Maintaining a garden cultivator is essential for ensuring its optimal performance and longevity. Knowing how each component functions and how to repair or replace them can make a significant difference in your gardening experience. Understanding the key elements that make up the machine can help you troubleshoot issues effectively and avoid costly repairs.
By familiarizing yourself with the various sections and mechanisms of the tool, you can confidently address common problems such as poor operation or mechanical failures. A breakdown of the device’s structure can provide clarity on how the parts work together and where to focus your attention when issues arise.
In this guide, we will explore the main components of a garden cultivator, offering valuable insights into their function and how to maintain them. With this knowledge, you will be better equipped to care for your machine and tackle any maintenance or repair tasks with ease.
Understanding the Garden Cultivator
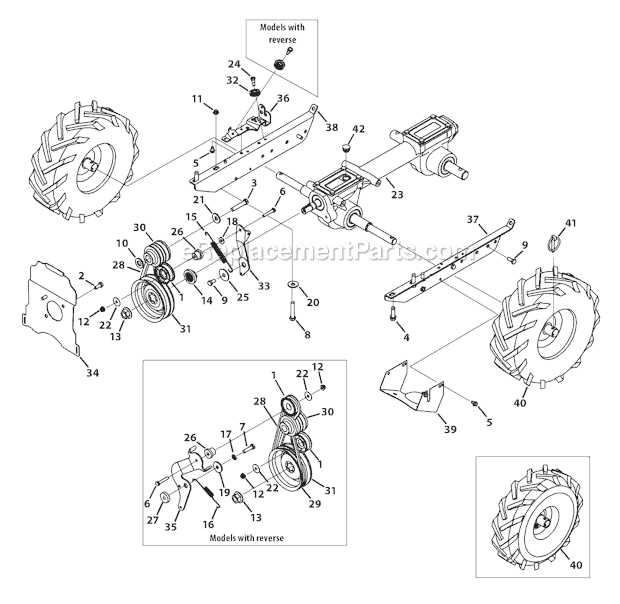
When it comes to gardening equipment, a powerful and reliable machine can make all the difference in achieving successful soil preparation. These tools are designed to break up compacted earth, making it easier to plant, aerate, and maintain your garden. Knowing how the machine is assembled and how its components interact is crucial for anyone who uses it regularly.
Each segment of the machine plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation. From the engine to the handles, each element has a specific function that contributes to the overall performance. Understanding how these components work together allows users to perform necessary repairs, replace worn-out parts, or simply ensure that everything is running as expected.
By gaining insight into the structure of the cultivator, users can more easily identify issues when they arise, preventing frustration and unnecessary downtime. Proper knowledge of the machine not only enhances its efficiency but also extends its lifespan, ensuring you get the most out of your investment.
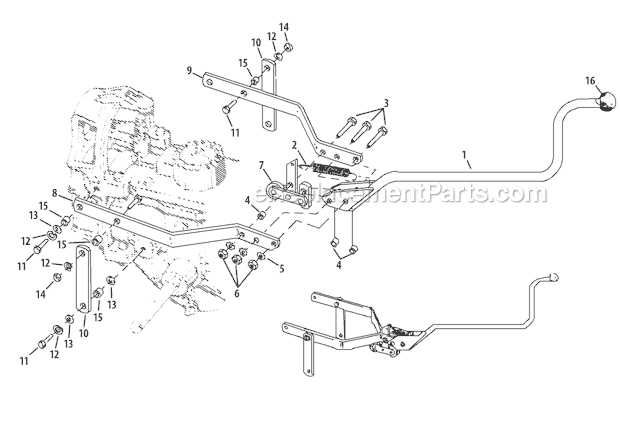
Common Parts of the Cultivator Model
Every gardening machine is made up of several key components that work together to achieve the desired results. Understanding these components is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Each part has a specific function that contributes to the overall efficiency of the tool, whether it’s for tilling the soil or ensuring the engine runs smoothly.
The engine is the heart of the machine, providing the power needed to drive the cultivator’s various mechanisms. Transmission systems are also crucial, as they regulate the speed and force applied to the cultivator’s working components. Handlebars allow users to control the machine and steer it through the soil, while blades or tines are responsible for breaking up the earth for planting.
Additionally, belts, wheels, and drive shafts ensure the proper movement and direction of the machine. Regular inspection of these elements is necessary to maintain optimal performance and prevent breakdowns. Identifying and understanding each of these components helps users address issues promptly and maintain their equipment’s functionality.
How to Identify Faulty Components
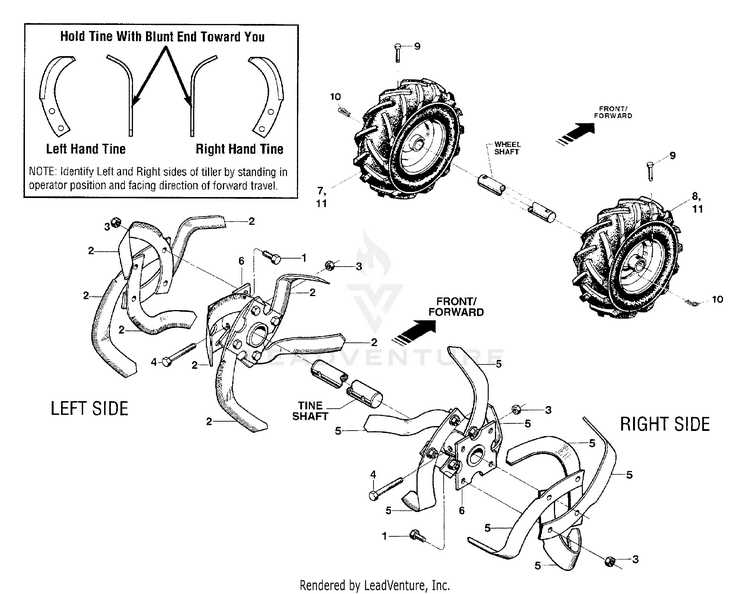
When dealing with mechanical equipment, it’s essential to recognize signs of wear or malfunction early. Identifying faulty parts quickly can prevent further damage and reduce repair costs. Regular inspection and understanding of how each part functions are crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Listen for unusual sounds: Abnormal noises such as grinding, rattling, or squealing can indicate that a component is not functioning properly. These sounds often point to issues like worn bearings, loose connections, or misalignment.
Examine for physical damage: Visible cracks, dents, or missing pieces are clear signs that a part is compromised. Pay close attention to areas that experience high stress or friction, as these are more prone to damage.
Monitor performance changes: A decline in efficiency or inconsistent operation often signals a problem. If the machinery struggles to perform tasks it once completed easily, it may be time to inspect key components for damage or wear.
Check for leaks: Fluid leaks can often be indicative of seal failures or damage to hoses or gaskets. Regularly checking for any leakage will help identify these issues early.
Test functionality: If the equipment isn’t responding as expected, faulty switches, connectors, or power sources could be to blame. Make sure each function is working as intended to ensure everything is in good condition.