Fungi are complex organisms with fascinating structures that serve various biological functions. To fully comprehend their nature, it is essential to explore the different elements that make up their bodies. These components work together to support growth, reproduction, and survival.
By studying the distinct sections of these organisms, researchers gain insights into how they interact with their environments. Each section plays a crucial role in maintaining the organism’s health and enabling its life cycle. Understanding this structure is vital for various scientific fields, including botany and environmental science.
Visual representations of these structures allow for clearer understanding and analysis, helping students and researchers identify key features more effectively. Learning the roles of these individual parts contributes to a broader understanding of how fungi thrive and evolve over time.
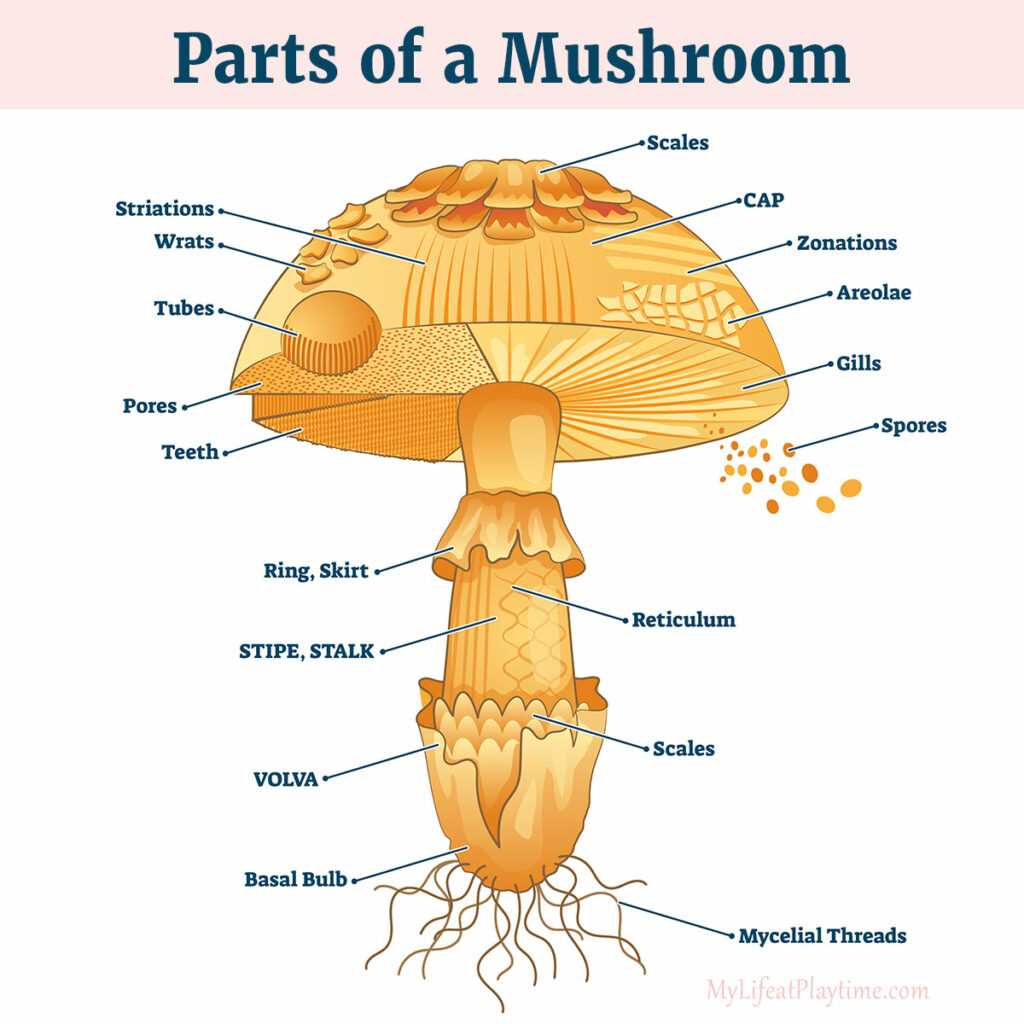
Key Components of a Mushroom Structure
Every organism in the fungal kingdom consists of various elements that work in harmony to ensure proper function. These essential sections enable the organism to perform crucial tasks such as nutrient absorption, reproduction, and growth. Understanding each component is vital to grasp the overall biology of these organisms.
The underground network, often referred to as the mycelium, serves as the main means of nutrient intake. It extends throughout the substrate, absorbing necessary substances for growth. Above ground, the fruiting body emerges, which houses the reproductive structures responsible for spore production.
Cap and gills are prominent features of the visible structure, where spores are created and released. The stalk, or stipe, supports these reproductive structures and helps elevate them above the ground. Each section plays a specific role in the organism’s life cycle, contributing to its survival and spread.
By exploring these distinct features, one can better understand how fungi adapt to various environments and carry out vital processes, ensuring their presence in ecosystems worldwide.
Understanding the Fungal Reproductive System
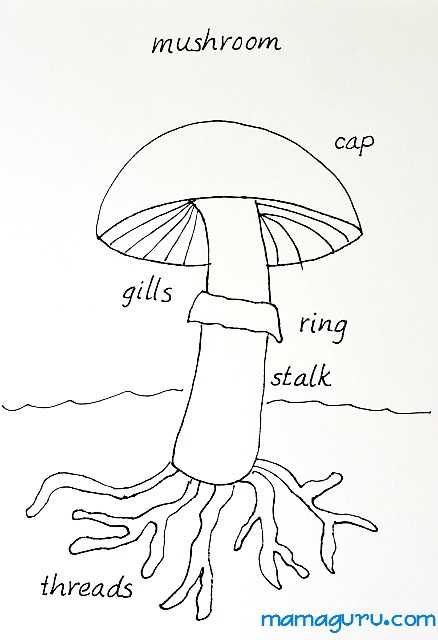
The process of reproduction in fungi is both fascinating and complex. This system allows these organisms to spread and thrive in a variety of environments. Reproduction typically occurs through the release of specialized cells that can germinate into new individuals, ensuring the continuation of the species.
In most fungi, reproduction involves two key mechanisms: sexual and asexual. Each plays an important role in the life cycle of the organism. Asexual reproduction generally involves the formation of spores, which can grow into new organisms under favorable conditions.
- Sexual Reproduction: Involves the fusion of two different types of cells, leading to the creation of genetically diverse offspring.
- Asexual Reproduction: Often relies on the production of spores that are dispersed to new areas, where they can develop into new individuals.
The reproductive structures of fungi vary, but they all share the common goal of ensuring the spread and survival of the species. These specialized parts produce and release spores, which are then carried by the wind or other environmental factors to new locations where they can grow and thrive.
The Role of Spore-Producing Parts
Reproduction in fungi heavily relies on specialized structures designed for spore production. These sections of the organism are responsible for generating and releasing spores, which serve as the primary means of reproduction. By dispersing these microscopic cells into the environment, the organism can ensure its spread and survival over large areas.
Spore Formation
The production of spores begins when certain cells within the organism undergo a transformation, producing reproductive cells that are capable of surviving harsh conditions. These cells are then released into the environment where they can potentially develop into new organisms under favorable circumstances.
Dispersal and Germination
Once released, spores are often carried by wind, water, or animals to new locations. When they land in suitable environments, they germinate and grow, starting the cycle again. This reproductive method allows for rapid colonization and the spread of the organism across diverse habitats.
Spore-producing structures are thus essential for the life cycle of fungi, enabling them to adapt and thrive in various ecosystems. These parts play a critical role in ensuring the persistence and genetic diversity of the species over time.
Importance of Mushroom Diagram for Study
Understanding the structure of fungi is essential for both students and researchers. Visual representations of their anatomy play a vital role in simplifying complex biological concepts. These illustrations help clarify the function of each section, allowing for a deeper understanding of how these organisms grow, reproduce, and interact with their environments.
Such visual aids are invaluable for dissecting the intricate relationships between different parts of the organism. They make it easier to identify and study key features, and are often used in educational settings to teach about fungi in a more interactive and engaging way.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Clarification of Structure | Visuals help break down complex biological details, showing the role of each section clearly. |
| Enhanced Learning | Illustrations provide a hands-on approach to learning, making concepts easier to grasp. |
| Scientific Research | Accurate depictions aid researchers in their studies, contributing to advancements in fungal biology. |
Visual resources play a crucial role in educational and scientific settings. They not only aid in the identification of various components but also contribute to a better understanding of the organism’s lifecycle and ecological significance.
How Diagrams Enhance Fungal Research
In the study of fungi, visual tools play an essential role in helping scientists analyze and understand the organism’s structure and behavior. These illustrations provide a clear and concise way to represent the various features and processes of fungi, making complex concepts more accessible. By using visual aids, researchers can easily identify key components and their functions, contributing to a deeper understanding of fungal biology.
Visual aids also facilitate the comparison of different species and their structures, allowing researchers to track variations and similarities across a wide range of organisms. This ability to identify patterns and connections enhances the accuracy of studies, aiding in the development of new discoveries in fungal science.
Additionally, these resources assist in effectively communicating findings to others. Whether in educational settings or scientific publications, accurate representations ensure that critical details are conveyed in a way that is both informative and easy to understand.