When it comes to maintaining a chainsaw, understanding its individual elements is essential for efficient operation and easy repairs. Identifying each piece, its role, and how they interact ensures smooth performance. This section aims to simplify the process of recognizing the key components of your tool and provides insights into how to use this knowledge for proper care.
Key Elements of a Chainsaw
A chainsaw consists of various components, each contributing to its function. Some parts manage the cutting action, while others control the engine or safety features. By understanding how these pieces fit together, you can easily troubleshoot or replace damaged elements.
Engine and Fuel System
- Engine: Powers the chainsaw and drives the chain mechanism.
- Fuel System: Includes components like the fuel tank, carburetor, and fuel lines, ensuring that the engine receives the right fuel mixture.
Cutting and Drive Mechanism
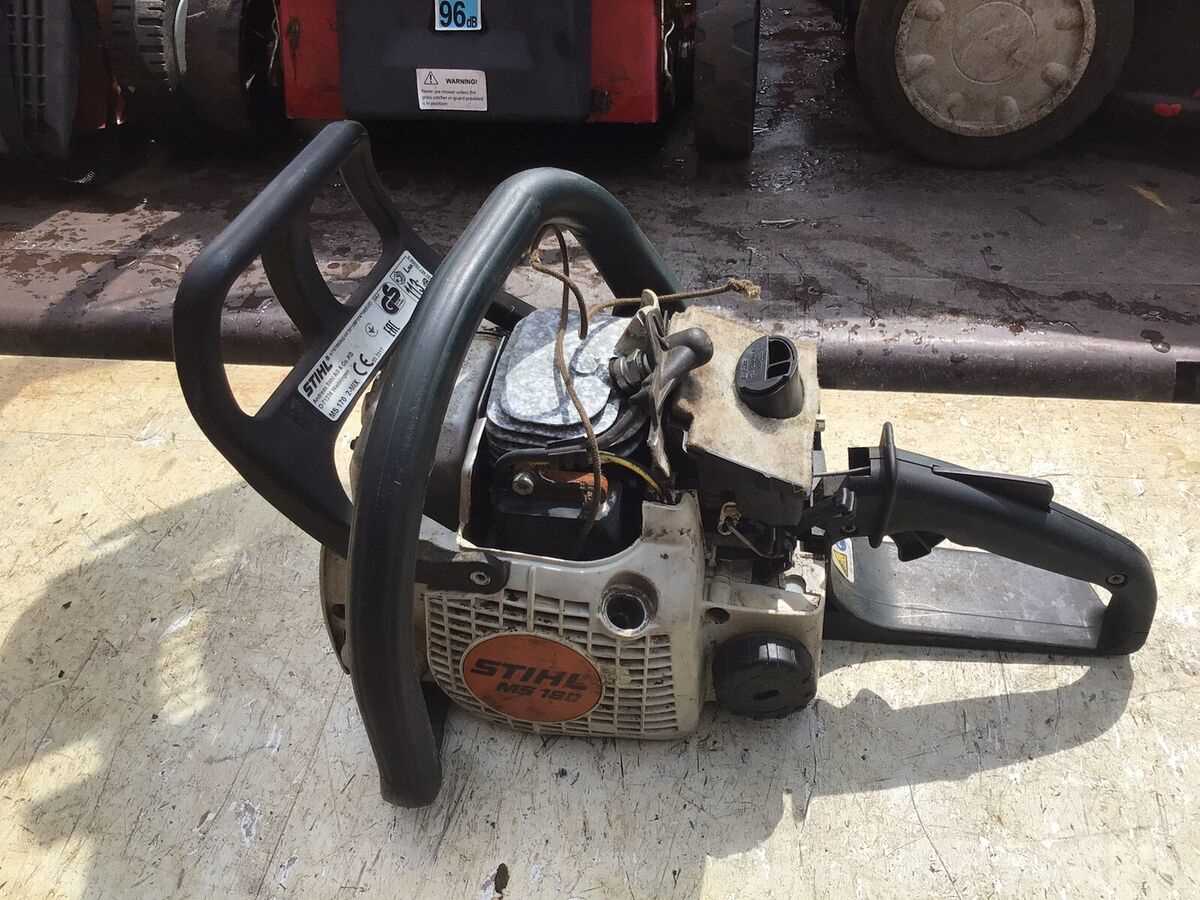

- Guide Bar: Supports and guides the chain as it cuts through wood.
- Chain: The primary cutting tool that moves along the guide bar.
- Drive Sprocket: Transfers power from the engine to the chain, enabling its movement.
Using Component Identification for Maintenance
Proper maintenance requires knowing when and how to replace certain components. By being familiar with the different parts of the tool, you can spot wear and tear early, preventing major breakdowns.
Routine Checks
- Inspect the cutting mechanism for wear and ensure it’s properly tensioned.
- Check the fuel system for leaks or blockages that could affect engine performance.
- Ensure the safety features, such as the chain brake, are functioning correctly.
Common Problems and Fixes

If the engine isn’t starting, the issue could lie within the spark plug, fuel system, or air filter. A loose or worn chain might require re-tensioning or replacement, while a malfunctioning brake might require inspection of the safety components.
Conclusion

Having a good understanding of your chainsaw’s design and components can save time and effort when performing maintenance. Regularly checking and identifying problematic parts can help you keep the tool running smoothly, avoiding costly repairs.
Understanding Chainsaw Components and Maintenance

Knowing how to navigate through the internal structure of your chainsaw can make maintenance and repairs easier and more efficient. This section provides insights into recognizing key components, how to use the tool’s layout for troubleshooting, and essential repair tips.
Every chainsaw is made up of a set of components that play distinct roles, from the engine to the cutting mechanism. Understanding the function of each part helps in identifying problems and ensuring the smooth operation of the machine. Recognizing the structure of the device will also assist when searching for replacements or during repairs.
The most important elements include the power system, the cutting components, and the safety features. For example, the engine drives the cutting action, while the guide bar and chain work together to cut through wood efficiently. A detailed look at the layout of these components can help users pinpoint issues more easily.
To make the most of your chainsaw’s layout, it’s essential to understand how to read and interpret the tool’s blueprint. Whether you need to replace a component or perform a detailed inspection, this knowledge will guide you through each part and its specific function, helping you to manage maintenance with ease.
Regular maintenance is essential for prolonging the life of your chainsaw. Checking for wear on the cutting mechanism, ensuring the engine is clean and well-maintained, and monitoring safety features are all critical steps. Knowing which components need attention can save you from costly repairs down the road.
Common issues include engine misfires, a dull chain, or a clogged air filter. Being familiar with the internal structure makes it easier to identify these problems. Once you recognize the part that needs attention, fixing it becomes a straightforward task that anyone can manage with the proper guidance.