
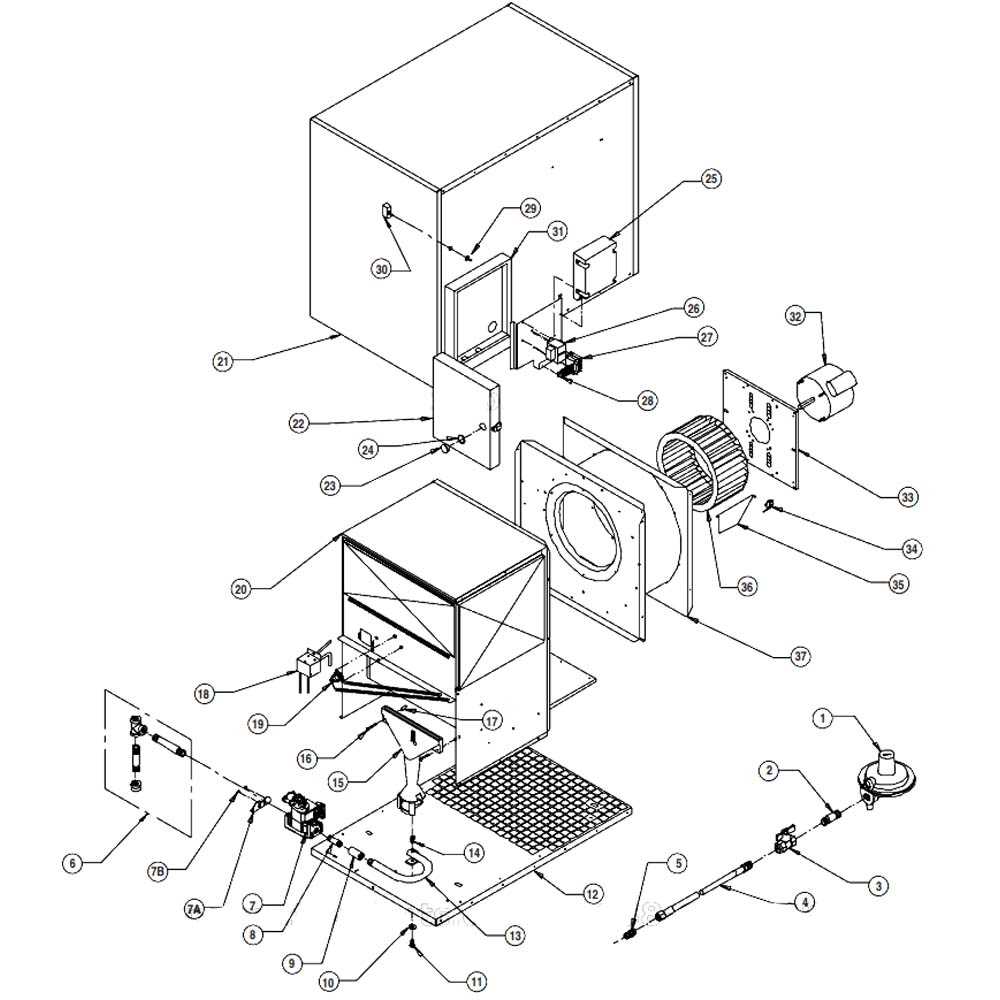
Proper maintenance and repair of heating systems require a clear understanding of their internal components. Recognizing how each element functions together ensures efficient operation and extends the lifespan of the unit. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional, having a clear guide to these essential components is key to troubleshooting and performing repairs.
Visual aids can be invaluable when working with heating systems, offering a detailed view of how each piece fits into the larger structure. These illustrations help to identify the most commonly replaced parts and provide insight into how to safely access and repair them. Understanding this layout makes the process more straightforward and minimizes the risk of damage or incorrect installation.
By familiarizing yourself with the core elements of your heating system, you can make more informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, and when it’s time to consult a technician. Knowledge of the system’s components also helps identify potential issues early, saving time and money in the long run.
Understanding Heating System Components
Every heating unit consists of several crucial elements that work together to produce and distribute warmth effectively. Understanding how these components interact is essential for maintaining system performance and ensuring its longevity. By identifying each key part, you can make more informed decisions when performing maintenance or repairs.
Core Components of Heating Systems
At the heart of every system, several primary components play a significant role in the heating process. These parts include the ignition mechanism, heat exchanger, blower motor, and safety sensors, each responsible for specific tasks. Together, they ensure smooth operation and optimal performance.
- Ignition System: Responsible for starting the heating process by igniting the fuel or heating element.
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers the heat to the air that circulates throughout the space.
- Blower Motor: Facilitates the movement of heated air to the vents and throughout the home.
- Safety Sensors: Monitor the system for any malfunctions and ensure safe operation by shutting it down if necessary.
Identifying Common Issues with System Components
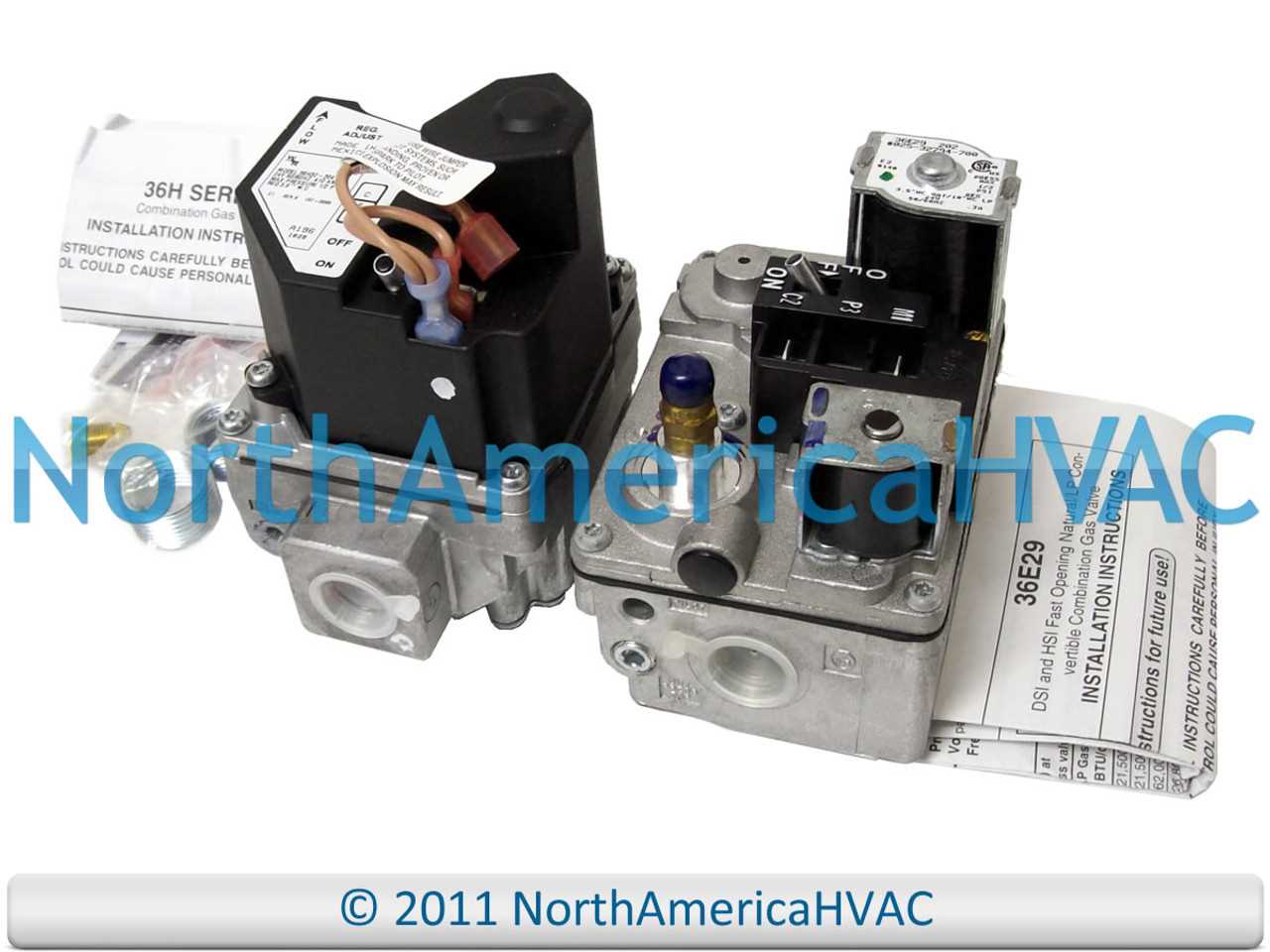

Being able to recognize when a part is malfunctioning can save time and reduce repair costs. Here are some common issues related to heating system components:
- Ignition Failure: A faulty ignition system can prevent the unit from starting properly, requiring replacement or cleaning.
- Clogged Heat Exchanger: Dust and debris can accumulate, reducing efficiency and causing overheating if not cleaned regularly.
- Blower Malfunctions: Issues with the blower motor can lead to poor airflow, causing uneven heating and longer system run times.
- Sensor Problems: A malfunctioning safety sensor can trigger false shutdowns or prevent the system from operating at full capacity.
How to Read Heating System Layouts
Understanding the layout of a heating unit is crucial for efficient repairs and maintenance. These layouts offer a detailed visual representation of all essential elements, showing their position within the system and how they interact. By learning to interpret these schematics, you can easily identify components that need attention and make informed decisions when troubleshooting or replacing parts.
Interpreting Symbols and Labels
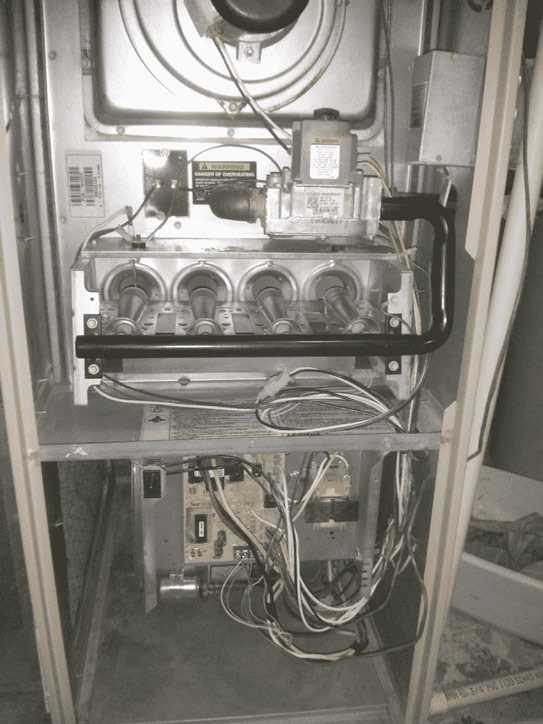

Heating system illustrations often use specific symbols and labels to represent different components. Familiarizing yourself with these symbols will allow you to quickly understand the function and location of each part. For instance, a circle might represent a motor, while a rectangle may indicate a heat exchanger. Pay attention to any labeled connections, arrows, and numbers that highlight the flow of air, fuel, or electrical current.
- Circle symbols: Typically represent motors or other rotating parts.
- Rectangles: Often used to indicate elements like the heat exchanger or filters.
- Arrows: Show the direction of airflow or fuel movement.
- Numbers: Indicate specific parts or assembly steps for clarity.
Locating Key Components and Connections
When examining a heating system layout, focus on the central components and their connections. Each part is usually drawn in relation to the others, allowing you to trace the airflow or electrical flow throughout the unit. Pay attention to the proximity of various parts to understand how they depend on one another. This can help you diagnose issues, such as blockages or electrical malfunctions, with greater accuracy.
Common Heating System Component Replacements
Over time, certain elements of a heating unit may wear out or become inefficient, requiring replacement. Knowing which parts are most likely to need attention can help you maintain the system’s performance and prevent unexpected breakdowns. Regularly replacing these components ensures smooth operation and extends the lifespan of the unit.
Frequently Replaced Elements
Some components are more prone to failure due to regular use and exposure to heat. These elements often require periodic inspection and replacement to maintain efficiency. Common parts that may need replacing include filters, motors, igniters, and thermocouples.
- Filters: Regular cleaning or replacing of air filters helps maintain proper airflow and efficiency.
- Motors: Blower motors can wear out over time and may need replacing to avoid poor airflow.
- Igniters: If the ignition system fails, the unit won’t start, necessitating a new igniter.
- Thermocouples: These sensors may need replacing if they fail to detect temperature changes or shut the system down prematurely.
Signs of Wear and Tear
Knowing the signs of a failing component can help you identify when replacement is necessary. Strange noises, poor airflow, or a complete lack of heat often point to a malfunctioning part. Regular maintenance and early detection can prevent more significant damage to the system and reduce repair costs.