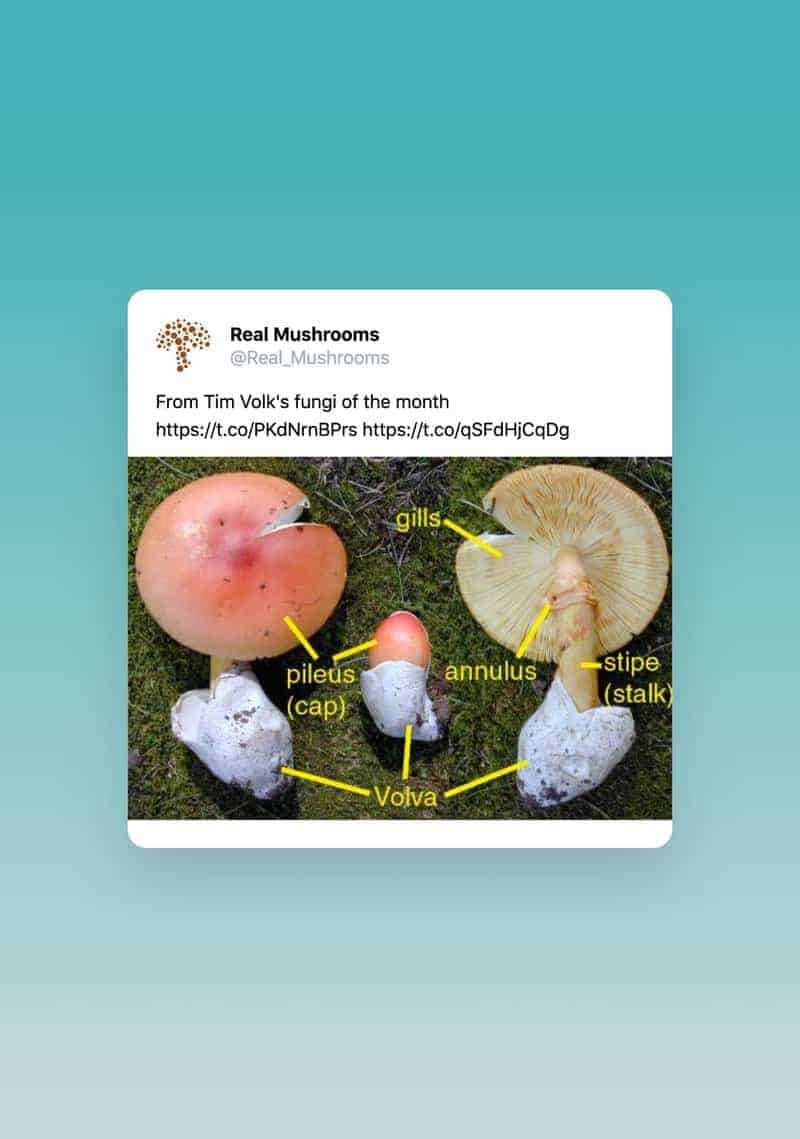
Fungi are complex organisms with intricate structures that play key roles in their growth and reproduction. Their unique anatomy supports various functions essential for survival and proliferation. By exploring the components of these organisms, we gain insights into their life cycle and ecological significance.
The central elements that make up these organisms work together to absorb nutrients, produce spores, and ensure the continuation of their species. Each section has its own specialized function, contributing to the overall health and development of the organism.
In this guide, we will examine the main components that define their structure, explaining their functions in the ecosystem. From the underground network to the visible reproductive structures, every element has a purpose in the organism’s life process.
Mushroom Anatomy Overview
Fungi possess a distinct structure that is crucial for their survival and reproduction. Their design is divided into several functional sections, each responsible for specific tasks in the organism’s life cycle. Understanding this framework allows us to appreciate the role of each component in its overall development and ecological contribution.
At the core, these organisms are made up of two primary sections: the underground network and the visible reproductive structure. Each plays a pivotal role in nutrient absorption, spore dispersal, and the propagation of the species.
Key Structures of Fungal Organisms
- Mycelium: The underground network that absorbs nutrients and anchors the organism to its environment.
- Stipe: The stalk-like structure that supports the reproductive organ and elevates it for spore dispersal.
- Cap: The uppermost part where spore-producing cells are located, often serving as a protective cover for developing spores.
- Gills: Located under the cap, these structures are where spores are released into the environment.
The Role of Each Component
The mycelium forms an intricate web that allows the organism to thrive in various environments, absorbing nutrients from organic matter. The stipe lifts the cap high enough to disperse spores effectively, ensuring the survival of the next generation. The cap itself protects the developing spores while also serving as the site for reproduction.
Each component is intricately connected, working in unison to ensure the organism’s continued growth and reproduction. The structure of these organisms is a testament to nature’s efficiency, designed to maximize their ability to spread and sustain life.
Key Functions of Mushroom Parts
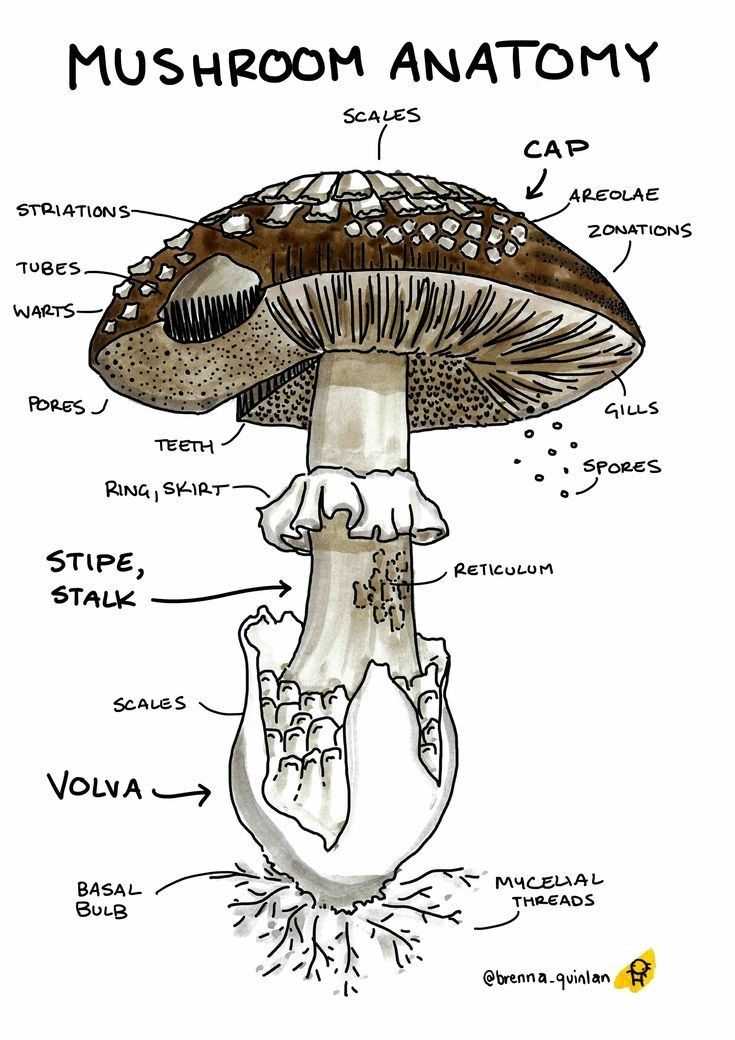
The structures of fungi perform a variety of essential functions that allow the organism to grow, reproduce, and thrive in its environment. From nutrient absorption to spore production, each section has a specific role that contributes to the overall health and life cycle of the organism. Understanding these functions provides a clearer view of how these organisms interact with their surroundings and ensure the survival of their species.
Primary Functions of Fungal Components
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Mycelium | Absorbs nutrients from the soil and decomposes organic matter to provide energy for the organism. |
| Stipe | Supports the reproductive structure and elevates it to enhance spore dispersal. |
| Cap | Protects developing spores and aids in their release when conditions are favorable. |
| Gills | Contains spore-producing cells that release spores into the air for reproduction. |
Reproductive and Growth Roles
Each component not only serves a vital role in sustaining the organism but also contributes to the reproductive process. The mycelium, as the primary feeding structure, ensures the organism has the energy required for growth. The cap and gills work together to ensure the successful production and dissemination of spores, which are essential for future generations. The stipe, by raising the reproductive structure above the ground, helps distribute spores over a wider area, increasing the chances of reproduction and species propagation.
Structure of Fungi Revealed
The design of fungal organisms is highly specialized, with each section fulfilling specific roles crucial for growth, reproduction, and survival. These organisms are composed of various interconnected components that function together as an efficient system. By studying the structure, we can better understand how each part contributes to its ecological role and the organism’s life cycle.
From the unseen network of filaments that stretch beneath the surface to the visible reproductive structures that produce spores, the architecture of fungi is both complex and effective. These components enable the organism to acquire nutrients, reproduce, and interact with its environment in ways that ensure its persistence in nature.
The intricate design of fungi showcases how nature utilizes simple yet highly efficient systems to perform essential biological processes. By exploring each part of their structure, we gain a deeper appreciation for the role these organisms play in ecosystems around the world.
Understanding the Cap and Stipe
The cap and stipe are two of the most noticeable structures in fungi, each with distinct roles in the organism’s life cycle. These components work together to support reproduction and ensure the survival of the species. The cap serves as the protective cover for developing reproductive cells, while the stipe elevates the cap to facilitate spore distribution.
The Role of the Cap
The cap, often seen as the uppermost part of the organism, is crucial for housing and protecting the reproductive cells. It ensures that the developing spores are shielded from the elements until they are mature and ready for release. Additionally, the cap plays a role in maximizing the spread of spores once they are released, ensuring that the organism can propagate successfully.
The Function of the Stipe

The stipe, commonly referred to as the stalk, serves as the supportive structure that lifts the cap above the ground. By elevating the reproductive structure, the stipe increases the organism’s ability to disperse spores over a larger area. This elevated positioning enhances the chances of reproduction and allows spores to travel more effectively, reaching new areas where they can grow.
How Mushroom Parts Contribute to Growth
The structures of fungi work in harmony to ensure the organism’s development and continued growth. From nutrient absorption to reproductive processes, each component plays a vital role in supporting the organism throughout its life cycle. By coordinating these functions, fungi can thrive in various environments and reproduce successfully.
Feeding and Nutrient Absorption
The underground network of filaments, known as the mycelium, is responsible for absorbing nutrients from organic matter. This vast network spreads throughout the substrate, breaking down decaying material and converting it into usable energy. The mycelium’s ability to efficiently extract nutrients is crucial for the growth of the visible structures, allowing them to reach maturity and begin the reproductive cycle.
Reproduction and Spore Dispersal
The reproductive structure, often elevated above the ground by the stipe, releases spores into the air to ensure species continuation. The cap not only protects developing spores but also plays a key role in their release when conditions are favorable. By dispersing spores across a wide area, the organism increases its chances of finding new environments in which to grow and proliferate.