
Every string instrument consists of several essential components that work together to create sound. Each element plays a specific role, whether it’s for producing vibrations, tuning, or supporting the musician’s technique. Understanding these key elements is crucial for anyone looking to learn more about how the instrument functions and how its design contributes to the overall sound quality.
The construction of these instruments has remained relatively consistent over the centuries, with each part serving a distinct purpose. The materials used, the shape, and the placement of each component are carefully designed to enhance performance and sound. Familiarity with these components provides deeper insight into their interaction and overall design.
In this section, we will explore the different sections of the instrument, their functions, and how they contribute to the overall experience. From the base to the head, each area is vital to achieving the desired outcome, whether in practice or performance.
Overview of String Instrument Components
The structure of a stringed instrument is built from various elements, each fulfilling a specific function that contributes to the overall sound production and ease of play. These key components are essential for the instrument’s functionality and performance, and understanding them helps in mastering its use.
Main Structural Elements
Several sections of the instrument are responsible for creating the acoustic properties and enabling the musician to produce sound. The overall design ensures the correct vibration, resonance, and stability for optimal playing.
- Body: The large, hollow structure where sound is produced. It amplifies vibrations from the strings and shapes the tone.
- Neck: The elongated piece that supports the strings and allows for their tuning and manipulation during play.
- Fingerboard: The smooth surface where the fingers press down on the strings to alter their pitch.
- Bridge: Positioned on the body, it transmits vibrations from the strings to the hollow chamber.
Functional Supporting Elements
In addition to the main structural components, there are several other parts that assist in the instrument’s functionality, tuning, and comfort for the musician.
- Tailpiece: The part that holds the strings at their lower end and helps maintain tension.
- Bow: The tool used by musicians to draw across the strings and produce sound.
- Pegs: These are used for tuning the strings by adjusting their tension.
Each component has its own specific role in the design and sound production of the instrument, and together, they ensure a harmonious performance. Understanding these elements helps to appreciate the craftsmanship and functionality behind stringed instruments.
Key Parts That Shape the Violin
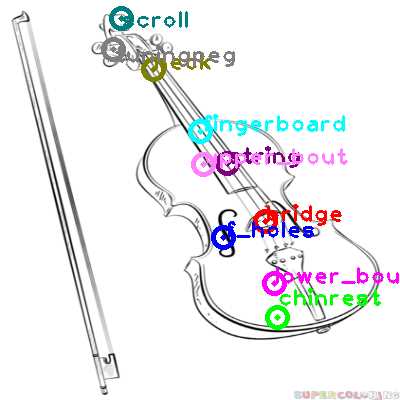
The overall design of a string instrument is influenced by several important components that determine its sound quality, playability, and overall functionality. These key elements interact to create the unique characteristics of the instrument, enabling musicians to achieve their desired tones and expressions. Understanding these crucial sections allows one to better appreciate the craftsmanship and performance potential of the instrument.
From the hollow body that amplifies vibrations to the tuning mechanisms that ensure proper pitch, each element has a vital role in shaping the experience of playing. The balance between these features contributes to the stability and precision needed in musical performance.
The following sections are the foundational components that play a significant role in the overall structure and sound production:
- Body: The central component responsible for amplifying sound. It helps in resonating vibrations produced by the strings and adds richness to the tone.
- Neck: The extended portion that holds the strings and allows the player to control pitch with precision.
- Bridge: A crucial element that transmits the vibrations from the strings to the body, affecting the instrument’s resonance.
- Fingerboard: The surface where the player presses the strings to produce various notes and melodies.
These key elements work in harmony to produce the desired musical output, influencing both the tone and the performance of the instrument in different settings.
Function of Each Violin Section
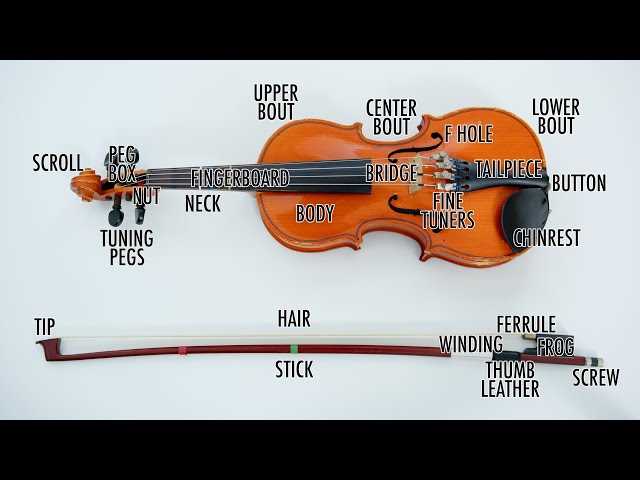
Each section of the instrument plays a distinct role in ensuring the correct production of sound and the overall performance. These components work together to shape the musical expression, offering both tonal quality and ease of play. Understanding their functions provides a deeper appreciation of how the instrument produces its characteristic sound.
Main Structural Functions
The main sections of the instrument are responsible for transmitting vibrations, supporting the strings, and enabling fine adjustments for pitch and tone. Each element interacts to amplify the sound produced when the strings are played.
- Body: It acts as the resonating chamber, amplifying the vibrations from the strings and enriching the tone.
- Neck: Supports the strings and allows for fine adjustments in pitch through the use of tuning mechanisms.
- Bridge: It transmits the vibrations from the strings to the body, helping to shape the overall sound produced by the instrument.
Supporting Elements for Playability
Additional components help enhance the player’s ability to control the instrument, tune it to the correct pitch, and ensure stability during performance. These elements offer both functional support and comfort for the musician.
- Fingerboard: The surface where the musician presses the strings to create different pitches, essential for precise note control.
- Pegs: Used to tune the strings by adjusting their tension, ensuring the instrument remains in tune during performance.
Each section is vital to the instrument’s ability to produce sound and maintain playability, with specific functions that contribute to both the aesthetic and technical aspects of performance.
Understanding How the Parts Work Together
The various sections of a string instrument are carefully designed to function in harmony, ensuring optimal sound production and smooth playability. Each element has a specific role, but it is the interaction between them that brings the instrument to life, allowing musicians to produce a wide range of tones and expressions. The synergy between the components is key to achieving the desired acoustic result.
Collaborative Functionality of Key Elements
The body, neck, and bridge are primary sections that shape the instrument’s sound. The strings are set in motion by the bow or fingers, and each component contributes to the transmission of vibrations throughout the structure. Together, they amplify and enrich the tones produced, with each element supporting the others in a seamless cycle of action and reaction.
- Body and Bridge: The body amplifies the vibrations that are transmitted by the bridge, which in turn directs these vibrations into the hollow structure, creating rich, resonant sounds.
- Neck and Fingerboard: The neck supports the strings, while the fingerboard allows the musician to alter pitch. Together, they provide the stability and flexibility needed for precise note changes.
Fine Adjustments for Precision
Additional elements, such as the tuning pegs and tailpiece, contribute to the instrument’s overall stability. They allow for minor adjustments that ensure the instrument remains in tune and the strings maintain proper tension. These small modifications play an essential role in fine-tuning the instrument for performance, ensuring the musician can produce accurate notes throughout their practice or performance.
- Pegs: Adjust the tension of each string, allowing for tuning and maintaining the desired pitch.
- Tailpiece: Secures the strings at the bottom and helps maintain the correct string tension for sound quality.
When these sections work together seamlessly, they produce a balanced and harmonious sound. Each element, while functioning individually, relies on the others to create the full range of musical possibilities.
Identifying the Instrument’s Structure
The structure of a stringed instrument is composed of several key sections that come together to form a unified whole. Each element plays an integral role in both the instrument’s function and its ability to produce sound. Understanding how to identify and differentiate these sections allows for a better understanding of the overall design and acoustics of the instrument.
Main Structural Components
The foundation of the instrument lies in its main structural components, which shape the tone and facilitate the creation of music. From the resonating chamber to the tuning mechanisms, each part is specifically designed for a unique purpose.
- Body: The large hollow chamber that amplifies vibrations from the strings, contributing significantly to the tone and volume of the sound.
- Neck: The long portion that holds the strings and allows the musician to manipulate the pitch through finger placement and tuning mechanisms.
- Bridge: Positioned above the body, it transfers vibrations from the strings to the hollow body, affecting the instrument’s resonance.
Additional Key Elements
Beyond the main structural components, other sections provide stability, fine-tuning, and comfort to the musician. These additional features ensure proper string tension and allow for precise adjustments to the instrument’s sound.
- Fingerboard: The surface where the player presses the strings to create different pitches, essential for navigating the instrument’s range.
- Pegs: Located on the neck, these are used to adjust the tension of the strings, ensuring they remain in tune during play.
By recognizing and understanding each component, one can appreciate the balance and craftsmanship behind the instrument, as well as its intricate role in creating music.