
In any heating unit, understanding the different components and how they function together is crucial for efficient operation and proper maintenance. This knowledge not only aids in identifying potential issues but also enhances the ability to troubleshoot effectively. Each element of the system plays a specific role, from initiating the heat cycle to ensuring that all mechanisms work seamlessly for optimal performance.
By studying the layout and connections of the various components, users can gain a clearer picture of how each part contributes to the overall heating process. Whether you’re dealing with a malfunction or performing routine maintenance, knowing where each component is located and how it interacts with others can save time and reduce repair costs.
Maintenance and care require familiarity with each part’s function, making it easier to spot wear and tear before it leads to serious problems. In this guide, we will explore the essential elements of these systems, focusing on their design, function, and how to manage common issues.
Hydro Flame Furnace Components Explained
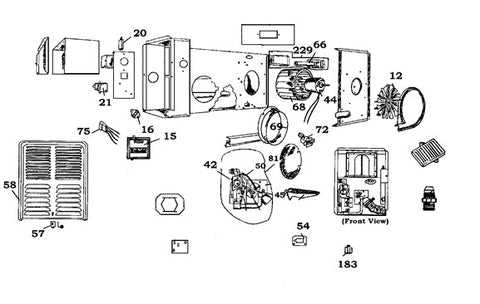
Understanding the key components of a heating system is essential for efficient operation and maintenance. Each part plays a unique role in ensuring proper functionality, from initiating the heating process to maintaining consistent output. By examining the individual elements, users can gain a better understanding of how to troubleshoot, repair, or replace them when needed.
Key Elements of the System
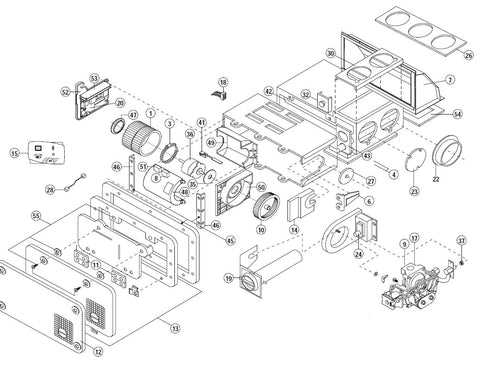
- Ignition System: Responsible for starting the heating cycle by igniting the fuel source. This includes components such as spark igniters and control modules.
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers heat from the combustion process to the air or water that circulates throughout the system, ensuring that heat is distributed efficiently.
- Blower Motor: Moves air through the system, ensuring that heated air is delivered to the desired spaces, maintaining consistent temperature control.
- Control Board: Manages the overall operation, ensuring that each component works together at the correct time to maintain optimal performance.
Functionality of Each Element
Each of these components serves a specific function within the system:
- Ignition System: Ignites the fuel to begin the heating cycle. If this component fails, the system will not start.
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers energy from the combustion process, which is essential for the system to produce heat efficiently. A malfunction here can reduce the unit’s heating capacity.
- Blower Motor: Helps circulate warm air throughout the space. An issue with the blower motor can result in inconsistent heating or a complete loss of airflow.
- Control Board: Directs the functioning of all other components. If the control board malfunctions, the entire system may fail to operate correctly.
Understanding the Parts and Functions
Every heating system relies on a set of specialized components that work in tandem to generate and distribute heat. Each element is carefully designed to perform a specific function, ensuring that the entire system operates smoothly and efficiently. A clear understanding of these functions helps users identify potential issues and maintain optimal performance.
Each component is essential for the proper operation of the system, from igniting the fuel to circulating the heated air or water. A malfunction in any part can disrupt the entire heating process, leading to inefficiencies or system failure. By knowing how these elements work together, users can better troubleshoot problems and make informed decisions about maintenance or repairs.
How to Read the Parts Diagram
Reading a system’s layout can provide invaluable insights into its structure and functionality. Understanding the connections and placement of each element helps in troubleshooting, maintenance, and repair. By familiarizing yourself with the visual representation, you can quickly identify specific components and their relationships within the overall system.
Identifying Key Components
The first step in interpreting the schematic is recognizing the main components. Each part is typically represented by a symbol or label that corresponds to its physical counterpart. Once identified, it’s easier to understand how each element interacts with others to maintain the system’s operation.
Understanding the Connections
Next, focus on the lines that represent the connections between components. These connections show how power, signals, or fluids flow through the system. Understanding these links is crucial for diagnosing faults and ensuring that the system operates efficiently.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Heating systems can experience various issues over time, many of which are caused by worn or malfunctioning components. Identifying common problems early can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs. Understanding typical issues and knowing how to troubleshoot effectively can ensure the system runs smoothly and efficiently.
Frequent Problems
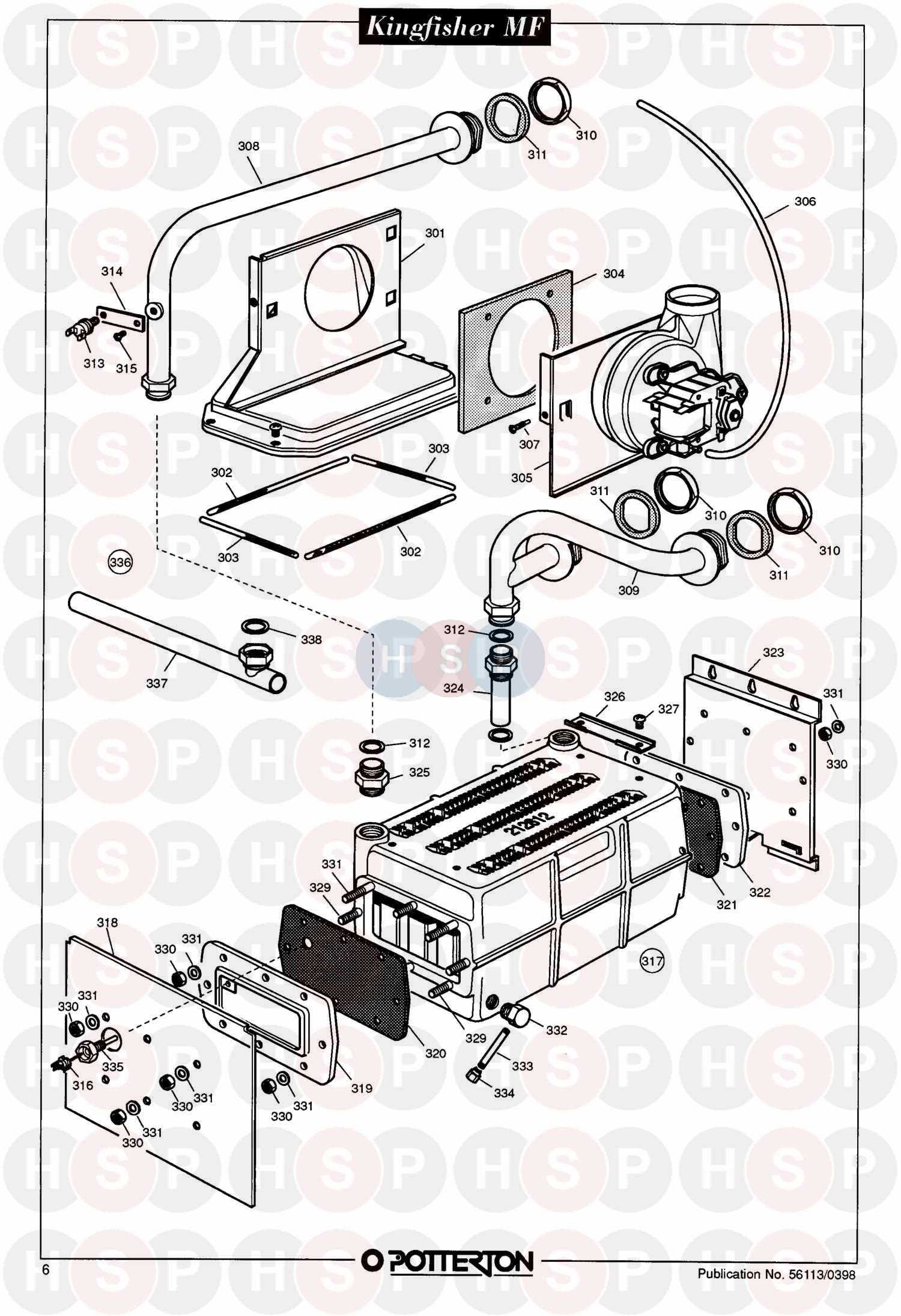
- Ignition Failure: If the system fails to start, the ignition system may be faulty. Check the igniter and control modules for damage or wear.
- Inconsistent Heating: When the system produces uneven heat, it may be due to issues with the blower motor or heat exchanger. Ensure these components are free of obstructions and operating correctly.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual noises could indicate problems with the blower or fan motor. Lubricating moving parts or replacing worn components may resolve this issue.
- Frequent Cycling: If the unit cycles on and off frequently, the thermostat or control board may be malfunctioning. Check settings and inspect the control system for issues.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Perform Regular Inspections: Periodically check all components for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to prevent sudden failures.
- Check the Power Supply: Ensure the system is properly connected to the power source and that the electrical components are functioning correctly.
- Clean and Replace Filters: Dirty filters can cause airflow problems, leading to overheating or reduced efficiency. Regular cleaning or replacement is key.
- Consult the Manual: Refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps and recommended maintenance practices for your system model.