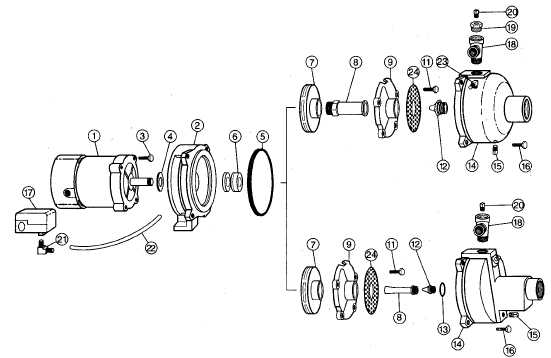
Every mechanical system relies on precise and well-designed components to function smoothly. When it comes to fluid management, knowing the roles and interactions of various elements is essential for ensuring optimal performance. This section will help you navigate the crucial components involved in the process and how they contribute to the overall system’s efficiency.
Proper understanding of the structure and function of each piece allows for better troubleshooting and maintenance. With a comprehensive guide, you can gain insight into how each part works together to facilitate effective fluid transfer and prevent operational disruptions. Whether you’re looking to repair or simply maintain your system, familiarity with the components is key to ensuring its longevity.
Understanding Myers Pump Components
In any fluid-moving system, a collection of carefully engineered elements works in harmony to ensure smooth operation. Each component has a specific function that contributes to the overall effectiveness of the system, and understanding these roles is crucial for optimal performance and troubleshooting. This section focuses on the most important elements that make up the mechanism and how they interact with each other.
Core Functional Elements
The key elements of the system include the intake, discharge, and drive mechanisms. The intake draws in the liquid, while the discharge expels it in a controlled manner. The drive system powers the entire mechanism, ensuring that all components work together seamlessly. Each element must be precisely aligned and maintained to avoid disruptions in fluid transfer.
Common Issues and Maintenance
Over time, wear and tear can affect any of these components, causing inefficiencies or even system failure. Common issues include blockages, leaks, or misalignments. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to detect and address problems before they lead to significant damage. Ensuring that all elements are functioning properly extends the lifespan of the system and reduces downtime.
How to Read Myers Pump Diagrams
Understanding a system’s blueprint is key to identifying its components and their interactions. A well-designed schematic offers a visual representation of how each element fits together, allowing you to easily spot potential issues and make informed decisions during maintenance or repair. In this section, we will explore how to interpret these technical illustrations effectively.
Identifying Key Symbols
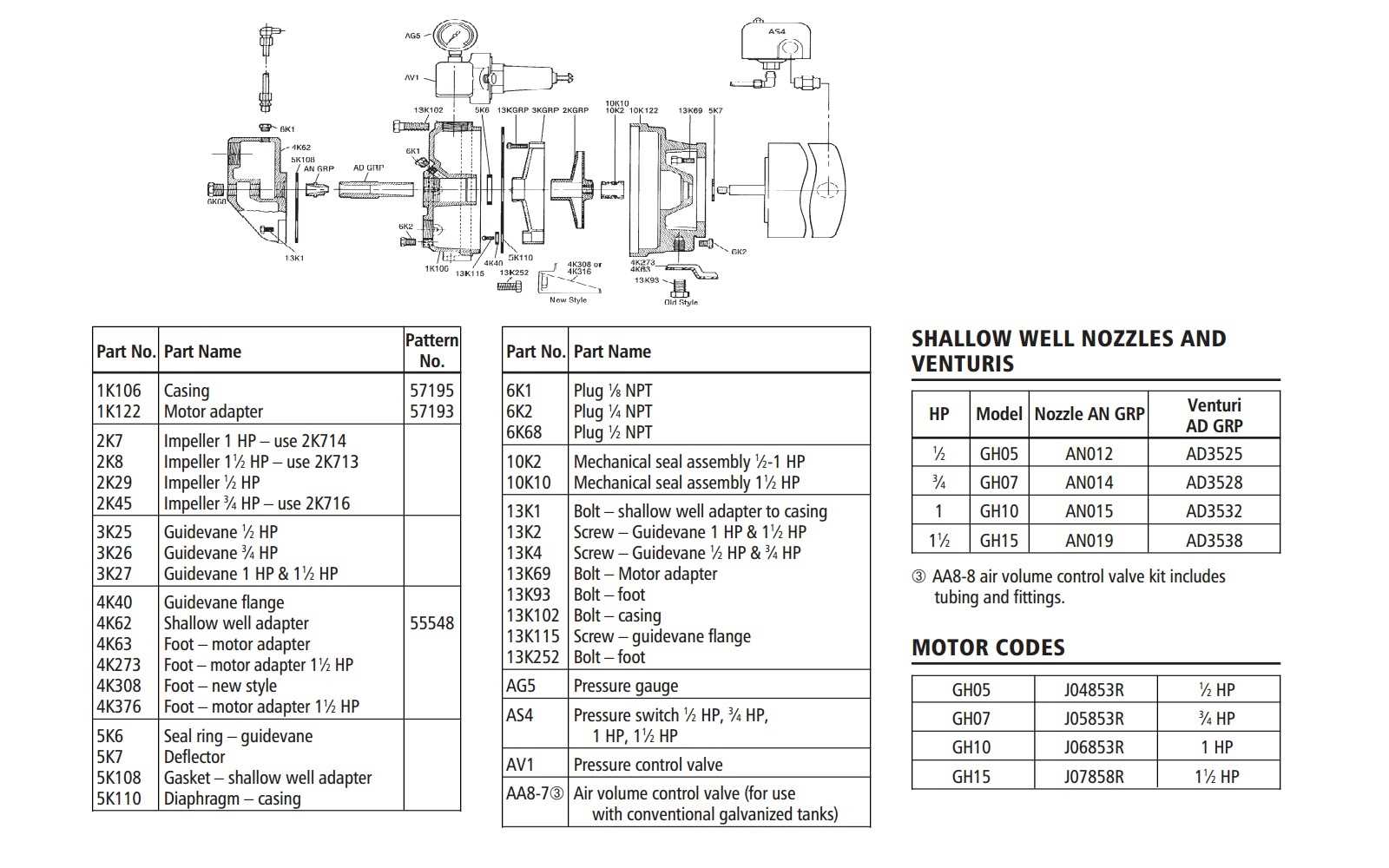
One of the first steps in reading technical schematics is familiarizing yourself with the symbols used to represent each component. These symbols are standardized, making it easier to understand the function of each part without needing a detailed description. Look for symbols representing elements like valves, seals, or motors, as these are the building blocks of the system.
Understanding Flow and Connections
Another crucial aspect is understanding how the various components are connected and how the fluid flows through the system. Lines, arrows, and labels indicate the path of the fluid, and any potential points where pressure or temperature changes may occur. Pay attention to these flow indicators as they highlight the system’s efficiency and where possible bottlenecks or issues may arise.
Key Parts for Pump Maintenance
Proper upkeep of a fluid-moving system requires regular attention to its core components. Identifying and maintaining these critical elements ensures that the entire mechanism operates smoothly, preventing costly repairs or breakdowns. This section highlights the essential components that should be monitored and serviced regularly for optimal performance.
Essential Components to Monitor
- Seals: Prevent leakage and ensure pressure is maintained within the system.
- Valves: Regulate the flow and direction of fluid, ensuring efficient operation.
- Motors: Provide the necessary power for the system to function properly.
- Bearings: Support moving parts, reducing friction and wear.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly inspect seals for signs of wear or damage to avoid leaks.
- Check valves for proper movement and ensure they are free from debris.
- Lubricate motors and bearings to prevent friction and overheating.
- Replace worn components promptly to prevent system failure.