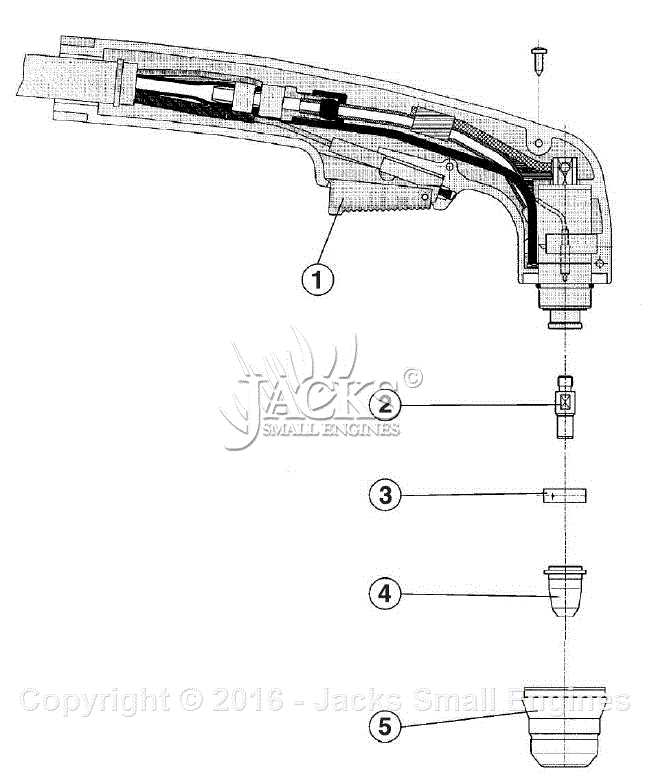
When a welding machine malfunctions, it can be challenging to pinpoint the exact cause. Identifying the source of the issue is crucial for effective troubleshooting and ensuring that repairs are made promptly. A clear understanding of the common signs of malfunction can help users quickly assess the condition of their equipment and take the necessary steps to resolve the problem.
Several key indicators can help you identify potential issues with your machine:
- Unstable Arc: If the arc is erratic or keeps extinguishing, the cause could be an issue with the power supply or improper settings.
- Wire Feed Problems: If the wire is not feeding properly, check for blockages in the feeder or insufficient tension on the spool.
- Insufficient Heat: Inadequate heat may indicate problems with the power connection, the settings, or internal components that control the temperature.
- Excessive Spatter: Too much spatter can result from incorrect gas flow, improper settings, or using the wrong type of filler material.
By regularly checking these indicators, you can maintain the performance of your equipment and minimize downtime due to technical issues.