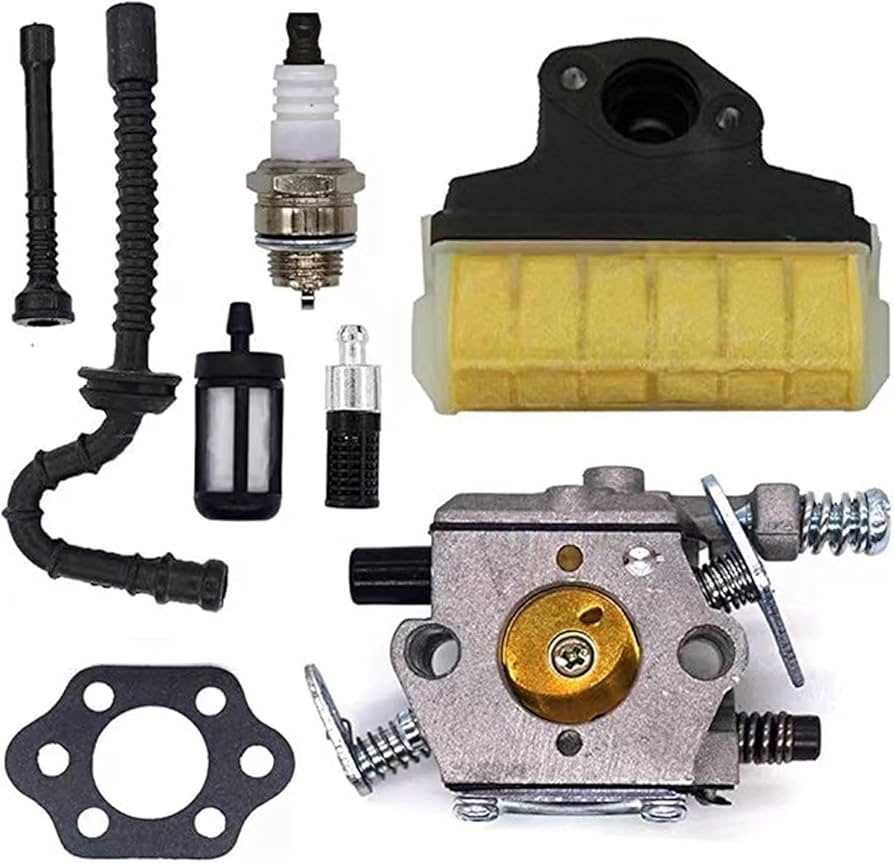

When it comes to maintaining and repairing your chainsaw, having a clear view of its internal structure is essential. Knowing where each part fits and understanding its function can make troubleshooting and repairs significantly easier.
Accurate identification of the various sections and components plays a crucial role in ensuring your tool operates efficiently. With the right information, even complex repairs become manageable, giving you the confidence to handle them yourself.
This guide will help you understand the key elements involved in maintaining your chainsaw, allowing for better care and extending its lifespan. Proper knowledge of how each piece works together is the first step to effective servicing.
Understanding Chainsaw Component Layout
To effectively maintain and repair your chainsaw, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of its overall structure. Every machine is made up of various interconnected parts, each serving a specific function. Having a solid grasp of these components ensures that repairs are done correctly and helps identify potential issues before they become serious problems.
Key Components of the Tool
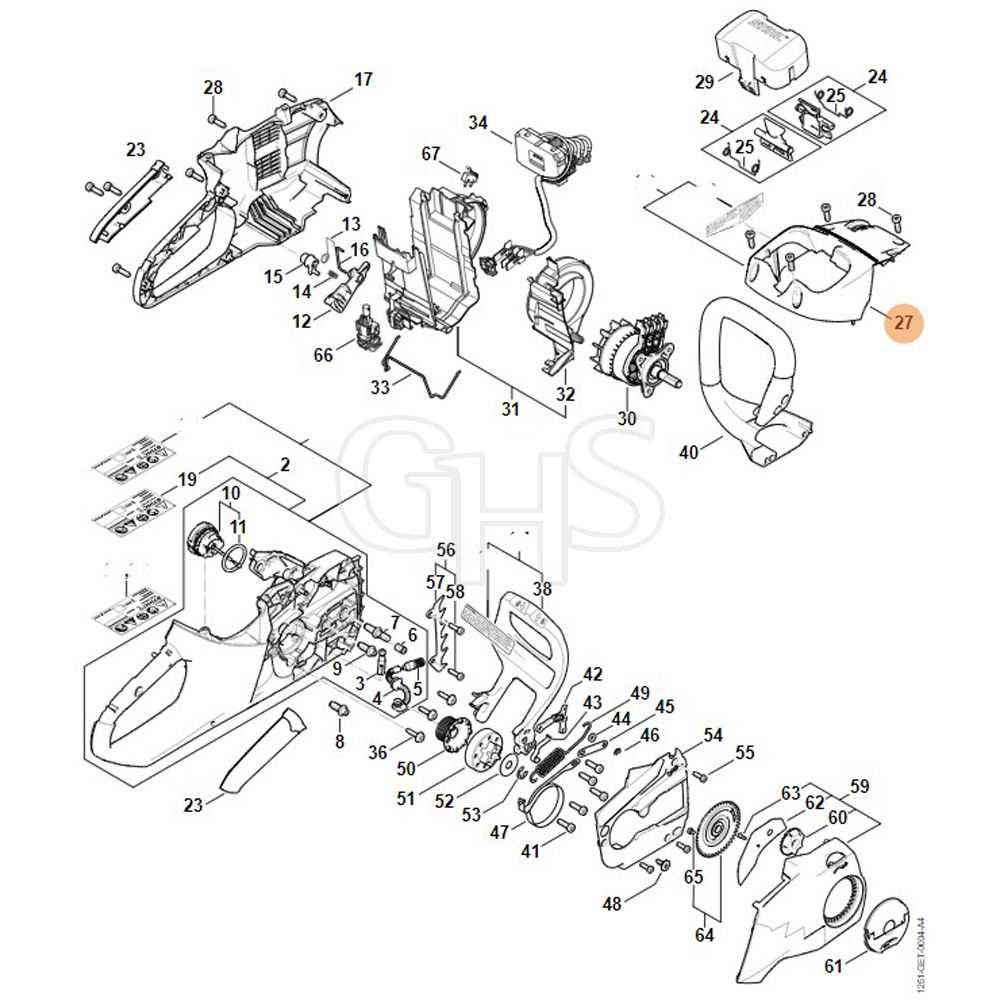
The main sections of the chainsaw include the engine, fuel system, cutting mechanism, and safety features. Understanding where these elements are located and how they interact with each other is vital for troubleshooting and ensuring smooth operation. Each part plays a unique role, from the power source to the guide bar, which ultimately determines the tool’s performance.
Assembly and Layout Insights
A proper layout shows how each element fits into the larger framework. Knowing the exact placement of each part allows for more efficient disassembly and reassembly. It also aids in recognizing when a part might be worn out or improperly positioned. Being familiar with the layout helps in both routine maintenance and more complex repairs.
How to Identify Chainsaw Components
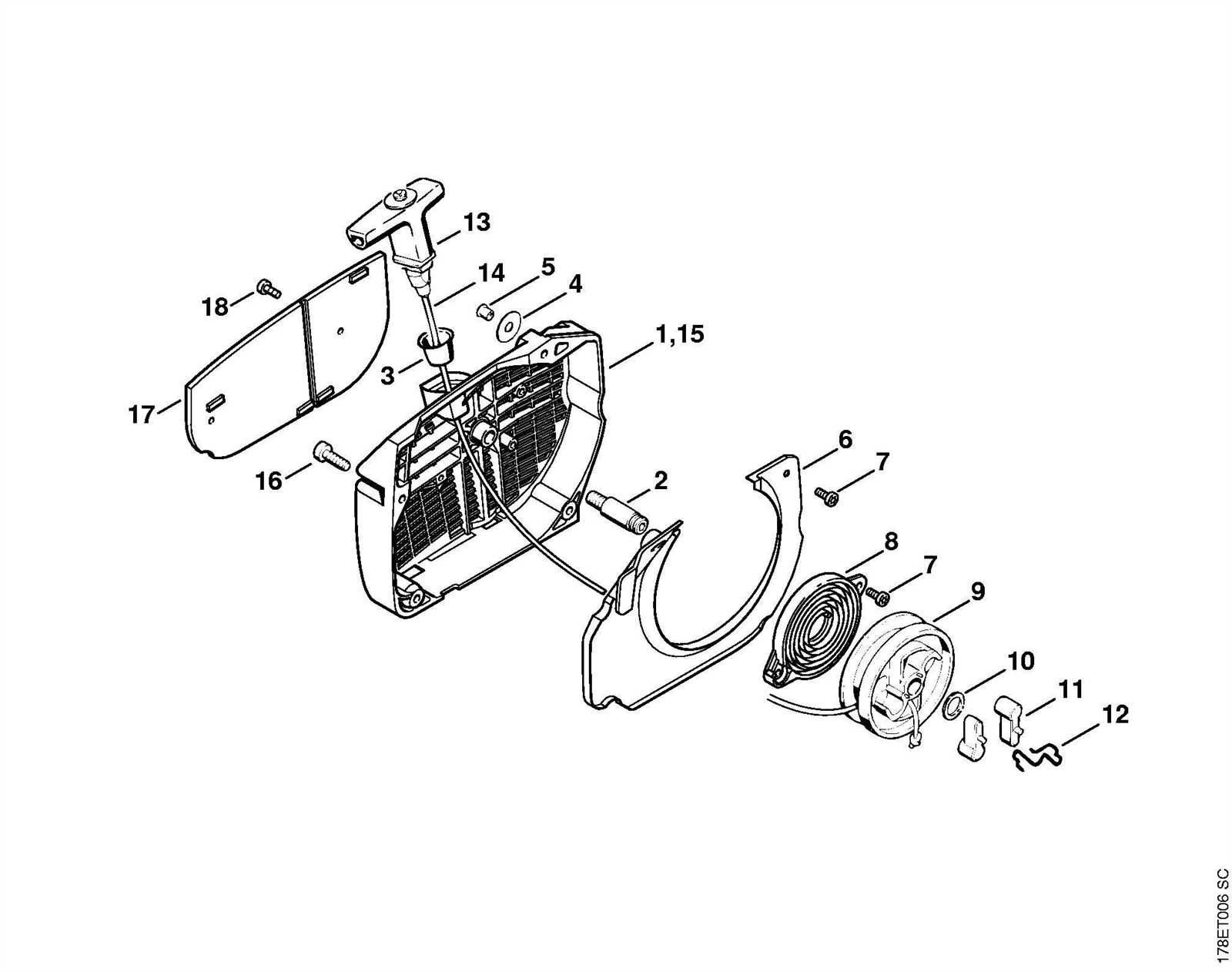
Accurately identifying the components of your tool is essential for both routine maintenance and repair. Each part of the machine plays a specific role in its overall performance, and knowing what each piece does allows for better troubleshooting and more effective repairs. A clear understanding of the key elements ensures that you can easily identify any issues that may arise and know how to fix them.
Recognizing the Engine and Power System

The engine is the heart of the machine, providing the power needed for operation. It’s essential to recognize the fuel system components, such as the carburetor and fuel lines. Identifying wear or blockages in these areas can significantly improve your tool’s performance. Pay close attention to any fuel-related issues, as they are often the root cause of power failures.
Examining the Cutting Mechanism
The cutting mechanism includes the guide bar, chain, and drive sprocket. Understanding the function of these parts is critical to maintaining cutting efficiency. Over time, the chain may stretch or become dull, affecting performance. Regular inspection helps in determining when these parts need replacement or adjustment to ensure smooth operation and safety.
Step-by-Step Repair Guide for Chainsaw
When your chainsaw starts showing signs of wear or malfunction, knowing how to perform repairs step by step can save time and money. A systematic approach ensures that you address each problem properly and prevent further damage. Follow these simple guidelines to restore your tool to optimal working condition with minimal effort.
Begin by inspecting the tool for any obvious issues. If there’s no visible damage but the machine isn’t functioning as it should, proceed with a detailed inspection of the engine, fuel system, and cutting mechanism. Once the problem areas are identified, carefully disassemble the necessary components to perform the required repairs or replacements.
After replacing or fixing the faulty parts, carefully reassemble the tool, ensuring all components are securely in place. Always test the chainsaw on a small task to confirm the repair was successful. Regular maintenance and early intervention can prevent more severe issues in the future, ensuring longer tool life.