The construction of any musical instrument is a delicate balance of form and function. Each element plays a crucial role in producing the sound and ensuring the instrument’s performance. In string instruments, a variety of parts work in harmony to create the rich, resonant tones that musicians seek to express through their art.
From the body that amplifies the vibrations to the tuning mechanism that allows for precise adjustments, understanding each segment’s function is essential. Whether you are an aspiring musician or an enthusiast, learning about the key elements of such an instrument provides insight into its design and operation.
Detailed knowledge of these elements can enhance both playing technique and appreciation for the craftsmanship behind the creation of the instrument. In this guide, we will break down the different sections of the structure and explain how they interact to produce beautiful melodies.
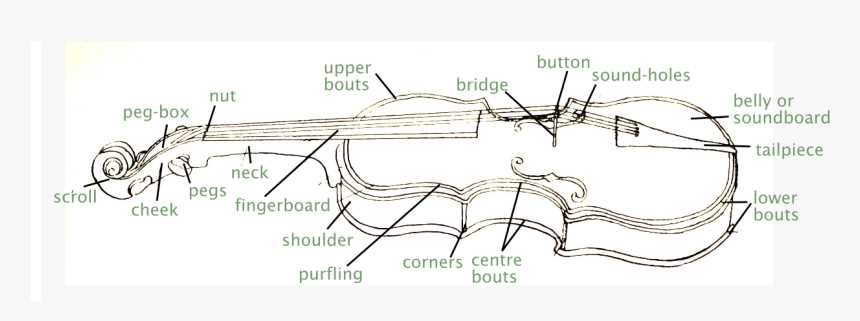
Understanding the Structure of a Violin
In order to fully appreciate how a string instrument functions, it is important to understand its intricate design. Each section plays a unique role in the overall performance, contributing to the creation of sound. The balance between the materials, shape, and arrangement of components defines the quality and characteristics of the tones produced.
The Frame and Resonating Body
The main body of the instrument serves as the primary resonator, amplifying the sound produced by the vibrating strings. The shape and construction of this section influence the timbre and volume. A hollow structure, typically made of wood, helps project the vibrations outward, enabling the rich acoustics that musicians seek. The curvature and specific dimensions are fine-tuned to enhance resonance and tonal clarity.
The Neck, Fingerboard, and Tuning Mechanism
The neck connects the resonating body to the strings, allowing for precise manipulation. Along its length runs the fingerboard, where the musician presses the strings to create different pitches. The tuning mechanism, usually located at the top of the neck, allows for fine adjustments to the tension of the strings, affecting both pitch and tone. This section is critical for the control and flexibility that performers require during play.
Key Components and Their Roles
Every string instrument consists of multiple elements, each serving a distinct purpose in sound production and playability. Understanding the function of each component is crucial for mastering the instrument and fully appreciating its craftsmanship. These sections work together in harmony to produce the unique tones and textures that musicians use to express their creativity.
The Soundboard and Bridge
The soundboard, often located in the center of the body, acts as the primary amplifier of vibrations. When the strings are bowed or plucked, the vibrations travel through the bridge to the soundboard, which enhances the sound and projects it outward. The bridge plays an essential role in transferring these vibrations, ensuring the proper resonance and tonal quality. Its placement and alignment directly impact the instrument’s sound and tuning stability.
The Strings and Tailpiece
The strings are the source of vibration that generates sound. They are stretched across the fingerboard and the bridge, with tension adjusted to create different pitches. The tailpiece, located at the bottom end of the instrument, helps secure the strings and maintain the correct tension. This section is vital for keeping the strings properly aligned, ensuring both stability and accurate pitch control during performance.
How a Violin Parts Work Together
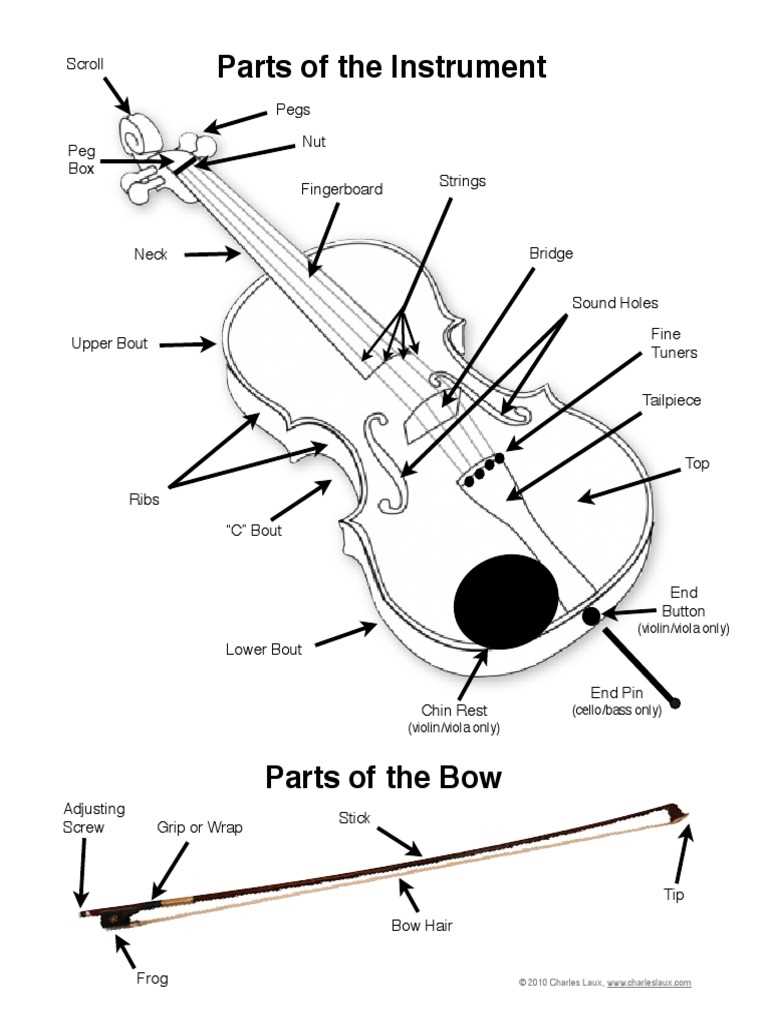
For a string instrument to function properly, its individual sections must work in unison. The interaction between the various components is what enables the creation of rich, resonant sounds. Each element is designed to complement the others, ensuring that vibrations are transmitted and amplified efficiently, ultimately producing a harmonious tone.
The Interaction Between Strings and Body
The strings vibrate when played, and these vibrations are transferred through the bridge to the body. The body’s resonance amplifies these vibrations, creating the volume and richness of sound. The shape and material of the body influence how effectively it amplifies the vibrations, while the strings determine the pitch and timbre. This synergy is crucial in producing a clear, powerful tone.
The Role of the Neck and Fingerboard
The neck and fingerboard provide the framework for controlling the pitch of the strings. As the musician presses down on the strings along the fingerboard, the effective length of the strings changes, altering the pitch. The tension in the strings is adjusted by the tuning pegs at the top of the neck, allowing the performer to fine-tune the instrument for precise pitch control. The smooth interaction of these elements gives the performer the flexibility to produce various notes and dynamics during play.