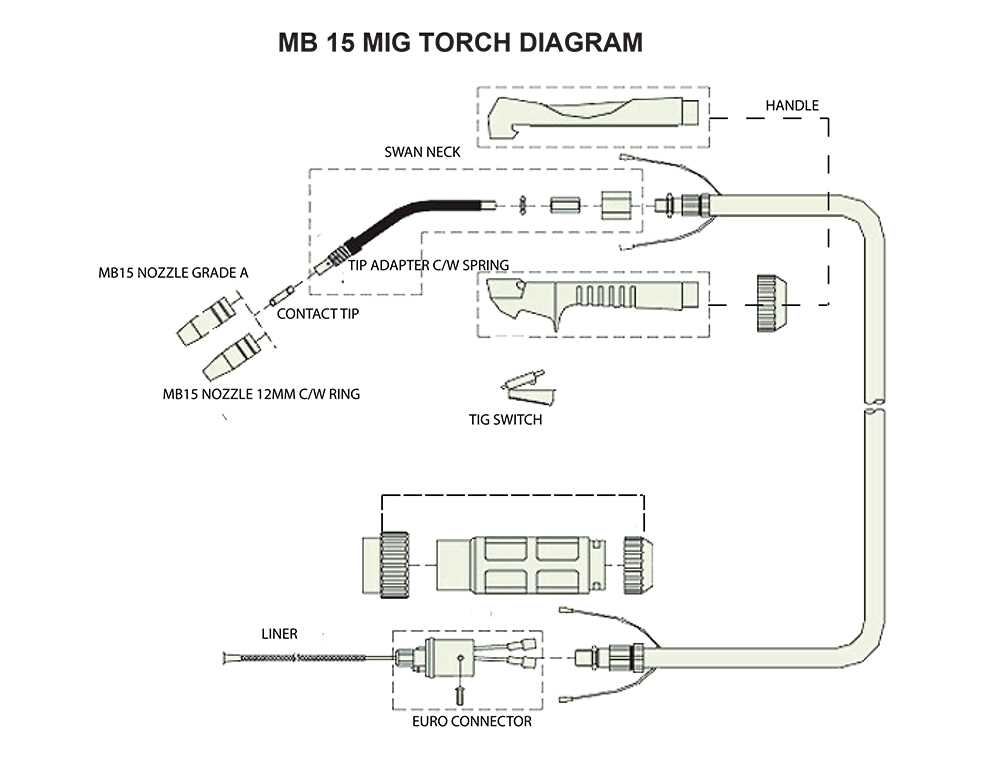
In every welding process, understanding the tools and their individual elements is crucial for achieving high-quality results. The structure of welding equipment consists of various components, each playing a specific role in the functionality and performance of the tool. Knowing how each part contributes to the overall operation can help prevent malfunctions and improve the overall efficiency of the equipment.
The key to successful usage lies in recognizing how different sections interact with one another. From the main handle to the nozzle, every element is designed to serve a particular function, ensuring the smooth flow of material and protection against heat damage. Understanding these interactions is essential for both beginners and seasoned welders alike.
Proper maintenance and quick identification of issues are also vital for extending the life of your equipment. By familiarizing yourself with the internal workings and common wear points, you can troubleshoot problems quickly and avoid costly repairs. Knowledge of these essential components can save time, reduce errors, and enhance your welding experience.
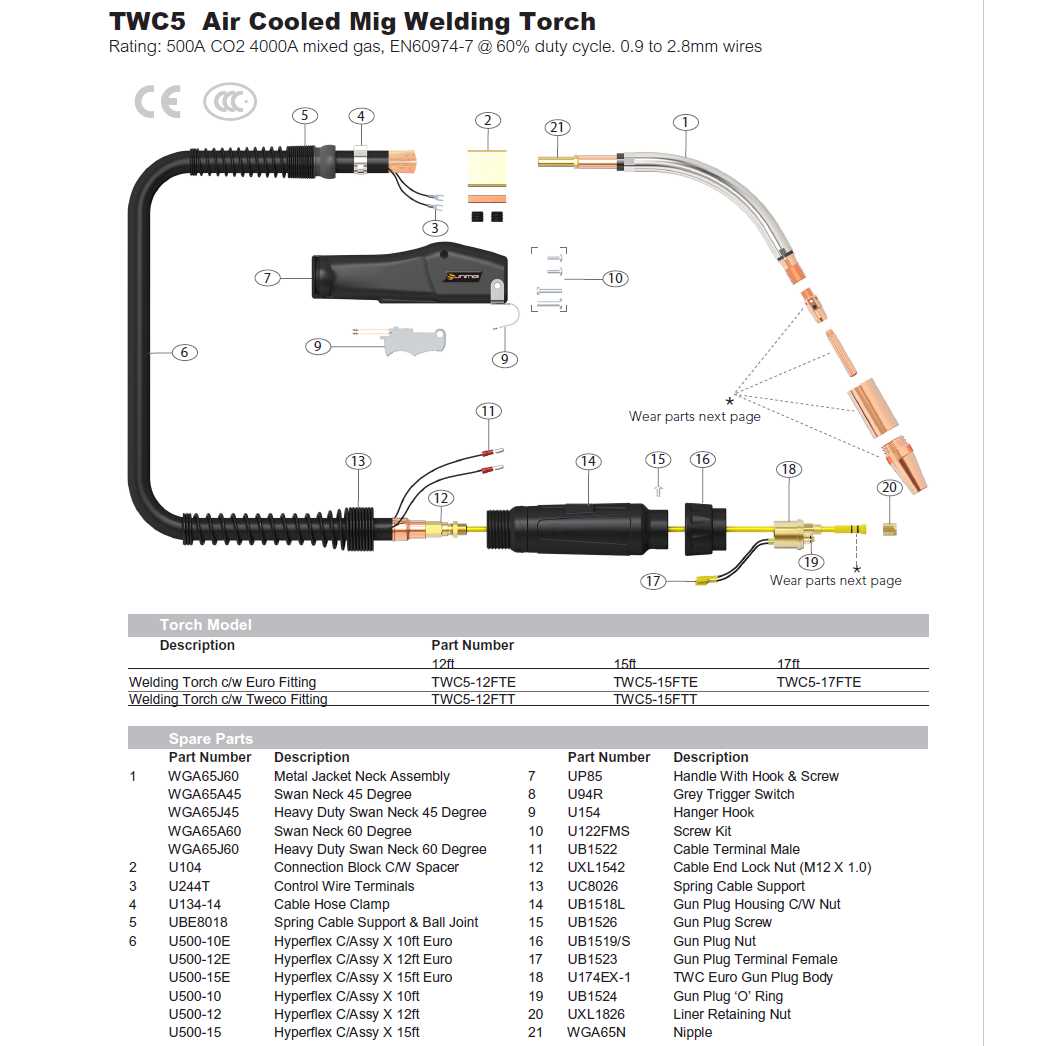
Mig Gun Parts Overview
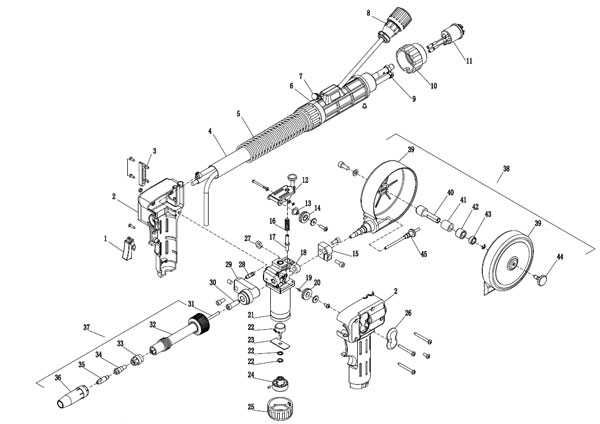
Welding tools consist of several crucial elements that work together to deliver precise results. Each component is designed to perform a specific function, ensuring that the operation is smooth and efficient. Understanding the individual roles of these components allows for better management and care of the equipment, reducing downtime and improving the quality of work.
At the core of these tools are the structural elements that provide stability and control. The handle, trigger, and cable connections form the foundation, making it easier for the operator to maneuver the tool. These parts are typically made of durable materials to withstand the heat and pressure during use.
Additional components, such as the nozzle and contact tip, play vital roles in directing the flow of welding material. These parts must be kept clean and in good condition to avoid blockages or irregular material deposition. The feed mechanism, which controls the movement of wire, ensures that the right amount of material is consistently delivered to the welding site.
By regularly checking and maintaining these essential components, welders can maximize the performance and longevity of their equipment, ensuring high-quality results every time.
Key Components and Their Functions
Understanding the core elements of a welding tool is essential for efficient use and proper maintenance. Each component plays a specific role in the overall operation, ensuring that the tool functions effectively and safely during welding tasks. Knowing how these elements interact helps improve performance and troubleshoot issues quickly.
Trigger and Handle
The trigger and handle form the primary interface between the operator and the tool. The handle provides a comfortable grip, while the trigger controls the activation of the tool. When pressed, the trigger initiates the flow of power, allowing the welder to begin their work. These elements are designed for ease of use, reducing strain during prolonged tasks.
Nozzle and Contact Tip
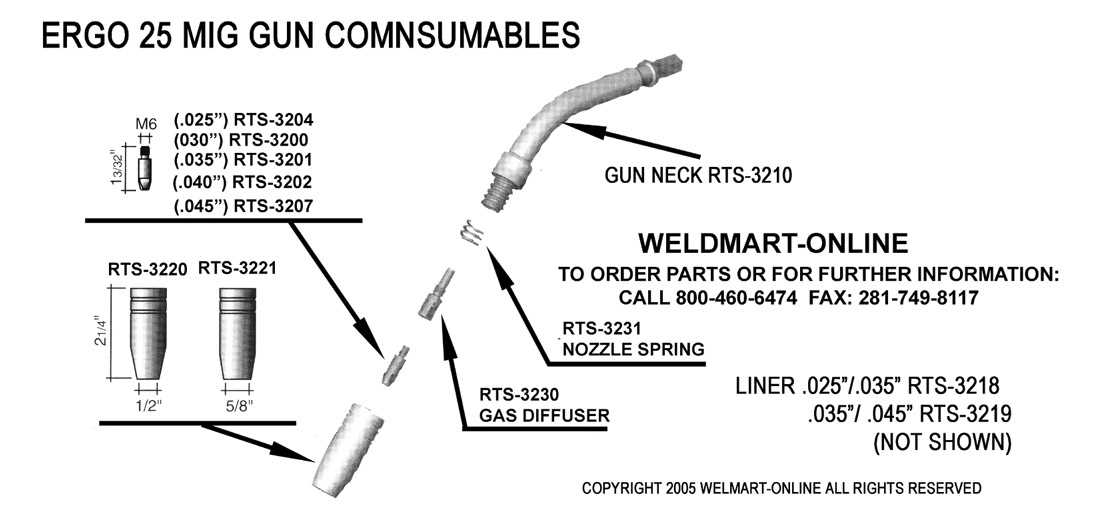
The nozzle and contact tip are essential for directing the flow of material during welding. The nozzle protects the inner components from heat, while the contact tip ensures that the wire is fed correctly to the weld site. Proper maintenance of these parts is critical to maintaining smooth material deposition and avoiding irregularities in the weld bead.
Identifying Common Welding Tool Issues
Even the most reliable equipment can experience issues over time. Recognizing common problems early can help prevent damage and ensure the tool continues to operate efficiently. From inconsistent wire feed to overheating, identifying these issues quickly is key to maintaining optimal performance.
Inconsistent Material Flow
One of the most common issues is an irregular feed of material, which can result in poor weld quality. This can be caused by blockages or worn-out components such as the contact tip or nozzle. Regularly inspecting these parts ensures smooth operation and prevents disruptions in the welding process.
Overheating and Excessive Wear
Excessive heat buildup is another frequent issue. When the tool overheats, it can cause damage to internal components, leading to premature wear and failure. This is often a result of improper maintenance or using the equipment beyond its rated capacity. Keeping the tool clean and allowing it to cool down between uses can help mitigate this problem.
Signs of Wear and Damage
Over time, every tool undergoes wear and tear, especially with frequent use in high-intensity tasks. Recognizing the early signs of damage can help prevent more significant issues and costly repairs. Identifying these signs early ensures your equipment continues to perform at its best and prevents poor-quality results.
Common Signs of Wear
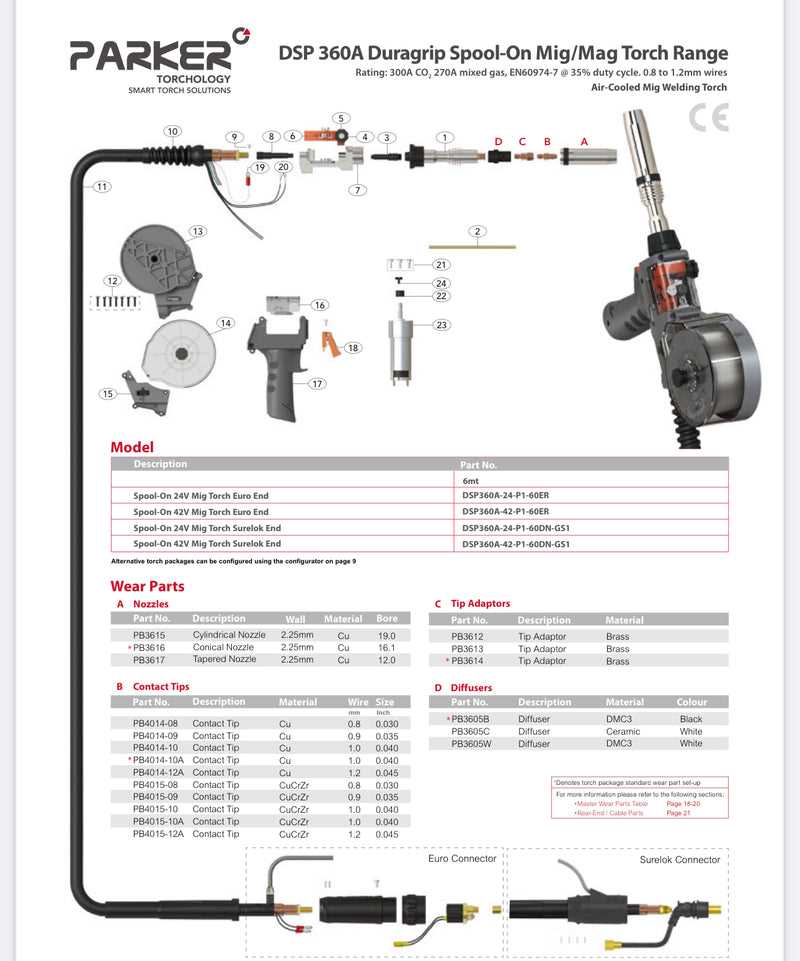
- Worn-out contact tips: Reduced performance in material flow due to the tip becoming flat or eroded.
- Damaged nozzle: Cracks or holes that disrupt the smooth flow of shielding gas and material.
- Loose connections: Unstable wire feed or power interruptions caused by loosened or corroded cables.
Indicators of Potential Failure
- Overheating: Prolonged exposure to excessive heat can cause internal parts to weaken or deform.
- Inconsistent welds: Uneven or poor-quality welds are often a result of internal damage or misalignment in the tool.
- Visible cracks: Cracks in the structure of the equipment or on the cable connectors can compromise safety and performance.
Proper Maintenance for Welding Equipment
To ensure long-lasting performance and consistent results, regular maintenance of your welding tools is essential. Proper care and upkeep prevent common issues, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of the equipment. Regularly inspecting and cleaning the tool will keep it functioning at its highest level.
Here are some key maintenance tasks that should be performed on a regular basis:
| Task | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning the Nozzle | Remove any built-up residue or debris to prevent blockages that may affect material flow. | After each use |
| Inspecting the Cable | Check for any fraying, wear, or damage that could disrupt power or wire feed. | Weekly |
| Checking the Wire Feed | Ensure smooth and consistent movement of wire to avoid material feed issues. | Every few days |
| Lubricating Moving Parts | Keep internal moving parts well-lubricated to avoid excessive wear and ensure smooth operation. | Monthly |
By following these maintenance tasks, you can significantly reduce the chances of malfunction, keeping your equipment running smoothly and efficiently for a longer period.