Maintaining a garden tilling machine requires knowledge of its essential elements and how they interact. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the machine performs efficiently and reliably. Understanding the various parts is key to effective repairs and proper care.
Identifying and understanding each piece can significantly improve your ability to troubleshoot issues, enhance performance, and extend the machine’s lifespan. Knowing what each part does and how it functions within the system is essential for anyone handling these devices.
Familiarity with the internal structure of the equipment helps prevent costly mistakes during assembly, maintenance, or replacement. It also equips you with the confidence to make informed decisions when the need for servicing arises.
Key Components of a Garden Tilling Machine

Every garden tilling machine consists of several crucial elements, each contributing to its overall functionality. These components work together to break up soil, prepare land for planting, and make gardening tasks more efficient. Understanding these key elements helps ensure the machine operates optimally for prolonged use.
Engine and Power System
The engine is the heart of any tilling machine, providing the necessary power to operate the device. It drives the transmission, which in turn powers the rotating tools. A well-maintained engine is essential for smooth operation and effective performance, especially when working with tough soil.
Cutting Blades and Tines
Cutting blades and tines are responsible for the primary task of breaking up the earth. These sharp, rotating tools dig into the soil, turning and loosening it for planting. They come in various designs, each suited for different soil types and tasks. Proper maintenance of these components ensures consistent performance and minimal wear.
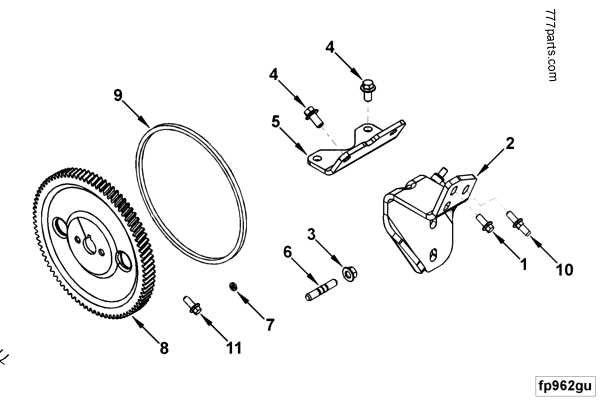
How to Read a Garden Tilling Machine Blueprint
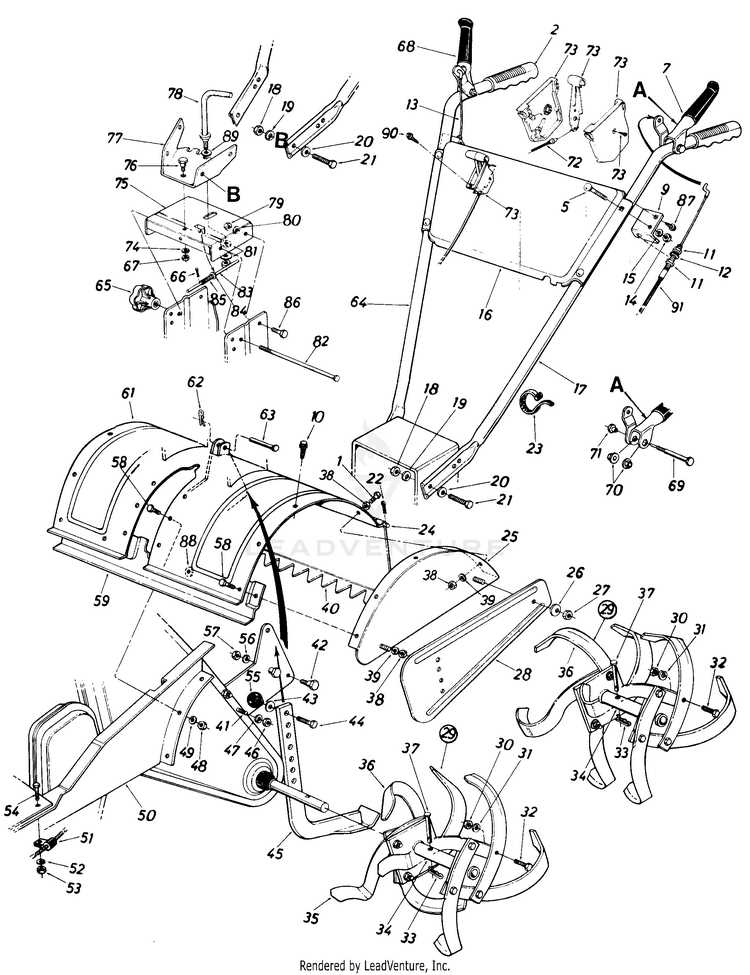
Understanding a blueprint for a garden tilling machine can significantly aid in repairs and maintenance. It provides a detailed view of the various components, their placements, and how they interconnect within the system. Knowing how to interpret these blueprints helps users quickly identify potential issues and efficiently perform tasks such as assembly or troubleshooting.
Identifying Key Symbols

Blueprints typically use symbols to represent different components. Each part is assigned a specific icon or marking, which corresponds to the actual item on the machine. These symbols make it easier to locate and identify elements at a glance. Familiarizing yourself with these symbols is crucial for interpreting the diagram correctly and accurately.
Understanding the Connections
Once you’ve identified the components, it’s important to understand how they connect with each other. Blueprints often show the relationships between parts, including how power flows or how one component interacts with another. This knowledge helps users assemble, repair, or replace components in the correct order and method.
Common Garden Tilling Machine Components and Their Functions
In any garden tilling machine, each component plays a vital role in its operation. Understanding these elements and their functions is essential for proper maintenance and efficient performance. These key components work together to ensure the machine performs effectively and meets the user’s needs.
Engine and Transmission
The engine is the primary power source that drives the entire machine. It generates the force needed to operate various systems, such as the transmission, which transfers the engine’s power to the rotating tools. Without a properly functioning engine and transmission, the machine would not be able to perform its intended tasks.
Cutting Tools and Tines
Cutting tools and tines are responsible for breaking up the soil. These elements rotate at high speeds, loosening compacted earth and making it easier to plant crops or tend to the garden. The design of these tools is important, as they are tailored to different soil conditions and tasks. Regular upkeep of these components ensures continued effectiveness and sharpness.