
Medical tools designed for auscultation play a critical role in diagnosing patients. Their construction is complex, with each element working in harmony to provide accurate readings. Understanding how each component functions allows healthcare professionals to make the most of these devices during examinations.
These diagnostic tools consist of various interconnected parts, each serving a specific function to amplify internal sounds, filter noise, and provide clarity. By learning about the design and role of each segment, one can gain a deeper appreciation for their reliability and efficiency in clinical settings.
Whether you are a medical student, professional, or simply curious, familiarizing yourself with the layout and purpose of these devices will help improve both usage and maintenance. A solid grasp of their construction ensures optimal performance and longevity over time.
Understanding the Stethoscope Components
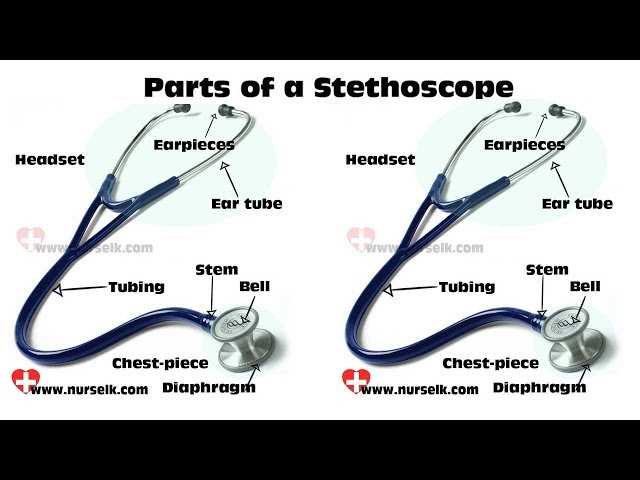
Medical auscultation devices are designed with several key elements, each contributing to their overall functionality. A proper understanding of how these components interact can improve both their use and longevity. By exploring the individual features of these instruments, you gain insight into their intricate design and purpose in clinical environments.
Main Structure and Construction

The main body of the tool is typically lightweight yet sturdy, ensuring comfort for long periods of use. It consists of a flexible tube that connects the listening apparatus to the healthcare professional. This component is essential for both the comfort and the effectiveness of the tool, allowing for easy movement while maintaining high-quality sound transmission.
Auscultation Features and Sound Amplification
The core functionality of the device lies in its ability to amplify internal sounds. The chest piece, which includes a diaphragm and bell, plays a pivotal role in capturing and transmitting these sounds clearly. The diaphragm is often used for higher frequencies, while the bell is better suited for lower frequencies, making them both indispensable for accurate diagnoses.
How Each Part of a Stethoscope Works
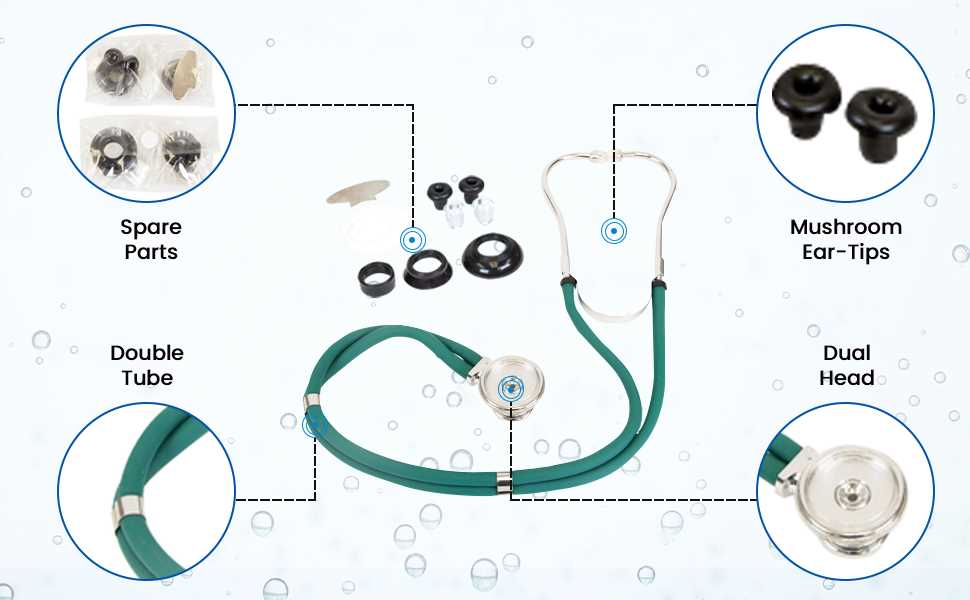

Each element of an auscultation tool plays a crucial role in capturing and transmitting internal sounds from the body to the user. Understanding the function of every component allows for better handling, maintenance, and troubleshooting, ensuring accuracy during medical examinations. Let’s break down how each feature contributes to the overall performance.
The flexible tube is the first point of contact between the listening device and the user. It carries sound from the chest piece to the earpieces. Its material is designed to minimize sound distortion and provide clarity while allowing the user the mobility to move freely during use. The sound travels through the tube, which is typically lightweight and insulated to maintain high quality.
The chest piece includes the diaphragm and bell, two key components that detect and amplify different types of body sounds. The diaphragm is primarily used to capture higher-frequency sounds, such as heartbeats and lung sounds. Its flat, rigid design enhances sound sensitivity. On the other hand, the bell is designed to pick up lower-frequency sounds, such as murmurs or abnormal heart rhythms. These specialized functions ensure that the tool is versatile and reliable in diverse diagnostic situations.
Finally, the earpieces are essential for effective listening. They are designed to fit comfortably in the user’s ears while also blocking out external noise, allowing the user to focus on the internal sounds coming through the tube. Proper fit and seal are crucial for accurate sound perception, making the earpieces an often-overlooked but vital component in the overall functioning of the device.
Identifying the Key Stethoscope Features
In order to make the most of a diagnostic tool, it is important to understand its essential features. Each element contributes to the overall functionality, and recognizing the key components helps in ensuring effective use and proper maintenance. By focusing on these critical features, healthcare professionals can optimize their diagnostic capabilities.
The chest piece is one of the most prominent features, typically consisting of a diaphragm and a bell. These elements serve different purposes, with the diaphragm capturing higher-frequency sounds such as heartbeats and breath sounds, while the bell is better suited for low-frequency sounds like murmurs. This dual functionality allows for comprehensive examination capabilities.
The flexible tubing connects the chest piece to the earpieces, ensuring clear transmission of sounds. It is designed to be durable yet flexible, allowing the user to move freely while maintaining high sound quality. The tube’s length and material also play a role in minimizing sound distortion, ensuring an accurate listening experience.
The earpieces are often overlooked, but they are vital for effective sound reception. They must fit comfortably and securely in the ears to block out ambient noise and provide a clear, undistorted signal. A proper seal is essential for accurate auscultation, which is why high-quality earpieces are integral to the overall design of the instrument.